Update on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyperthyroidism
... treat Graves’ hyperthyroidism. Methimazole is usually preferred because of its longer duration of action, allowing for once-daily dosing, more rapid efficacy, and lower incidence of side effects. PTU is preferred during pregnancy because of the potential teratogenic effects of methimazole. Patients ...
... treat Graves’ hyperthyroidism. Methimazole is usually preferred because of its longer duration of action, allowing for once-daily dosing, more rapid efficacy, and lower incidence of side effects. PTU is preferred during pregnancy because of the potential teratogenic effects of methimazole. Patients ...
Endemic Goiter Now Abstract
... common preventable cause of mental retardation. It can be prevented by iodine treatment before conception, but whether it can be prevented or ameliorated by treatment during pregnancy or after delivery is not known. Foods such as cassava and millet contain substances that can be converted to thiocya ...
... common preventable cause of mental retardation. It can be prevented by iodine treatment before conception, but whether it can be prevented or ameliorated by treatment during pregnancy or after delivery is not known. Foods such as cassava and millet contain substances that can be converted to thiocya ...
Interpreting Thyroid Function Tests
... causes of altered mental status. TSH is elevated at 13. On further testing, free T4 is normal, but T3 is low. • Is this patient hypothyroid? ...
... causes of altered mental status. TSH is elevated at 13. On further testing, free T4 is normal, but T3 is low. • Is this patient hypothyroid? ...
Posterior Pituitary Disorders
... Thyroid Carcinoma: etiology – 1.) x-ray therapy to the neck, 2.) familial (in medullary carcinoma) ...
... Thyroid Carcinoma: etiology – 1.) x-ray therapy to the neck, 2.) familial (in medullary carcinoma) ...
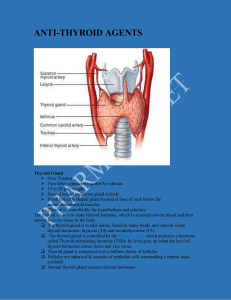
Anti-thyroid agent
... • Only free form of hormone is available for action and metabolism • Metabolism occurs by deiodination and conjugation, mainly in liver and kidneys • T4 is deiodinated to T3 (active) or rT3 (inactive) by deiodination • Conjugated products are excreted in bile – enterohepatic circulation • Finally ex ...
... • Only free form of hormone is available for action and metabolism • Metabolism occurs by deiodination and conjugation, mainly in liver and kidneys • T4 is deiodinated to T3 (active) or rT3 (inactive) by deiodination • Conjugated products are excreted in bile – enterohepatic circulation • Finally ex ...
Kent Holtorf, MD
... While the standard of care for most thyroid diseases has little controversy and is supported by a consistent consensus among practitioners, there is significant controversy regarding the essentially two standards of care for the diagnosis and treatment of hypothyroidism. The old standard of care for ...
... While the standard of care for most thyroid diseases has little controversy and is supported by a consistent consensus among practitioners, there is significant controversy regarding the essentially two standards of care for the diagnosis and treatment of hypothyroidism. The old standard of care for ...
Name
... Functional Anatomy of the Endocrine Glands - Exercise 27 Activity 1: Identifying the Endocrine Organs Activity 2: Examining the Microscopic Structure of Endocrine Glands Thyroid gland - colloid-filled follicles, follicle cells, parafollicular cells. Parathyroid gland - chief cells. Adrenal gland - c ...
... Functional Anatomy of the Endocrine Glands - Exercise 27 Activity 1: Identifying the Endocrine Organs Activity 2: Examining the Microscopic Structure of Endocrine Glands Thyroid gland - colloid-filled follicles, follicle cells, parafollicular cells. Parathyroid gland - chief cells. Adrenal gland - c ...
Surgical importance of Thyroid Gland
... Hypercortisolism can occur from; (1) Adenomas of: - Anterior pituitary ↑ ACTH, adrenal hyperplasia and excess cortisol secretion; Hypothalamus high levels of corticotropin- releasing hormone (CRH), ↑ ACTH release; Tumors “ectopic secretion” of ACTH by a tumors, Adenomas of the adrenal cortex. (lo ...
... Hypercortisolism can occur from; (1) Adenomas of: - Anterior pituitary ↑ ACTH, adrenal hyperplasia and excess cortisol secretion; Hypothalamus high levels of corticotropin- releasing hormone (CRH), ↑ ACTH release; Tumors “ectopic secretion” of ACTH by a tumors, Adenomas of the adrenal cortex. (lo ...
