TAKE HOME EXAM –URINARY SYSTEM REPRODUCTIVE
... Fill in the blank-with the correct answer. 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as _______________ ...
... Fill in the blank-with the correct answer. 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as _______________ ...
Denis Wilson, MD
... hypometabolic symptoms in patients with normal thyroid blood tests (whether taking T4-containing medicine or not) “I was first diagnosed about 10 yrs ago and successfully treated [with T3]. Since then it reoccurred again about 4-5 yrs later and treated with success.” -L.G. “I have successfully compl ...
... hypometabolic symptoms in patients with normal thyroid blood tests (whether taking T4-containing medicine or not) “I was first diagnosed about 10 yrs ago and successfully treated [with T3]. Since then it reoccurred again about 4-5 yrs later and treated with success.” -L.G. “I have successfully compl ...
Multi-nodular goiter (MNG) is a medical term describing an enlarged
... for surgery . The technique of Ultrasonography has been used to find the changes in the size of nodules in patients suspected for thyroid malignancy. Thyroid surgery may remove compression as well as symptoms like difficulty in swallowing, cough etc. It can also cure thyroid gland over activity asso ...
... for surgery . The technique of Ultrasonography has been used to find the changes in the size of nodules in patients suspected for thyroid malignancy. Thyroid surgery may remove compression as well as symptoms like difficulty in swallowing, cough etc. It can also cure thyroid gland over activity asso ...
THE HUMBLE EGG - Baliga Diagnostics Pvt Ltd
... called the isthmus. The thyroid gland has a very rich blood supply, giving it is brownish red colour. Functions of the thyroid gland The thyroid gland secretes thyroid hormones T3 and T4. The hormone production is under control of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) secreted by the hypothalamic-pituit ...
... called the isthmus. The thyroid gland has a very rich blood supply, giving it is brownish red colour. Functions of the thyroid gland The thyroid gland secretes thyroid hormones T3 and T4. The hormone production is under control of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) secreted by the hypothalamic-pituit ...
1Which of the following hormones is not secreted by the pituitary
... a deficiency of thyroxine which leads to an excess of thyroid stimulating hormone. an excess of growth hormone which stimulates thyroid cell hypertrophy. an excess of dietary sodium. ...
... a deficiency of thyroxine which leads to an excess of thyroid stimulating hormone. an excess of growth hormone which stimulates thyroid cell hypertrophy. an excess of dietary sodium. ...
Endocrinology - Commons
... Directions: (Matching) Match the hormone from the column on the right with the target or source organ, or normal/abnormal function on the left. (An answer from the right column may be used more than once, most are to be used only once – research carefully and choose the best, most typical answer.) ...
... Directions: (Matching) Match the hormone from the column on the right with the target or source organ, or normal/abnormal function on the left. (An answer from the right column may be used more than once, most are to be used only once – research carefully and choose the best, most typical answer.) ...
BIO242 Lab 27 Endocrine
... A. Draw and clearly label the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and posterior pituitary. State the types of cell found in each region (are they neuronal, or endocrine)? B. Clearly list ALL of the hormones released by EACH region of the pituitary. Thyroid A. Draw and clearly label a portion of the thyr ...
... A. Draw and clearly label the pars distalis, pars intermedia, and posterior pituitary. State the types of cell found in each region (are they neuronal, or endocrine)? B. Clearly list ALL of the hormones released by EACH region of the pituitary. Thyroid A. Draw and clearly label a portion of the thyr ...
Does hyperthyroidism cause coronary vasospasms?
... euthyroidism was restored by medical therapy [3]. This hypersensitive reaction offers a possible explanation why hyperthyroidism may induce coronary vasospasms in medium-sized muscular arteries such as the coronaries despite an overall vasodilative effect. The first case with angiographic confirmati ...
... euthyroidism was restored by medical therapy [3]. This hypersensitive reaction offers a possible explanation why hyperthyroidism may induce coronary vasospasms in medium-sized muscular arteries such as the coronaries despite an overall vasodilative effect. The first case with angiographic confirmati ...
Ultrasound Pathology (HB)
... Lymphocytic infiltration of extraocular orbital muscles, salivary, and lacrimal glands Only 30% are hypothyroid Some have hypocalcemia due to infiltration of parathyroids Considered to be the most severe manifestation of IgG4 disease. Avoid surgery, except for diagnostic biopsy or debulking when nee ...
... Lymphocytic infiltration of extraocular orbital muscles, salivary, and lacrimal glands Only 30% are hypothyroid Some have hypocalcemia due to infiltration of parathyroids Considered to be the most severe manifestation of IgG4 disease. Avoid surgery, except for diagnostic biopsy or debulking when nee ...
Pathology of the Thyroid Gland
... Hyperfunctioning multinodular goiter Hyperfunctioning adenoma Subacute lymphocytic (painless) thyroiditis ...
... Hyperfunctioning multinodular goiter Hyperfunctioning adenoma Subacute lymphocytic (painless) thyroiditis ...
ST120 Endocrine System
... signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options. Demonstrate knowledge of medical terminology related to the endocrine system verbally and in the written form. ...
... signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options. Demonstrate knowledge of medical terminology related to the endocrine system verbally and in the written form. ...
