Ettinger: Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 7th Edition
... Some hyperthyroid cats have a change in behavior and when this happens, they tend to become irritable, mean, or easily upset. Vomiting and diarrhea are a little less common. Some hyperthyroid cats have unusually bulky stools and others have unusually large amounts of stool. Relatively uncommon but w ...
... Some hyperthyroid cats have a change in behavior and when this happens, they tend to become irritable, mean, or easily upset. Vomiting and diarrhea are a little less common. Some hyperthyroid cats have unusually bulky stools and others have unusually large amounts of stool. Relatively uncommon but w ...
Integrated Medicine Practice 75 Burnmill Road Market
... Hypothyroidism means that the thyroid gland is producing too little thyroid hormone. The symptoms of hypothyroidism are gradual and are sometimes mistaken for depression. Facial expressions become dull, the voice becomes hoarse, eyelids droop, and the face and eyes become puffy and swollen. Thyroid ...
... Hypothyroidism means that the thyroid gland is producing too little thyroid hormone. The symptoms of hypothyroidism are gradual and are sometimes mistaken for depression. Facial expressions become dull, the voice becomes hoarse, eyelids droop, and the face and eyes become puffy and swollen. Thyroid ...
020409 Endocrine System gl 2842KB Jan
... Hyperthyroidism (Thyrotoxicosis) • Excessive circulating thyroid hormone. • Graves disease; Most common cause ...
... Hyperthyroidism (Thyrotoxicosis) • Excessive circulating thyroid hormone. • Graves disease; Most common cause ...
4-Thyroid
... also referred to as Thyrotoxicosis. Hyperthyroidism may be 1. A primary condition that results from an overactive thyroid gland. 2. Secondary to excessive stimulation of the thyroid by TSH from the pituitary. 3. Grave’s disease: the most common causes of hyperthyroidism 4. Plummer’s disease: toxic g ...
... also referred to as Thyrotoxicosis. Hyperthyroidism may be 1. A primary condition that results from an overactive thyroid gland. 2. Secondary to excessive stimulation of the thyroid by TSH from the pituitary. 3. Grave’s disease: the most common causes of hyperthyroidism 4. Plummer’s disease: toxic g ...
Feline Hyperthyroidism
... anesthesia and not all cats are good surgical candidates. Additionally, varying complications of surgery may occur including damage to nerves and blood vessels of the neck, damage to the parathyroid gland function, and recurrence of hyperthyroidism as unrecognized tissue can be left behind by even t ...
... anesthesia and not all cats are good surgical candidates. Additionally, varying complications of surgery may occur including damage to nerves and blood vessels of the neck, damage to the parathyroid gland function, and recurrence of hyperthyroidism as unrecognized tissue can be left behind by even t ...
Montgomery County Health Department Tiny thyroid gland produces
... functions and can cause symptoms like weight loss, sweating, rapid heart rate, and high blood pressure. Not enough hormone (hypothyroidism) slows down your body’s functions, and can lead to symptoms like feeling tired, gaining weight, and not being able to tolerate cold temperatures. Other thyro ...
... functions and can cause symptoms like weight loss, sweating, rapid heart rate, and high blood pressure. Not enough hormone (hypothyroidism) slows down your body’s functions, and can lead to symptoms like feeling tired, gaining weight, and not being able to tolerate cold temperatures. Other thyro ...
Thyroid gland II
... on the thyrotrop cells, more than on the anterior hypothalamus (site of release of TRH). • The feedback mechanism controlling thyroid gland activity act mainly on the ant pituitary. ...
... on the thyrotrop cells, more than on the anterior hypothalamus (site of release of TRH). • The feedback mechanism controlling thyroid gland activity act mainly on the ant pituitary. ...
Thyroid eye disease - British Thyroid Foundation
... TED is sometimes misdiagnosed as conjunctivitis, allergy or hay-fever ...
... TED is sometimes misdiagnosed as conjunctivitis, allergy or hay-fever ...
