Hypothyroidism
... disease, goiter or pregnancy, even if subclinical hypothyroid • Hypothyroidism in pregnancy is associated with low birth weight, increased risk for miscarriage, premature birth and fetal loss. TSH goal = 0.5 to 2.5 microunits/mL ...
... disease, goiter or pregnancy, even if subclinical hypothyroid • Hypothyroidism in pregnancy is associated with low birth weight, increased risk for miscarriage, premature birth and fetal loss. TSH goal = 0.5 to 2.5 microunits/mL ...
Endocrine System Notes
... A. Located at the base of the neck, just below Larynx B. Hormone – Thyroxin C. Controls metabolism D. Too little thyroxin may lead to sluggishness, weight gain E. Too much thyroxin may lead to hyperactivity, increased appetite, no weight gain ...
... A. Located at the base of the neck, just below Larynx B. Hormone – Thyroxin C. Controls metabolism D. Too little thyroxin may lead to sluggishness, weight gain E. Too much thyroxin may lead to hyperactivity, increased appetite, no weight gain ...
The formation of a goiter
... The information contained in this material is intended for general reference only. As a result of ongoing medical advances and developments, the information in this material may not always be completely up to date and, for this reason, such information is provided on an “as is” and “as available” ba ...
... The information contained in this material is intended for general reference only. As a result of ongoing medical advances and developments, the information in this material may not always be completely up to date and, for this reason, such information is provided on an “as is” and “as available” ba ...
Hormone Review Guide
... wall and in milk-letdown by forcing milk into ducts from the milk glands Regulate energy metabolism Regulate energy metabolism Lowers blood levels of calcium and phosphate ions when they are too high Increases blood calcium ion concentration and decreases phosphate ion concentration “Fight or flight ...
... wall and in milk-letdown by forcing milk into ducts from the milk glands Regulate energy metabolism Regulate energy metabolism Lowers blood levels of calcium and phosphate ions when they are too high Increases blood calcium ion concentration and decreases phosphate ion concentration “Fight or flight ...
Endocrine Disorders
... rarely fatal › Follicular – again slow growing – rarely fatal › Medullary – less common – more aggressive › Anaplastic – least common – most aggressive ...
... rarely fatal › Follicular – again slow growing – rarely fatal › Medullary – less common – more aggressive › Anaplastic – least common – most aggressive ...
Thyroid Function Tests - American Thyroid Association
... some individuals with a low TSH, only the T3 is elevated and the FT4 or FTI is normal. T3 testing rarely is helpful in the hypothyroid patient, since it is the last test to become abnormal. Patients can be severely hypothyroid with a high TSH and low FT4 or FTI, but have a normal T3. In some situati ...
... some individuals with a low TSH, only the T3 is elevated and the FT4 or FTI is normal. T3 testing rarely is helpful in the hypothyroid patient, since it is the last test to become abnormal. Patients can be severely hypothyroid with a high TSH and low FT4 or FTI, but have a normal T3. In some situati ...
Medullary carcinoma
... Acromegaly • Growth hormone adenoma occurs after puberty • Protruding jaw • Broaden lower face • Enlarged hands ...
... Acromegaly • Growth hormone adenoma occurs after puberty • Protruding jaw • Broaden lower face • Enlarged hands ...
Document
... • Value/Belief: how do relationships or activities help you cope? How do cultural beliefs or practices affect how you care for yourself? Are there any specific treatments you would not use to treat this condition? ...
... • Value/Belief: how do relationships or activities help you cope? How do cultural beliefs or practices affect how you care for yourself? Are there any specific treatments you would not use to treat this condition? ...
Resistance to Thyroid Hormone and Down Syndrome: Coincidental
... Conversely, DS, resulting from the presence of an extra copy of human chromosome 21, is the most common genetic disorder in humans. DS is associated with a high prevalence of thyroid function disorders, mainly subclinical hypothyroidism. Indeed, given the high prevalence of mildly elevated TSH conce ...
... Conversely, DS, resulting from the presence of an extra copy of human chromosome 21, is the most common genetic disorder in humans. DS is associated with a high prevalence of thyroid function disorders, mainly subclinical hypothyroidism. Indeed, given the high prevalence of mildly elevated TSH conce ...
A Study on Serum FSH, LH and Prolactin Levels in Women with
... (AIA) method. By using TOSOH automated immunoassay system. ...
... (AIA) method. By using TOSOH automated immunoassay system. ...
File - Coach Frei Science
... Located posterior to the stomach Pancreas as an endocrine gland produces: 1. insulin - a hormone that promotes the uptake of glucose by cells 2. glucagon - a hormone that causes the liver to breakdown stored glycogen and release it as glucose into the bloodstream ...
... Located posterior to the stomach Pancreas as an endocrine gland produces: 1. insulin - a hormone that promotes the uptake of glucose by cells 2. glucagon - a hormone that causes the liver to breakdown stored glycogen and release it as glucose into the bloodstream ...
The Endocrine System - respiratorytherapyfiles.net
... intervals (usually 3 hours). Used to diagnose diabetes mellitus with higher accuracy than other blood glucose tests. ...
... intervals (usually 3 hours). Used to diagnose diabetes mellitus with higher accuracy than other blood glucose tests. ...
Thyroid Gland Development
... Nuclear TR (receptors) are present in the brain of 10 week old fetuses increasing rapidly by 16 weeks a period of very active cortical neurogenesis. The number of T₃ -occupied receptors in the whole fetal brain increases about 500 fold between 10-18 weeks , a finding that confirms that maternal thy ...
... Nuclear TR (receptors) are present in the brain of 10 week old fetuses increasing rapidly by 16 weeks a period of very active cortical neurogenesis. The number of T₃ -occupied receptors in the whole fetal brain increases about 500 fold between 10-18 weeks , a finding that confirms that maternal thy ...