Endocrine Disorders
... Complications to both mother and fetus may occur. Increased incidence of spontaneous abortions Increased birth size; predisposition to obesity for child. ...
... Complications to both mother and fetus may occur. Increased incidence of spontaneous abortions Increased birth size; predisposition to obesity for child. ...
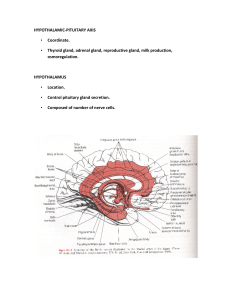
HYPOTHALAMIC-PITUITARY AXIS • Coordinate. • Thyroid gland
... HYPOTHALAMIC-HYPOPHYSIAL PORTAL SYSTEM ...
... HYPOTHALAMIC-HYPOPHYSIAL PORTAL SYSTEM ...
FILL IN THE BLANKS: ENDOCRINE HORMONES (Student Copy
... normal effects, may be caused by adrenal medulla tumor called Pheochromocyto ma ...
... normal effects, may be caused by adrenal medulla tumor called Pheochromocyto ma ...
PDF - True-2-me
... What is the pituitary gland and where is it located? The pituitary is a small gland (no larger than a pea) located at the base of the brain near the optic nerves. It rests in a saddle-like compartment in the skull called the “sella turcica”. The pituitary gland plays a key role as the master gland o ...
... What is the pituitary gland and where is it located? The pituitary is a small gland (no larger than a pea) located at the base of the brain near the optic nerves. It rests in a saddle-like compartment in the skull called the “sella turcica”. The pituitary gland plays a key role as the master gland o ...
(tsh) test in master health checkups
... They are both absorbed well by the gut, so can be given orally3,4,5. Disorders:Thyroid disorders include hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism . All these disorders may give rise to goiter, that is, an enlarged thyroid. Hypothyroidism:Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not ma ...
... They are both absorbed well by the gut, so can be given orally3,4,5. Disorders:Thyroid disorders include hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism . All these disorders may give rise to goiter, that is, an enlarged thyroid. Hypothyroidism:Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not ma ...
Capstone Screening Project – Hypothyroidism
... Hypothyroidism is when the thyroid gland, located in the neck region, is not producing enough of the thyroid hormone, thyroxine, or T4, to keep the body functioning properly. When the body does not have enough thyroid hormone, the body’s processes start to slow down. Symptoms can be getting tired, f ...
... Hypothyroidism is when the thyroid gland, located in the neck region, is not producing enough of the thyroid hormone, thyroxine, or T4, to keep the body functioning properly. When the body does not have enough thyroid hormone, the body’s processes start to slow down. Symptoms can be getting tired, f ...
Natural Solutions for an Underactive Thyroid Gland
... function. It is important that these two minerals are well balanced for optimum functioning of the thyroid gland. Vitamin A supports thyroid hormone production. Vitamin C, Zinc, and B vitamins all help to support the adrenal glands, which in turn, help to support thyroid function. Selenium is essent ...
... function. It is important that these two minerals are well balanced for optimum functioning of the thyroid gland. Vitamin A supports thyroid hormone production. Vitamin C, Zinc, and B vitamins all help to support the adrenal glands, which in turn, help to support thyroid function. Selenium is essent ...
BRS Physiology Cases and Problems 2nd Edition
... 7. Synthetic T4 (or L-thyroxine) is processed in the body just like endogenous T4. In the target tissues, Tg, whether endogenous or synthetic, is converted either to T3 or to reverse T3 (rT 3 ). T3 is the most active form of thyroid hormone, and rT 3 is inactive. Therefore, this conversion step in t ...
... 7. Synthetic T4 (or L-thyroxine) is processed in the body just like endogenous T4. In the target tissues, Tg, whether endogenous or synthetic, is converted either to T3 or to reverse T3 (rT 3 ). T3 is the most active form of thyroid hormone, and rT 3 is inactive. Therefore, this conversion step in t ...
الشريحة 1
... covalently to iodine. The two principal thyroid hormones are: thyroxine (also known as T4 or L-3,5,3',5'-tetraiodothyronine) triiodotyronine (T3 or L-3,5,3'-triiodothyronine) As shown in the following diagram, the thyroid hormones are basically two tyrosines linked together with the critical additio ...
... covalently to iodine. The two principal thyroid hormones are: thyroxine (also known as T4 or L-3,5,3',5'-tetraiodothyronine) triiodotyronine (T3 or L-3,5,3'-triiodothyronine) As shown in the following diagram, the thyroid hormones are basically two tyrosines linked together with the critical additio ...
BIOLOGY 120 TAKE HOME EXAM
... 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as __________________. 4. Parathyroid hormone functions by in ...
... 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as __________________. 4. Parathyroid hormone functions by in ...
Endocrine system: physiological peculiarities, symptoms and
... Deficiency of luteinizing hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH), together referred to as the gonadotropins, leads to different symptoms in men and women. Women experience oligo- or amenorrhea (infrequent/light or absent menstrual periods respectively) and infertility. Men lose facial, s ...
... Deficiency of luteinizing hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH), together referred to as the gonadotropins, leads to different symptoms in men and women. Women experience oligo- or amenorrhea (infrequent/light or absent menstrual periods respectively) and infertility. Men lose facial, s ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.