Alterations of Hormonal Regulation
... Thyroid gland produces thyroxine hormone An autoimmune disorder Significantly accelerates metabolism o Sudden weight loss, a rapid or irregular heartbeat, sweating, nervousness or irritability o Fatigue, muscle weakness, difficulty sleeping o Tremor, sweating o Changes in menstrual patterns o ...
... Thyroid gland produces thyroxine hormone An autoimmune disorder Significantly accelerates metabolism o Sudden weight loss, a rapid or irregular heartbeat, sweating, nervousness or irritability o Fatigue, muscle weakness, difficulty sleeping o Tremor, sweating o Changes in menstrual patterns o ...
A 39-Year-Old Man with Abdominal Pain, Nausea, Vomiting and
... patients include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, weight loss and diarrhea.1,2 Excess thyroid hormone may decrease gastric emptying and trigger emesis centers in the hypothalamus.3,4 Thyrotoxicosis also increases the risks of gastritis, achlorhydria and peptic ulcer disease.5,6 Contrary to popular belief ...
... patients include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, weight loss and diarrhea.1,2 Excess thyroid hormone may decrease gastric emptying and trigger emesis centers in the hypothalamus.3,4 Thyrotoxicosis also increases the risks of gastritis, achlorhydria and peptic ulcer disease.5,6 Contrary to popular belief ...
OPTIONS CENTER HEALTH TOPIC
... The thyroid gland is a very important gland located in the front of the neck. It secretes several lifesustaining hormones directly into the circulation. The activity of this gland in normal individuals is controlled by the pituitary gland in the brain. The thyroid hormones control energy production ...
... The thyroid gland is a very important gland located in the front of the neck. It secretes several lifesustaining hormones directly into the circulation. The activity of this gland in normal individuals is controlled by the pituitary gland in the brain. The thyroid hormones control energy production ...
Canine Hypothyroidism - Arroyo Animal Clinic
... Clinical signs are often slowly progressive and sometimes go unnoticed by owners who see their dogs ever day. Many times people think their dog is just getting older or slowing down. Common metabolic signs include weight gain (while feeding same amount of food), lethargy, mental dullness, exercise i ...
... Clinical signs are often slowly progressive and sometimes go unnoticed by owners who see their dogs ever day. Many times people think their dog is just getting older or slowing down. Common metabolic signs include weight gain (while feeding same amount of food), lethargy, mental dullness, exercise i ...
Thyroid and Cortisol Levels
... Thyroid and cortisol levels The thyroid is a gland located in the neck that produces thyroid hormone (thyroxine or T4). This hormone is responsible for a myriad of different functions within the body including metabolic rate, temperature regulation, and blood pressure and to influence other hormone ...
... Thyroid and cortisol levels The thyroid is a gland located in the neck that produces thyroid hormone (thyroxine or T4). This hormone is responsible for a myriad of different functions within the body including metabolic rate, temperature regulation, and blood pressure and to influence other hormone ...
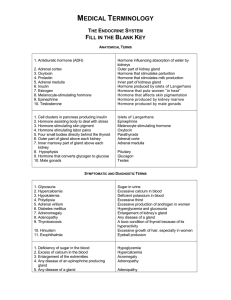
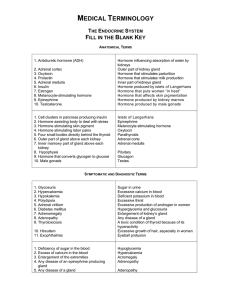
NERVOUS SYSTEM: MATCHING EXERCISE
... Sugar in urine Excessive calcium in blood Deficient potassium in blood Excessive thirst Excessive production of androgen in women Hyperglycemia and glucosuria Enlargement of kidney’s gland Any disease of a gland A toxic condition of thyroid because of its hyperactivity Excessive growth of hair, espe ...
