January 15.indd - Rita`s Care at Home
... hormones that help control the function of many of your body’s organs, including your heart, brain, liver, kidneys, and skin. Making sure that your thyroid gland is healthy is important to your body’s overall well-being. Some patients who have an enlarged thyroid gland may also produce too much or t ...
... hormones that help control the function of many of your body’s organs, including your heart, brain, liver, kidneys, and skin. Making sure that your thyroid gland is healthy is important to your body’s overall well-being. Some patients who have an enlarged thyroid gland may also produce too much or t ...
Hypothyroidism is associated with a faulty increase in Hemoglobin
... Hypothyroidism: a condition where the thyroid gland is underactive and doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormone. Treatment requires taking thyroid hormone pills. Thyroid Hormone Therapy: patients with hypothyroidism are most often treated with Levothyroxine in order to return their thyroid hormone lev ...
... Hypothyroidism: a condition where the thyroid gland is underactive and doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormone. Treatment requires taking thyroid hormone pills. Thyroid Hormone Therapy: patients with hypothyroidism are most often treated with Levothyroxine in order to return their thyroid hormone lev ...
Aim: How does the endocrine system work to maintain homeostasis?
... The Endocrine System • Just like the nervous system, the endocrine controls body activities • Controls body activities through messengers (hormones) • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their hormones into the blood stream. ...
... The Endocrine System • Just like the nervous system, the endocrine controls body activities • Controls body activities through messengers (hormones) • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their hormones into the blood stream. ...
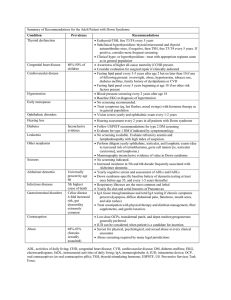
Thyroidism
... Eating too much of foods that contain iodine. Graves’s disease (most common cause of hyperthyroidism). Inflammation (thyroiditis) of the thyroid due to viral infections, some medicines, or after pregnancy. Noncancerous growths of the thyroid gland or pituitary gland. Some tumors of the testes or ova ...
... Eating too much of foods that contain iodine. Graves’s disease (most common cause of hyperthyroidism). Inflammation (thyroiditis) of the thyroid due to viral infections, some medicines, or after pregnancy. Noncancerous growths of the thyroid gland or pituitary gland. Some tumors of the testes or ova ...
Parathyroid Glands
... Arterial supply usually from inferior thyroid art Superior glands usually imbedded in fat on posterior surface of middle or upper portion of thyroid lobe Lower glands near the lower pole of thyroid gland In 1-5% pts, inferior gland in deep mediastinum ...
... Arterial supply usually from inferior thyroid art Superior glands usually imbedded in fat on posterior surface of middle or upper portion of thyroid lobe Lower glands near the lower pole of thyroid gland In 1-5% pts, inferior gland in deep mediastinum ...
Thyroid disorders Lecture
... Because this drug contains the active form T3 this can cause fast supra-physiological levels then soon go back to normal & so on (fluctuation) This is considered a major problem specially in elderly patients & patients with cardiac problems ...
... Because this drug contains the active form T3 this can cause fast supra-physiological levels then soon go back to normal & so on (fluctuation) This is considered a major problem specially in elderly patients & patients with cardiac problems ...
Synthesis of Thyroid Hormones
... of calcitonin. Calcitonin acts primarily in children to lower blood calcium levels when levels get too high. Calcitonin causes decreased tubular reabsorption of Ca2+ in the kidneys, leading to calcium loss in urine. It inhibits bone resorption activity of osteoclasts and calcium absorption in intest ...
... of calcitonin. Calcitonin acts primarily in children to lower blood calcium levels when levels get too high. Calcitonin causes decreased tubular reabsorption of Ca2+ in the kidneys, leading to calcium loss in urine. It inhibits bone resorption activity of osteoclasts and calcium absorption in intest ...
Hypothyroidism
... Check serum thyroid hormone (T4) levels after 6 weeks of therapy Serum thyroid hormone (T4) concentrations should be monitored and timed so that a blood sample is obtained 6 hours after administering the medication for pets receiving thyroid hormone supplementation twice a day; a blood sample sh ...
