Thyroid Function Testing
... the thyrotrope cells in the anterior pituitary gland. It is the first-line test for the diagnosis of thyroid disease in high-risk individuals and it is the only test funded by Medicare to screen for thyroid disease when there is no history of thyroid problems. TSH can also be used to monitor patient ...
... the thyrotrope cells in the anterior pituitary gland. It is the first-line test for the diagnosis of thyroid disease in high-risk individuals and it is the only test funded by Medicare to screen for thyroid disease when there is no history of thyroid problems. TSH can also be used to monitor patient ...
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
... Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to synthesize and secrete thyroid hormone. TSH serum measurements are used to detect primary hypo- and hyperthyroidism. TSH is the most sensitive test for thyroid hormone function. TSH is produced in the pituitary gland. The production o ...
... Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to synthesize and secrete thyroid hormone. TSH serum measurements are used to detect primary hypo- and hyperthyroidism. TSH is the most sensitive test for thyroid hormone function. TSH is produced in the pituitary gland. The production o ...
Summary of Results of the Thyroid UK Medication Survey 2008
... time spans and informed us of your thoughts about how you are treated (or not) by your doctors. There were various other comments too including “I would like more info available to patients about the management of this condition plus options available, what can one expect?”; “Good luck!! Would like ...
... time spans and informed us of your thoughts about how you are treated (or not) by your doctors. There were various other comments too including “I would like more info available to patients about the management of this condition plus options available, what can one expect?”; “Good luck!! Would like ...
Thyroid Gland Disorders - gshbreastendocrine.co.za
... many, drugs are used for control until remission occurs. In some, remission does not occur or the disease is recurrent and partial thyroid ablation has to be considered: the options are either I131 or surgery. Most patients are started on propanolol and neomercazole and remission is awaited over 6-1 ...
... many, drugs are used for control until remission occurs. In some, remission does not occur or the disease is recurrent and partial thyroid ablation has to be considered: the options are either I131 or surgery. Most patients are started on propanolol and neomercazole and remission is awaited over 6-1 ...
The Endocrine System
... cells called Lnagerhans. Langerhans secrete two hormonesglucagon and insulin- that regulate the level of glucose (blood sugar), in blood. Glucagon stimulates the liver to convert glycogen to glucose, raising the blood sugar level. Insulin, decreases blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to for ...
... cells called Lnagerhans. Langerhans secrete two hormonesglucagon and insulin- that regulate the level of glucose (blood sugar), in blood. Glucagon stimulates the liver to convert glycogen to glucose, raising the blood sugar level. Insulin, decreases blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to for ...
thyroid dysfunction in adults
... factor for autoimmune thyroid disorders. In subclinical disease, the presence of TPO-Ab increases the longterm risk of progression to clinically significant thyroid ...
... factor for autoimmune thyroid disorders. In subclinical disease, the presence of TPO-Ab increases the longterm risk of progression to clinically significant thyroid ...
detection of thyroid nodule in ultrasound images using
... Abstract— Thyroid Gland is a major player in regulating your metabolism. It is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body and it consists of two connected lobes. This gland is found in the neck, below the Adam's apple. The thyroid’s main role in the endocrine system is to regulate your metaboli ...
... Abstract— Thyroid Gland is a major player in regulating your metabolism. It is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body and it consists of two connected lobes. This gland is found in the neck, below the Adam's apple. The thyroid’s main role in the endocrine system is to regulate your metaboli ...
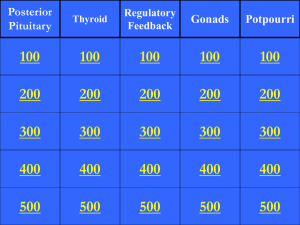
Endocrine System Jeopardy Round 1
... pituitary are connected by special neurons and these neurons signal the relase of posterior pituitary hormones such as ADH and ocytocin ...
... pituitary are connected by special neurons and these neurons signal the relase of posterior pituitary hormones such as ADH and ocytocin ...
Thermo-Burn II full product info.
... proprietary blended & effective weight loss ingredients. By combining all of these benefits into one capsule, Thermo-Burn II will deliver results you can feel! These Stages include: ¾ ...