Case 9377 Congenital hypothyroidism with ectopic lingual thyroid
... Though extremely rare nowadays in developed countries due to newborn screening of hypothyroidism, cretinism is still a major epidemiological concern in several countries. It is mainly the consequence of inadequate thyroid hormone production by the newborn just after delivery [3]. In some countries i ...
... Though extremely rare nowadays in developed countries due to newborn screening of hypothyroidism, cretinism is still a major epidemiological concern in several countries. It is mainly the consequence of inadequate thyroid hormone production by the newborn just after delivery [3]. In some countries i ...
File
... H-shaped/ Main hormone – THYROXINE – is controlled by the secretion of TSH Thyroxine controls the rate of ________________ CALCITONIN – controls calcium ion concentration in the body, prevents hypercalcemia PARATHYROID GLANDS Four glands, each the size of a _________________ Attached to po ...
... H-shaped/ Main hormone – THYROXINE – is controlled by the secretion of TSH Thyroxine controls the rate of ________________ CALCITONIN – controls calcium ion concentration in the body, prevents hypercalcemia PARATHYROID GLANDS Four glands, each the size of a _________________ Attached to po ...
etanercept. They concluded that the risk of TB is greater with
... occurrence of clinical hyperthyroidism in our patients could be coincidental or related to HAART. The higher prevalence of overt disease in our HIV cohort study, compared with studies reporting overt disease in 0.5% and 0.2% in general Chinese [3] and Japanese [4] populations, respectively, suggests ...
... occurrence of clinical hyperthyroidism in our patients could be coincidental or related to HAART. The higher prevalence of overt disease in our HIV cohort study, compared with studies reporting overt disease in 0.5% and 0.2% in general Chinese [3] and Japanese [4] populations, respectively, suggests ...
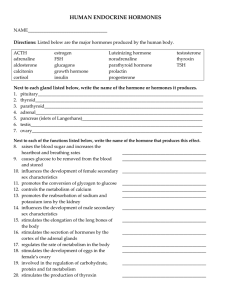
human endocrine hormones
... HUMAN ENDOCRINE HORMONES NAME___________________________________ Directions: Listed below are the major hormones produced by the human body. ACTH adrenaline aldosterone calcitonin cortisol ...
... HUMAN ENDOCRINE HORMONES NAME___________________________________ Directions: Listed below are the major hormones produced by the human body. ACTH adrenaline aldosterone calcitonin cortisol ...
A Massage Therapist`s Guide to Pathology
... 1. T3, T4 stimulate conversion of fuel into energy 2. T4 → T3 iv. In early hypothyroidism: 1. TSH high 2. T4 low 3. T3 normal v. Contributing factors: 1. Hashimoto thyroiditis: autoimmune attack 2. Complication of treatment for hyperthyroidism: result of taking radioactive iodine or thyroid surgery ...
... 1. T3, T4 stimulate conversion of fuel into energy 2. T4 → T3 iv. In early hypothyroidism: 1. TSH high 2. T4 low 3. T3 normal v. Contributing factors: 1. Hashimoto thyroiditis: autoimmune attack 2. Complication of treatment for hyperthyroidism: result of taking radioactive iodine or thyroid surgery ...
Endocrine System
... Causes: Too little good, too much insulin or diabetes medicine, or extra exercise. Onset: Suddon, may progress to insulin shock. Symptoms: Shaking, fast heartbeat, sweating, anxious, dizziness, hunger, impaired vision, weakness fatigue, headache, and irritablility. What can you do? Drink ½ glass of ...
... Causes: Too little good, too much insulin or diabetes medicine, or extra exercise. Onset: Suddon, may progress to insulin shock. Symptoms: Shaking, fast heartbeat, sweating, anxious, dizziness, hunger, impaired vision, weakness fatigue, headache, and irritablility. What can you do? Drink ½ glass of ...
THYROID ADAPTATION DURING NORMAL PREGNANCY
... • The thyroid gland regulates the amount of iodide it actively traps and can withstand fluctuations in dietary supply. • In the lumen, colloid iodide is incorporated into the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin (also made in the follicle cells) to produce inactive mono-iodotyrosine and di-iodotyrosi ...
... • The thyroid gland regulates the amount of iodide it actively traps and can withstand fluctuations in dietary supply. • In the lumen, colloid iodide is incorporated into the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin (also made in the follicle cells) to produce inactive mono-iodotyrosine and di-iodotyrosi ...
Effects of thyroid dysfunction and nitric oxide on - biomed
... Hyperthyroidism is defined as increased circulating levels of T3 and T4 and decreased TSH levels. To restore euthyroidism radioactive iodine (131 I) therapy, antithyroid drugs and thyroidectomy are possible therapies. Hypothyroidism is characterized by low circulating levels of the thyroid hormones ...
... Hyperthyroidism is defined as increased circulating levels of T3 and T4 and decreased TSH levels. To restore euthyroidism radioactive iodine (131 I) therapy, antithyroid drugs and thyroidectomy are possible therapies. Hypothyroidism is characterized by low circulating levels of the thyroid hormones ...
Thyroid Emergencies
... Acute autoimmune thyroiditis (may later lead to hypothyroidism) Infectious thyroiditis Postpartum thyroiditis Factitious (taking PO excess thyroid hormone) Metastatic thyroid cancer Struma ovarii (dermoid tumors or teratomas of the ovary) ...
... Acute autoimmune thyroiditis (may later lead to hypothyroidism) Infectious thyroiditis Postpartum thyroiditis Factitious (taking PO excess thyroid hormone) Metastatic thyroid cancer Struma ovarii (dermoid tumors or teratomas of the ovary) ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.