Endocrine Review Quesitons
... ____5. Hormones that help the body deal with stress by increasing blood pressure, and heart and breathing rates are produced by the a. pancreas b. parathyroid c. adrenal medulla d. adrenal cortex ____6. Addison's disease may be caused by a. lack of thyroxin c. too much parathyroid secretion b. the l ...
... ____5. Hormones that help the body deal with stress by increasing blood pressure, and heart and breathing rates are produced by the a. pancreas b. parathyroid c. adrenal medulla d. adrenal cortex ____6. Addison's disease may be caused by a. lack of thyroxin c. too much parathyroid secretion b. the l ...
Endocrine Review Quesitons
... b. accumulation of tissue fluid d. All choices are correct __A__8. The hormone that has an antagonistic effect of insulin is a. glucogon b. ANP c. TSH d. parathyroid hormone __C__9. Excessive levels of insulin can lead to a. hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) b. cretinism c. hypoglycemia (low sugar) d ...
... b. accumulation of tissue fluid d. All choices are correct __A__8. The hormone that has an antagonistic effect of insulin is a. glucogon b. ANP c. TSH d. parathyroid hormone __C__9. Excessive levels of insulin can lead to a. hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) b. cretinism c. hypoglycemia (low sugar) d ...
Hypothyroidism - British Thyroid Foundation
... Hypothyroidism – clinical features and treatment 1. The causes of hypothyroidism The thyroid is a gland in the neck which makes two thyroid hormones, thyroxine (T4) and tri-iodothyronine (T3). Thyroxine is inactive and is converted by the tissues and organs that need it into tri-iodothyronine. The r ...
... Hypothyroidism – clinical features and treatment 1. The causes of hypothyroidism The thyroid is a gland in the neck which makes two thyroid hormones, thyroxine (T4) and tri-iodothyronine (T3). Thyroxine is inactive and is converted by the tissues and organs that need it into tri-iodothyronine. The r ...
The Endocrine System - Greer Middle College Charter
... Diabetes insipidus (DI) is an uncommon condition that occurs when the kidneys are unable to conserve water as they perform their function of filtering blood. The amount of water conserved is controlled by antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also called vasopressin. ADH is a hormone produced in a region of t ...
... Diabetes insipidus (DI) is an uncommon condition that occurs when the kidneys are unable to conserve water as they perform their function of filtering blood. The amount of water conserved is controlled by antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also called vasopressin. ADH is a hormone produced in a region of t ...
So Your Thyroid Tested Normal, HUH?
... it’s a pretty important little gland. Sadly, it’s also one that fails on an alarmingly frequent level. The #4 most prescribed drug in the U.S. is for thyroid dysfunction. Body Clues: I have many clients who have come into my office with many, if not all, of the physical signs of thyroid malfunction ...
... it’s a pretty important little gland. Sadly, it’s also one that fails on an alarmingly frequent level. The #4 most prescribed drug in the U.S. is for thyroid dysfunction. Body Clues: I have many clients who have come into my office with many, if not all, of the physical signs of thyroid malfunction ...
Radioactive Iodine - American Thyroid Association
... or to shrink thyroid glands that are functioning normally but are causing problems because of their size (see Goiter brochure). Patients are asked to follow some radiation precautions after treatment in order to limit radiation exposure to others (see chart). I-131 may occasionally cause mild pain i ...
... or to shrink thyroid glands that are functioning normally but are causing problems because of their size (see Goiter brochure). Patients are asked to follow some radiation precautions after treatment in order to limit radiation exposure to others (see chart). I-131 may occasionally cause mild pain i ...
THiRST: Thyroid Hormone Replacement therapy in ST elevation
... 1973 Coronary Drug Project: Large clinical study examining effect of “inactive” thyroid analog D-T4 (6 mg/day) on 8,341 patients with AMI Main finding: D-T4 led to small, but significant increase in arrhythmias and worse outcome Problem: “Inactive” D-T4 dose too high, biologically active, and admini ...
... 1973 Coronary Drug Project: Large clinical study examining effect of “inactive” thyroid analog D-T4 (6 mg/day) on 8,341 patients with AMI Main finding: D-T4 led to small, but significant increase in arrhythmias and worse outcome Problem: “Inactive” D-T4 dose too high, biologically active, and admini ...