... proprietary blended & effective weight loss ingredients. By combining all of these benefits into one capsule, Thermo-Burn II will deliver results you can feel! These Stages include: ¾ ...
The Endocrine System - Lawndale High School
... • Released during childbirth and in nursing women • Causes contractions during childbirth and milk ejection during nursing ...
... • Released during childbirth and in nursing women • Causes contractions during childbirth and milk ejection during nursing ...
Chapter 10 Endocrine System
... are called neurosecretions because they are produced and released by neurons. ...
... are called neurosecretions because they are produced and released by neurons. ...
Chapter 10
... So let’s say there’s too much glucose in your blood. Your pancreatic islets cells send insulin into the blood which tells your cells to start absorbing all the glucose, thereby decreasing the concentration of glucose in your blood. The hormone in this situation is insulin, and you can deduce how it ...
... So let’s say there’s too much glucose in your blood. Your pancreatic islets cells send insulin into the blood which tells your cells to start absorbing all the glucose, thereby decreasing the concentration of glucose in your blood. The hormone in this situation is insulin, and you can deduce how it ...
17. Pituitary and Adrenal Glands
... b) in males: it is required for sperm production. LH – a) in females: responsible for ovulation and for luteinization. Regulates estrogen and progesterone. b) in males: stimulates interstitial cells (in testes) to secrete testosterone. * called interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH) PRL – ...
... b) in males: it is required for sperm production. LH – a) in females: responsible for ovulation and for luteinization. Regulates estrogen and progesterone. b) in males: stimulates interstitial cells (in testes) to secrete testosterone. * called interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH) PRL – ...
Thyroid
... deiodinators of thyroxin and convert it to the functionally more potent triiodothyronine. Triiodothyronine then bids to a nuclear receptor in cells of the target organ the net result of which is an increase in oxygen consumption and metabolic rate. Thyroid hormone has general ...
... deiodinators of thyroxin and convert it to the functionally more potent triiodothyronine. Triiodothyronine then bids to a nuclear receptor in cells of the target organ the net result of which is an increase in oxygen consumption and metabolic rate. Thyroid hormone has general ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... Disorders of the Thyroid Gland - Thyrotoxicosis • Hypermetabolic state • Caused by presence of excess thyroid hormone (T3/T4) – Hyperthyroidism = Overproduction of T hormones • Primary – Instrinsic overproduction by thyroid • Secondary – TSH-secreting adenoma of pituitary ...
... Disorders of the Thyroid Gland - Thyrotoxicosis • Hypermetabolic state • Caused by presence of excess thyroid hormone (T3/T4) – Hyperthyroidism = Overproduction of T hormones • Primary – Instrinsic overproduction by thyroid • Secondary – TSH-secreting adenoma of pituitary ...
Peripheral thyroid hormones and response to selective serotonin
... shorter length of stay in hospital (as a measure of response to antidepressant treatment) in men who had been admitted to hospital with major depression. Furthermore, in this study, changes in peripheral thyroid hormone levels decreased with antidepressant treatment. The reduction in peripheral thyr ...
... shorter length of stay in hospital (as a measure of response to antidepressant treatment) in men who had been admitted to hospital with major depression. Furthermore, in this study, changes in peripheral thyroid hormone levels decreased with antidepressant treatment. The reduction in peripheral thyr ...
The Endocrine System
... • Follicle-Stimulating Hormone: FSH regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, and reproductive processes of the body. FSH and luteinizing hormone (LH) act synergistically in reproduction. Specifically, an increase in FSH secretion by the anterior pituitary causes ovulation. ...
... • Follicle-Stimulating Hormone: FSH regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, and reproductive processes of the body. FSH and luteinizing hormone (LH) act synergistically in reproduction. Specifically, an increase in FSH secretion by the anterior pituitary causes ovulation. ...