... Check serum thyroid hormone (T4) levels after 6 weeks of therapy Serum thyroid hormone (T4) concentrations should be monitored and timed so that a blood sample is obtained 6 hours after administering the medication for pets receiving thyroid hormone supplementation twice a day; a blood sample sh ...
TSH needs to be monitored in patients treated with levothyroxine
... adults are treated with multiple medications including levothyroxine, it is important for endocrinologists to be aware of potential drug interactions that can affect the effectiveness of levothyroxine. Even though some changes in serum TSH may be small, it is essential for the treating physicians to ...
... adults are treated with multiple medications including levothyroxine, it is important for endocrinologists to be aware of potential drug interactions that can affect the effectiveness of levothyroxine. Even though some changes in serum TSH may be small, it is essential for the treating physicians to ...
How does your thyroid affect your health?
... While thyroid disorders are more common in women at midlife, younger women do experience thyroid abnormalities which can impact their physical and emotional wellbeing. In addition to the physical symptoms of thyroid disorders, there may also be an emotional impact of this condition. Weight gain may ...
... While thyroid disorders are more common in women at midlife, younger women do experience thyroid abnormalities which can impact their physical and emotional wellbeing. In addition to the physical symptoms of thyroid disorders, there may also be an emotional impact of this condition. Weight gain may ...
Summary of Recommendations for the Adult Patient with Down
... Euthyroid-TSH, free T3/T4 every 5 years Subclinical hypothyroidism- thyroid microsomal and thyroid autoantibodies once, if negative, then TSH, free T3/T4 every 5 years. If positive, consider more frequent screening. Clinical hypo- or hyperthyroidism—treat with appropriate regimen same as in ge ...
... Euthyroid-TSH, free T3/T4 every 5 years Subclinical hypothyroidism- thyroid microsomal and thyroid autoantibodies once, if negative, then TSH, free T3/T4 every 5 years. If positive, consider more frequent screening. Clinical hypo- or hyperthyroidism—treat with appropriate regimen same as in ge ...
R code for thyroid uptake measurement
... thyroid uptake and scan is a two part exam. Here is generally what will happen: You will complete some paper work. FUNCTION. HOW DOES THE THYROID GLAND FUNCTION? The major thyroid hormone secreted by the thyroid gland is thyroxine, also called T4 because it contains four iodine atoms. CPT Code(s) 84 ...
... thyroid uptake and scan is a two part exam. Here is generally what will happen: You will complete some paper work. FUNCTION. HOW DOES THE THYROID GLAND FUNCTION? The major thyroid hormone secreted by the thyroid gland is thyroxine, also called T4 because it contains four iodine atoms. CPT Code(s) 84 ...
THYROID HORMONE THYROID HORMONE DYSGENESIS I
... Figure 1. Iodine from the blood is taken into the follicular cell by an iodide transport protein. Iodine is then attached to tyrosine (T) on thyroglobulin (Tgb) in the colloid. Thyroid hormones (T4,T3) form on the iodinated Tgb, then are released from Tgb in the cell, and then move to the blood. In ...
... Figure 1. Iodine from the blood is taken into the follicular cell by an iodide transport protein. Iodine is then attached to tyrosine (T) on thyroglobulin (Tgb) in the colloid. Thyroid hormones (T4,T3) form on the iodinated Tgb, then are released from Tgb in the cell, and then move to the blood. In ...
The Endogenous and Exogenous Principals
... simply restoring both serum T4 and TSH concentrations to normal (most people would be under treated), as in our experience most patients feel well only with a dose resulting in high / normal free T4 and low / normal TSH concentration, and those patients with continuing symptoms despite ‘adequate ( b ...
... simply restoring both serum T4 and TSH concentrations to normal (most people would be under treated), as in our experience most patients feel well only with a dose resulting in high / normal free T4 and low / normal TSH concentration, and those patients with continuing symptoms despite ‘adequate ( b ...
Thyroid Gland
... Thyroid Gland The thyroid is a small gland inside the neck, located in front of the (trachea) The thyroid hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products with a release of energy in the pro ...
