Subclinical Hyperthyroidism Associated With an
... considered if TSH is persistently lower than 0.1 mIU/L in all individuals aged 65 years or older and that treatment should also be considered if TSH is low but at least 0.1 mIU/L in individuals who are at least 65 years old. Our results from pooling data of all available prospective cohorts, showing ...
... considered if TSH is persistently lower than 0.1 mIU/L in all individuals aged 65 years or older and that treatment should also be considered if TSH is low but at least 0.1 mIU/L in individuals who are at least 65 years old. Our results from pooling data of all available prospective cohorts, showing ...
ประกอบการสอนนักศึกษาแพทย์ชั้นปีที่4 จัดทาโดย
... Refers to the classic physiologic manifestations of excessive quantities of thyroid hormones. Hyperthyroidism Reserved for disorders that result from sustained overproduction of hormone by thyroid itself. ...
... Refers to the classic physiologic manifestations of excessive quantities of thyroid hormones. Hyperthyroidism Reserved for disorders that result from sustained overproduction of hormone by thyroid itself. ...
File - Ms. G`s Classroom
... In females, stimulates the maturation of a follicle and egg inside the ovary. In males, stimulates sperm production. Stimulate ovulation in females and the formation of the corpus luteum from the empty follicle Produced by the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary. Acts on the kidneys to increa ...
... In females, stimulates the maturation of a follicle and egg inside the ovary. In males, stimulates sperm production. Stimulate ovulation in females and the formation of the corpus luteum from the empty follicle Produced by the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary. Acts on the kidneys to increa ...
Thyroid Testing - Quest Diagnostics
... Thyroid function tests are used to define hyper function, euthyroidism, or hypofunction of thyroid disease. Thyroid testing may be reasonable and necessary to: • Distinguish between primary and secondary hypothyroidism • Confirm or rule out primary hypothyroidism • Monitor thyroid hormone levels (fo ...
... Thyroid function tests are used to define hyper function, euthyroidism, or hypofunction of thyroid disease. Thyroid testing may be reasonable and necessary to: • Distinguish between primary and secondary hypothyroidism • Confirm or rule out primary hypothyroidism • Monitor thyroid hormone levels (fo ...
Body Systems - Bishop Ireton High School
... Example- when blood glucose levels are high, insulin is produced to remove glucose from blood. Glucose is stored in the cells. When blood glucose levels are low, glucagon is produced to cause cells to release stored glucose into the blood. When desired level is reached, hormone production is turne ...
... Example- when blood glucose levels are high, insulin is produced to remove glucose from blood. Glucose is stored in the cells. When blood glucose levels are low, glucagon is produced to cause cells to release stored glucose into the blood. When desired level is reached, hormone production is turne ...
Hypothyroidism - Mid-Missouri Reproductive
... ovary (ovulation). Typically, for those patients who have periods (menstruate) each month, an egg is released from the ovary each month. But women who have hypothyroidism may release an egg less frequently or not at all. Hypothyroidism can also interfere with the development of an embryo (fertilized ...
... ovary (ovulation). Typically, for those patients who have periods (menstruate) each month, an egg is released from the ovary each month. But women who have hypothyroidism may release an egg less frequently or not at all. Hypothyroidism can also interfere with the development of an embryo (fertilized ...
thyroid hormones
... degradation of insulin, with decreased cholesterol and increased sensitivity; triglycerides; increased increased cholesterol and ...
... degradation of insulin, with decreased cholesterol and increased sensitivity; triglycerides; increased increased cholesterol and ...
Thyroid and Anti thyroid Drugs
... degradation of insulin, with decreased cholesterol and increased sensitivity; triglycerides; increased increased cholesterol and ...
... degradation of insulin, with decreased cholesterol and increased sensitivity; triglycerides; increased increased cholesterol and ...
Thyroid Disease: How Your Thyroid Works
... doctor may suggest a different medicine to help you feel better while you and your doctor decide what your treatment should be. During and after treatment, you will have regular blood tests to check your thyroid hormones to see if the treatment is working. In rare cases, surgery may be done. Do you ...
... doctor may suggest a different medicine to help you feel better while you and your doctor decide what your treatment should be. During and after treatment, you will have regular blood tests to check your thyroid hormones to see if the treatment is working. In rare cases, surgery may be done. Do you ...
Dr. Michelle Salga ND, BHRT Doctor of Naturopathic Medicine dr
... The butterfly-shaped thyroid gland is located in the front of your neck and wraps partially around the windpipe. The gland is responsible for making thyroid hormones that control the metabolism of all cells in your body. If the thyroid overproduces hormones, you can have a condition called hyperthyr ...
... The butterfly-shaped thyroid gland is located in the front of your neck and wraps partially around the windpipe. The gland is responsible for making thyroid hormones that control the metabolism of all cells in your body. If the thyroid overproduces hormones, you can have a condition called hyperthyr ...
Medical Causes of Hypothyroidism
... Exposure to various forms of medical treatments can leave an individual lacking adequate thyroxine in the body. Treatments such as lithium, radioactive iodine and surgery can be responsible as certain research have proven. For instance, someone who takes doses of lithium as a form of treatment for m ...
... Exposure to various forms of medical treatments can leave an individual lacking adequate thyroxine in the body. Treatments such as lithium, radioactive iodine and surgery can be responsible as certain research have proven. For instance, someone who takes doses of lithium as a form of treatment for m ...
Hypothyroidism
... The most common type found in the U.S. is Hashimoto's thyroiditis. That means the body's immune system is attacking thyroid tissue. Therefore, the thyroid gland is unable to make enough hormone. Pituitary gland disease, thyroid surgery and radiation therapy for thyroid cancer will also cause low lev ...