What is Congenital Hypothyroidism? What is the Thyroid Gland
... What is the Thyroid Gland? The thyroid is a bow tie shaped gland located in the neck, below the Adam's apple. The thyroid gland is part of the endocrine system. This gland is responsible for secreting a hormone called thyroxine (T4) which plays a vital role in normal growth and development in childr ...
... What is the Thyroid Gland? The thyroid is a bow tie shaped gland located in the neck, below the Adam's apple. The thyroid gland is part of the endocrine system. This gland is responsible for secreting a hormone called thyroxine (T4) which plays a vital role in normal growth and development in childr ...
Human Endocrine System
... •The level of one hormone in the blood stimulates or inhibits the production of a second hormone. •The blood level of the second hormone in turn stimulates or inhibits the production of the first. •TSH (secreted by the pituitary gland) and thyroxin (secreted by thyroid) is a classic example of negat ...
... •The level of one hormone in the blood stimulates or inhibits the production of a second hormone. •The blood level of the second hormone in turn stimulates or inhibits the production of the first. •TSH (secreted by the pituitary gland) and thyroxin (secreted by thyroid) is a classic example of negat ...
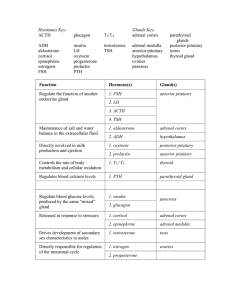
Endocrine System Worksheet Key
... • endocrine system includes organs or glands in the body that are responsible for the control of various , ÿnctions. Use the terms in the word box to label the diagram and identify the gland to which each hormone (in the box at the bottom) is associated. ...
... • endocrine system includes organs or glands in the body that are responsible for the control of various , ÿnctions. Use the terms in the word box to label the diagram and identify the gland to which each hormone (in the box at the bottom) is associated. ...
Hyperthyroidism: Diagnosis and Treatment
... Hyperthyroidism: Diagnosis and Treatment The proper treatment of hyperthyroidism depends on recognition of the signs and symptoms of the disease and determination of the etiology. The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease. Other common causes include thyroiditis, toxic multinodular ...
... Hyperthyroidism: Diagnosis and Treatment The proper treatment of hyperthyroidism depends on recognition of the signs and symptoms of the disease and determination of the etiology. The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease. Other common causes include thyroiditis, toxic multinodular ...
Diabetes and Endocrinology
... with epithelial cells which encircle the inner colloid space (colloid lumen). Cell surfaces facing the lumen are made up of microvilli and surfaces distal to the lumen lie in close proximity to capillaries. The thyroid is stimulated by the pituitary hormone TSH to produce two hormones, thyroxine ( ...
... with epithelial cells which encircle the inner colloid space (colloid lumen). Cell surfaces facing the lumen are made up of microvilli and surfaces distal to the lumen lie in close proximity to capillaries. The thyroid is stimulated by the pituitary hormone TSH to produce two hormones, thyroxine ( ...
The Endocrine System
... • The ovaries produce estrogen in females – Estrogen is used to develop and maintain female sex characteristics – Prepares the uterus for fertilization of an egg ...
... • The ovaries produce estrogen in females – Estrogen is used to develop and maintain female sex characteristics – Prepares the uterus for fertilization of an egg ...
Is it safe to treat hyperthyroid patients with I
... Objectives: Thyroid storm is extremely rare. However, hyperthyroid patients with severe thyrotoxicosis are frequently not treated immediately with I-131 for fear of thyroid storm but are placed on thiouracil drugs for varying periods of time. We demonstrate herein that it is safe to treat these pati ...
... Objectives: Thyroid storm is extremely rare. However, hyperthyroid patients with severe thyrotoxicosis are frequently not treated immediately with I-131 for fear of thyroid storm but are placed on thiouracil drugs for varying periods of time. We demonstrate herein that it is safe to treat these pati ...
Endocrinology
... a. pancreas b. thyroid c. liver d. adrenal 18. Too much ACTH release could cause hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Since sugar is a solute, this could also cause: a. increased blood pressure b. increased blood calcium c. decreased body temperature d. decreased metabolism ...
... a. pancreas b. thyroid c. liver d. adrenal 18. Too much ACTH release could cause hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Since sugar is a solute, this could also cause: a. increased blood pressure b. increased blood calcium c. decreased body temperature d. decreased metabolism ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.