... Thyroid Gland The thyroid is a small gland inside the neck, located in front of the (trachea) The thyroid hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products with a release of energy in the pro ...
Is it Fat? Or could it be PHAT?
... glands in our body. Let's take a moment for an overview on these glands: Pituitary - Think of this as the master gland of the body. It produces HGH (human growth hormone), regulates thyroid function, and is responsible for metabolic energy and controls the sleep and wakefulness cycles. Hypothalamus ...
... glands in our body. Let's take a moment for an overview on these glands: Pituitary - Think of this as the master gland of the body. It produces HGH (human growth hormone), regulates thyroid function, and is responsible for metabolic energy and controls the sleep and wakefulness cycles. Hypothalamus ...
presentation source
... Long half-life, 13-103 days If toxicity occurs, it may persist long after drug administration is discontinued 15-30 days or more are required to load the body stores with sufficient Amiodarone for full efficacy Loading doses are 0.8-1.2g daily for about 2 wks, maintenance dose is 200-400mg d ...
... Long half-life, 13-103 days If toxicity occurs, it may persist long after drug administration is discontinued 15-30 days or more are required to load the body stores with sufficient Amiodarone for full efficacy Loading doses are 0.8-1.2g daily for about 2 wks, maintenance dose is 200-400mg d ...
Endocrine syste
... Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3) – speed up cells release of energy from foods, stimulate cellular metabolism Calcitonin – maintains homeostasis of blood calcium, decreases the amount of calcium in the blood, act on bone to inhibit its breakdown, therefore calcium does not move out of bone. ...
... Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3) – speed up cells release of energy from foods, stimulate cellular metabolism Calcitonin – maintains homeostasis of blood calcium, decreases the amount of calcium in the blood, act on bone to inhibit its breakdown, therefore calcium does not move out of bone. ...
ENDOCRINE EMERGENCIES
... POORLY RESPONSIVE VITALS: T 92, P 50/M, R 10/M, BP 90/60 COOL DRY SKIN,PUFFY EYES THYROID NOT PALPABLE, NO NECK SCAR DTR: SLOW RETURN STOOL: MELENA ...
... POORLY RESPONSIVE VITALS: T 92, P 50/M, R 10/M, BP 90/60 COOL DRY SKIN,PUFFY EYES THYROID NOT PALPABLE, NO NECK SCAR DTR: SLOW RETURN STOOL: MELENA ...
Negative Feedback
... above the 9-11 mg/100ml level, the thyroid releases calcitonin, which then inhibits osteoclasts, increases bone calcium production, and stimulates osteoblasts to created more bone, which brings the blood calcium levels down. ...
... above the 9-11 mg/100ml level, the thyroid releases calcitonin, which then inhibits osteoclasts, increases bone calcium production, and stimulates osteoblasts to created more bone, which brings the blood calcium levels down. ...
Hypothyroidism
... – Well nourished woman with a blood pressure of 80/60 mmHg and a pulse rate of 50-100 beats per minute. Temperature was 95.2 F – She had a puffy face and examination of the neck revealed no bruits. The jugular venous pressure was normal. Cardiac auscultation was normal and the lungs were clear. Per ...
... – Well nourished woman with a blood pressure of 80/60 mmHg and a pulse rate of 50-100 beats per minute. Temperature was 95.2 F – She had a puffy face and examination of the neck revealed no bruits. The jugular venous pressure was normal. Cardiac auscultation was normal and the lungs were clear. Per ...
Thyroid - Open Source Medicine
... o T3 deficiency results in myxedema (accumulation of mucopolysaccharide in the skin resulting in swelling and edema not due to fluid) Required for heat production: needed to survive cold climates Required for various other processes: o Lactation o Digestion o Kidney function o CV function o Reproduc ...
... o T3 deficiency results in myxedema (accumulation of mucopolysaccharide in the skin resulting in swelling and edema not due to fluid) Required for heat production: needed to survive cold climates Required for various other processes: o Lactation o Digestion o Kidney function o CV function o Reproduc ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.