... The most common type found in the U.S. is Hashimoto's thyroiditis. That means the body's immune system is attacking thyroid tissue. Therefore, the thyroid gland is unable to make enough hormone. Pituitary gland disease, thyroid surgery and radiation therapy for thyroid cancer will also cause low lev ...
Document
... T3 and T4 are fat-soluble, so they diffuse out of the follicular cells as they are released from thyroglobulin. More than 9x as much T4 is secreted as T3. But T3 is about 5x as potent as T4. Also liver and kidneys each have an enzyme that can remove one iodine atom from T4, converting it into T3. Th ...
... T3 and T4 are fat-soluble, so they diffuse out of the follicular cells as they are released from thyroglobulin. More than 9x as much T4 is secreted as T3. But T3 is about 5x as potent as T4. Also liver and kidneys each have an enzyme that can remove one iodine atom from T4, converting it into T3. Th ...
1-The immune system and endocrine disorders 2017)
... Testicular pain involving swelling, inflammation and infection ...
... Testicular pain involving swelling, inflammation and infection ...
thyroid dysfunction
... pituitary gland secretes thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). Too little T3 or T4 in the blood prompts the pituitary to release more TSH, causing thyroid activity to increase. Too much T3 or T4 decreases the amount of TSH released by the pituitary. Because it controls the release of T3 and T4, measurin ...
... pituitary gland secretes thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). Too little T3 or T4 in the blood prompts the pituitary to release more TSH, causing thyroid activity to increase. Too much T3 or T4 decreases the amount of TSH released by the pituitary. Because it controls the release of T3 and T4, measurin ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
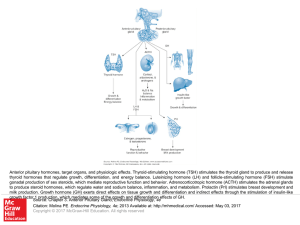
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
Slide ()
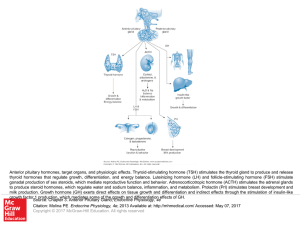
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
Goiter (Thyroid Enlargement) in Birds
... Under normal conditions, the thyroid gland produces several hormones, including thyroxine. Iodine is necessary for their production. There is a feedback mechanism to control the amount of hormone production. If the brain senses the thyroid hormones are too low, it will signal the thyroid gland to pr ...
... Under normal conditions, the thyroid gland produces several hormones, including thyroxine. Iodine is necessary for their production. There is a feedback mechanism to control the amount of hormone production. If the brain senses the thyroid hormones are too low, it will signal the thyroid gland to pr ...
hyperthyroidism
... Methimazole can be administered through the skin (transdermally); transdermal methimazole must be prepared by a pharmacist; resolution of signs resulting from the excessive levels of thyroid hormones in the body (thyrotoxicosis) takes longer with transdermal methimazole than with methimazole given ...
... Methimazole can be administered through the skin (transdermally); transdermal methimazole must be prepared by a pharmacist; resolution of signs resulting from the excessive levels of thyroid hormones in the body (thyrotoxicosis) takes longer with transdermal methimazole than with methimazole given ...
title - JustAnswer
... Methimazole can be administered through the skin (transdermally); transdermal methimazole must be prepared by a pharmacist; resolution of signs resulting from the excessive levels of thyroid hormones in the body (thyrotoxicosis) takes longer with transdermal methimazole than with methimazole given b ...
... Methimazole can be administered through the skin (transdermally); transdermal methimazole must be prepared by a pharmacist; resolution of signs resulting from the excessive levels of thyroid hormones in the body (thyrotoxicosis) takes longer with transdermal methimazole than with methimazole given b ...
The Number Games and Thyroid Function
... • Rare congenital defect affecting 0.03% of the population • Recent reports show that this is rare and should not influence choice of drug in pregnancy • No other teratogenicity • Both drugs can cause agranulocytosis – patients must report sore throats ...
... • Rare congenital defect affecting 0.03% of the population • Recent reports show that this is rare and should not influence choice of drug in pregnancy • No other teratogenicity • Both drugs can cause agranulocytosis – patients must report sore throats ...
Calcitonin - Quest Diagnostics
... calcitonin is stimulated by calcium. Calcitonin decreases osteoclastic bone resorption, but the physiological role in man is uncertain. Calcitonin measurement is indicated for the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), the majority of whom produce the hormone. Se ...
... calcitonin is stimulated by calcium. Calcitonin decreases osteoclastic bone resorption, but the physiological role in man is uncertain. Calcitonin measurement is indicated for the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), the majority of whom produce the hormone. Se ...
The Endocrine System
... • Function: Raises blood sugar level and increases heart beat and breathing rates. ...
... • Function: Raises blood sugar level and increases heart beat and breathing rates. ...
Hyperthyroidism
... by a pharmacist; resolution of signs resulting from the excessive levels of thyroid hormones in the body (thyrotoxicosis) takes longer with transdermal methimazole than with methimazole given by mouth β-blockers—sometimes used to treat some of the heart and nervous system effects of excess thyroid ...
... by a pharmacist; resolution of signs resulting from the excessive levels of thyroid hormones in the body (thyrotoxicosis) takes longer with transdermal methimazole than with methimazole given by mouth β-blockers—sometimes used to treat some of the heart and nervous system effects of excess thyroid ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.