* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Number Games and Thyroid Function
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
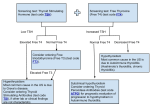
The Number Games and Thyroid Function Arshia Panahloo Consultant Endocrinologist St George’s Hospital Presentation Today: • • • • • Common thyroid problems and treatments Pregnancy related thyroid problems The ‘suppressed TSH’ Thyroid Cancer Review of common pitfalls- QUIZ HYPOTHALAMUS Portal Circulation HYPOTHALAMIC FACTOR PITUITARY PITUITARY HORMONE END ORGAN HYPOTHALAMUS Portal Circulation HYPOTHALAMIC FACTOR PITUITARY PITUITARY HORMONE END ORGAN HORMONE END ORGAN Portal Circulation PITUITARY NEGATIVE FEEDBACK HYPOTHALAMUS TRH PITUITARY TRI IODOTHYRONINE TSH THYROXINE THYROID Typical Thyroid Hormone Levels in Thyroid Disease TSH T4 T3 Hypothyroidism High Low Low Hyperthyroidism Low High High Thyroid Hormone • The plasma thyroid hormones are – 3,5,3`,5`-tetraiodo L-thyronine (thyroxine T4) – 3,5,3`-triiodo L-thyronine (triiodothyronine T3) • Receptor is nuclear (type2) • Circulate bound to protein – Thyroid Binding Globulin – Albumin – Prealbumin • Plasma half life T3 (1-3 days) T4 (4-7 days) • Dietary Iodine requirement 50μg/day Thyroid Hormone Production • 100 mcg of thyroid hormone are produced daily • Most as T4 and 10% as T3 • 80% of T4 converts to the more active T3 in the kidney and liver or reverse T3 • T3 is ten times more active than T4 • reverse T3 has little activity Over production Thyrotoxicosis • • • • • Graves disease (80%) Multinodular Goitre (15%) Toxic Solitary Nodule (2%) Thyroiditis (1%) Rare – TSH secreting pituitary tumour – Excess Thyroxine ingestion – trophoblast tumours Robert James Graves (1796- 1853) Thyrotoxicosis • • • • • Tachycardia Palpitation Lid Lag Agitation Increased locomotor Sympathetic activity Overactivity • Weight loss • Heat intolerance • Fever • • • • Poor appetite Myopathy Increased Growth Diarrhoea • Grave’s • thyroid eye disease: – – – – – Pretibial Myxodema Exopthalmos Chemosis lid lag Diplopia on upgaze Treatment • • • • Carbimazole Propythiouracil Beta Blockers Surgery Carbimazole vs. Propylthiouracil •Serum half-life •Duration of action •Dosing •Compliance •Cost •Side-effects Carbimazole PTU 4-6 hr 24 hr 1-2 x daily Higher £4.46 (20mg) Lower 75 min 12-24 hr 2-3 x day Lower £74.79 (300mg) Higher Side-effects of Antithyroid Drugs •Skin rash, itching •Upper GI side-effects •Arthralgia •Vasculitis, SLE-like syndrome •Blood dyscrasia •Hepatotoxicity •Congenital malformations PTU and Liver Injury •JCI 2009, 94:1881 Cooper et al.. •US FDA database: severe liver injury in 22 adults in 20 years •9 died, 5 needed transplant • Severe liver injury in 12 children •3 died, 6 needed transplant •Estimated risk of severe liver failure: 1/1000 •Raised Liver enzymes: 15/54 (28%) Hyperthyroidism in pregnancy • Grave’s Disease affects 2 per 1000 pregnancies • It is important to ensure patient euthyroid as soon as possible, preferably prior to conception, to avoid complications: – Maternal • Thyroid storm • Congestive cardiac failure • Pre-eclampsia – Fetal • Fetal growth restriction • Prematurity • stillbirth The Foetal pituitary thyroid axis • • • • Controlled in similar way to adult Iodine supplied transplacentally < 12/40 maternal T4 but not T3 crosses placenta T4 binds to foetal brain cells, and is converted intracellularly to T3. This is important for brain development. • >12/40 fetal thyroid function is independent of mother, provided mothers iodine intake is adequate. Pregnancy specific thyroid changes • T4 synthesis increases 20-40% • Half life of thyroid binding globulin increases from 15 min to 3 days. Must measure only Free T4 and T3 • hCG and TSH have similar alpha sub-units and receptors. • In first trimester hCG can stimulate TSH receptor, and can give a picture of hyperthyroidism. • Worse in hyperemesis and multiple pregnancies and trophoblastic disease • Thyroid function must be interpreted with caution Propylthiouracil or Carbimazole in pregnancy? • Both have similar placental transfer • Earlier reports suggested carbimazole causes aplasia cutis congenita of the scalp • Rare congenital defect affecting 0.03% of the population • Recent reports show that this is rare and should not influence choice of drug in pregnancy • No other teratogenicity • Both drugs can cause agranulocytosis – patients must report sore throats Treatment of Hyperthyroidism in pregnancy • PTU first line in first trimester • If intolerant to PTU, use carbimazole • Switch to carbimazole second trimester due to liver toxicity with PTU • Lowest dose possible, as both drugs cross the placenta • Propanolol can be used if tachycardia, tremor or anxiety • Difficult to distinguish between signs of thyrotoxicosis and pregnancy • Serial TFT important every 6 -8 weeks • Failure to gain weight despite good appetite, pulse rate >100 are signs of thyrotoxicosis