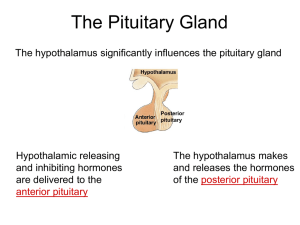
Hypothalamic/Pituitary Axis: Adrenals and Thyroid
... * The glucocorticoids (such as hydrocortisone and corticosterone) affect carbohydrate and protein metabolism. Some glucocorticoids also affect water and electrolyte balance. * These molecules have anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive activityfor which they are most commonly prescribed. ...
... * The glucocorticoids (such as hydrocortisone and corticosterone) affect carbohydrate and protein metabolism. Some glucocorticoids also affect water and electrolyte balance. * These molecules have anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive activityfor which they are most commonly prescribed. ...
Acute Thyroid Hormone Supplement Overdosage
... part by pharmacokinetics. L-thyroxine is poorly absorbed in dogs. Only 10% to 50% of an orally administered dose is absorbed in dogs5 as compared with 48% to 80% absorption in people.6 Peak plasma concentrations in dogs are expected four to 12 hours after oral dosing.4 In plasma, most of the T3 and ...
... part by pharmacokinetics. L-thyroxine is poorly absorbed in dogs. Only 10% to 50% of an orally administered dose is absorbed in dogs5 as compared with 48% to 80% absorption in people.6 Peak plasma concentrations in dogs are expected four to 12 hours after oral dosing.4 In plasma, most of the T3 and ...
Thyroid and Parathyroid glands
... manifestations of hyperparathyroidism, especially those related to hypercalcemia. Phosphates. Oral phosphates inhibit bone resorption and interfere with calcium absorption. IV phosphates are used only when serum calcium levels must be lowered rapidly. Calcitonin. Calcitonin decreases skeletal calciu ...
... manifestations of hyperparathyroidism, especially those related to hypercalcemia. Phosphates. Oral phosphates inhibit bone resorption and interfere with calcium absorption. IV phosphates are used only when serum calcium levels must be lowered rapidly. Calcitonin. Calcitonin decreases skeletal calciu ...
Thyroid gland diseases
... Hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis) Toxic diffuse goiter. Grave’s diseaseis the condition resulting from the effect of excessive amounts of thyroid hormones on body tissues. Thyrotoxicosis is a main syndrome. Sometimes the term hyperthyroidism can be used in a narrower sense to denote this state when t ...
... Hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis) Toxic diffuse goiter. Grave’s diseaseis the condition resulting from the effect of excessive amounts of thyroid hormones on body tissues. Thyrotoxicosis is a main syndrome. Sometimes the term hyperthyroidism can be used in a narrower sense to denote this state when t ...
Thyroid Disease Gideline- (slide show)
... • Subjects with a TSH of >10mU/L and FT4 below the reference range have overt primary hypothyroidism and should be treated with thyroid hormone replacement. • The minimum period to achieve stable concentrations after a change in dose of thyroxine is two months and thyroid function tests should not n ...
... • Subjects with a TSH of >10mU/L and FT4 below the reference range have overt primary hypothyroidism and should be treated with thyroid hormone replacement. • The minimum period to achieve stable concentrations after a change in dose of thyroxine is two months and thyroid function tests should not n ...
Owl 1038-1041 Questions
... 3. Why are Glucagon and Insulin considered antagonistic hormones? (refer to the diagram at bottom of 1038 if you need to) 4. Read the short definition of Negative and Positive Feedback, then make a “Diagram Definition” of each, but simply creating a diagram with the words used in the definitions. 5. ...
... 3. Why are Glucagon and Insulin considered antagonistic hormones? (refer to the diagram at bottom of 1038 if you need to) 4. Read the short definition of Negative and Positive Feedback, then make a “Diagram Definition” of each, but simply creating a diagram with the words used in the definitions. 5. ...
Endocrine fill-in guided notes
... Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (_______)- stimulates growth of the thyroid gland Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (_________)- stimulates growth of the adrenal gland Follicle-stimulating Hormone (_______) – growth of the ovarian follicles, production of estrogen in females; & production of sperm in ma ...
... Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (_______)- stimulates growth of the thyroid gland Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (_________)- stimulates growth of the adrenal gland Follicle-stimulating Hormone (_______) – growth of the ovarian follicles, production of estrogen in females; & production of sperm in ma ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.