... Sugar in urine Excessive calcium in blood Deficient potassium in blood Excessive thirst Excessive production of androgen in women Hyperglycemia and glucosuria Enlargement of kidney’s gland Any disease of a gland A toxic condition of thyroid because of its hyperactivity Excessive growth of hair, espe ...
fill in blank key
... Sugar in urine Excessive calcium in blood Deficient potassium in blood Excessive thirst Excessive production of androgen in women Hyperglycemia and glucosuria Enlargement of kidney’s gland Any disease of a gland A toxic condition of thyroid because of its hyperactivity Excessive growth of hair, espe ...
... Sugar in urine Excessive calcium in blood Deficient potassium in blood Excessive thirst Excessive production of androgen in women Hyperglycemia and glucosuria Enlargement of kidney’s gland Any disease of a gland A toxic condition of thyroid because of its hyperactivity Excessive growth of hair, espe ...
endocrine problems
... body breaks down food and either uses that energy immediately or stores it for the future • Thyroid hormones influence virtually every organ system in the body. • also regulate the consumption of oxygen and the production of heat ...
... body breaks down food and either uses that energy immediately or stores it for the future • Thyroid hormones influence virtually every organ system in the body. • also regulate the consumption of oxygen and the production of heat ...
Feline Hyperthyroidism - Winn Feline Foundation
... Thyroid Function Testing, such as a T3 Suppression or TRH Stimulation test could be considered when repeat total T4 measures remain within the reference range, free T4 concentrations are equivocal, or thyroid scintigraphy is unavailable.1 Once hyperthyroidism has been confirmed, there are several tr ...
... Thyroid Function Testing, such as a T3 Suppression or TRH Stimulation test could be considered when repeat total T4 measures remain within the reference range, free T4 concentrations are equivocal, or thyroid scintigraphy is unavailable.1 Once hyperthyroidism has been confirmed, there are several tr ...
Framingham, Reynolds, CRP Canadian Lipid Guidelines
... • the presence of hyperthyroidism due either to Graves disease or toxic nodular goiter (other types of hyperthyroidism have been implicated as well), and • usually a low serum potassium level. • The electromyogram, performed while the patient is experiencing weakness, – shows myopathic changes with ...
... • the presence of hyperthyroidism due either to Graves disease or toxic nodular goiter (other types of hyperthyroidism have been implicated as well), and • usually a low serum potassium level. • The electromyogram, performed while the patient is experiencing weakness, – shows myopathic changes with ...
Congenital Hypothyroidism
... B ultrasound scanning for thyroid gland ECG may show low voltage P and T waves with diminished amplitude of QRS complexes. Cholesterol level is usually elevated. ...
... B ultrasound scanning for thyroid gland ECG may show low voltage P and T waves with diminished amplitude of QRS complexes. Cholesterol level is usually elevated. ...
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
... • Serum TSH levels of more than 2.500 uU/mL and even above 5.000 uU/mL may represent conditions including euthyroid TSH elevation or subclinical hypothyroidism. Consider repeating TSH testing in 6 months in the absence of symptoms. If a repeat serum TSH is resulted as high, measurement of FT4 is in ...
... • Serum TSH levels of more than 2.500 uU/mL and even above 5.000 uU/mL may represent conditions including euthyroid TSH elevation or subclinical hypothyroidism. Consider repeating TSH testing in 6 months in the absence of symptoms. If a repeat serum TSH is resulted as high, measurement of FT4 is in ...
Hyper/Hypothyroidism
... should receive no pharmacologic therapy at present. In older persons with abnormal results on thyroid function testing, such as are seen in this patient, the tests should be repeated several times over a period of months to ensure the stability and accuracy of the results. The normal thyroid-stimula ...
... should receive no pharmacologic therapy at present. In older persons with abnormal results on thyroid function testing, such as are seen in this patient, the tests should be repeated several times over a period of months to ensure the stability and accuracy of the results. The normal thyroid-stimula ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.