Treatment of Hyperthyroidism in pregnancy • TSH receptor antibody falls in the second and third trimester, and rises in the puerperium • TFT should be measured 6 weekly • Anti-thyroid medication titrated • Most women can reduce their dose and a third stop treatment in pregnancy • This prevents fetal hypothyroidism • Anti-thyroid medication will need to be started post partum to avoid relapse Lactation • There are differences between PTU and carbimazole during lactation • 0.077% PTU and 0.47% carbimazole reaches breast milk. • High dose Carbimazole could cause neonatal hypothyroidism • Switch to PTU, may need monitoring of neonatal TFT if patient on carbimazole Fetal consequences of thyrotoxicosis • TSH receptor antibodies can cross placenta and cause Graves disease after 20 weeks (risk is low) • Effect proportional to antibody titres • Must be measured in all women who may have had Graves disease treated in past with radioactive iodine or surgery at 22/40 • If titres high, should monitor for signs of fetal thyrotoxicosis: – – – – – – Fetal tachycardia Growth restriction Oligohydramnios Fetal goitre can obstruct delivery IUD Hydrops fetalis Hypothyroidism: Types • • Primary hypothyroidism – From thyroid destruction – Hashimotos Disease – Post radioactive iodine – Post surgery – Thyroiditis – Antithyroid drugs Central or secondary hypothyroidism – From deficient TSH secretion, – Generally due to sellar lesions such as pituitary tumor or craniopharyngioma – Infrequently is congenital • Central or tertiary hypothyroidism – From deficient TSH stimulation above level of pituitary – Lesions of pituitary stalk or hypothalamus – Is much less common than secondary hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism • • • • Bradycardia Mental Slowness Poor Memory Decreased locomotor activity Sympathetic • Weight gain Underactivity • Cold intolerance • Hypothermia • • • • • Poor appetite Myopathy Decreased growth Constipation Dry skin and hair • Hoarse voice • Puffy face • Menstrual Irregularity Hypothyroidism and Pregnancy • Hypothyroid women have increase prevalence of: – – – – – – Infertility Abortion Anaemia Gestational hypertension Placental abruption Post partum haemorrhage • Adverse neonatal outcome: – Premature birth – Low birth weight – Neonatal respiratory distress • In one study women with sub-clinical hypothyroidism also had ↑ preterm delivery and neonatal resp distress Hypothyroidism • • • • 0.3-0.5% of pregnancies Sub-clinical hypothyroidism in 2-3% Antibodies found in 5-15% Most common cause autoimmune thyroiditis, and iodine deficiency Thyroid Function Tests Pregnancy JCEM 2012 • If hypothyroid in pregnancy, adjust dose of T4, so TSH ≤ 2.5 • Aim for normal TSH in preconception period • Normal ↑ in thyroxine dose of 30% • Universal screening for TPO antibodies in either before or during pregnancy not recommended. • But positive TPO are associated with increase miscarriage, preterm delivery, hypothyroidism and post-partum thyroiditis. Thyroid Function Tests Pregnancy • Only first trimester hypothyroidism influences fetal wellbeing • It is important to be euthyroid in the preconception period • In hypothyroid women TFT should be checked in each trimester • Antenatal care is usually midwife led unless other risk factors Targetted TFT testing seeking pregnancy or newly pregnant • Women over 30 • With FH of autoimmune thyroid disease or hypothyroidism • Women with Goiter • Positive antibodies • Symptoms of thyroid disease • Type-1 diabetes • Infertility • History of miscarriage and preterm delivery • Head and neck irradiation and thyroid surgery • On T4 replacement Causes of Thyroiditis • • • • Hashimotos’s Riedels De Quervain’s Silent • Post Partum • Drugs – – – – DXT Lithium Amiodarone Interferon • Superative Post partum Thyroiditis • • • • Common 6 to 12 months postpartum Patients present with transient thyrotoxicosis Resolves by 12 months Occurs in patient who are TPO Ab +,Grave’s disease in remission, and chronic viral hepatitis • Screen for TSH 3 and 6 months post-partum • Annual TSH • Increase risk of permanent hypothyroidism in 5 to 10 years Carcinoma of the Thyroid • Patients are initially treated with total thyroidectomy • Followed by radio-iodine ablation therapy • Followed by life-long suppressive thyroxine therapy to prevent recurrence • Please do not lower dose of Thyroxine in these patients. Tumours of the anterior pituitary can cause syndromes of hormone excess • • • • GH ACTH TSH LH/FSH • PRL •Acromegaly •Cushing’s disease •Secondary thyrotoxicosis •(Non-functioning pituitary tumour) •Prolactinoma Suppressed TSH PRIOR TO ADJUSTING MEDICATION •Is the suppressed TSH secondary to thyroid over-activity? •Excess thyroxine replacement? •Hypopituitarism and TSH deficiency? •Has the patient had treatment for thyroid Cancer? Pitfalls in Interpreting Thyroid Function • Pregnancy • Hypopituitarism • Thyroid Cancer Short QUIZ