Surgical treatment of Graves` disease: subtotal thyroidectomy might
... amount of the thyroid remnant. Summary. Objective. The aim of this prospective study was to report our results after thyroidectomy for Graves’ disease. In addition, the relationship between the thyroid remnant and postoperative thyroid function was studied. Material and methods. Forty-nine consecuti ...
... amount of the thyroid remnant. Summary. Objective. The aim of this prospective study was to report our results after thyroidectomy for Graves’ disease. In addition, the relationship between the thyroid remnant and postoperative thyroid function was studied. Material and methods. Forty-nine consecuti ...
Chapter 16 Cholinesterase Inhibitors
... Full benefits may take 6–12 months Therapeutic uses Graves’ disease Adjunct to radiation therapy Preparation for thyroid gland surgery Thyrotoxic crisis ...
... Full benefits may take 6–12 months Therapeutic uses Graves’ disease Adjunct to radiation therapy Preparation for thyroid gland surgery Thyrotoxic crisis ...
Chapter 20: Endocrine Organs
... 28. Explain how the pineal gland is visible on an X-radiograph of the brain and why this is of benefit in image analysis. 29. How is the secretion of melatonin regulated by retinal activity? 30. Which gland is most likely to be responsible for the symptoms of jet lag? 31. What spherical structure is ...
... 28. Explain how the pineal gland is visible on an X-radiograph of the brain and why this is of benefit in image analysis. 29. How is the secretion of melatonin regulated by retinal activity? 30. Which gland is most likely to be responsible for the symptoms of jet lag? 31. What spherical structure is ...
Do you have high metabolism?
... restlessness and irritability, heart palpitations and a high pulse, weight loss despite increased eating, trembling hands, increased sweating, diarrhoea, menstruation disturbances, fatigue and sleeping problems. ...
... restlessness and irritability, heart palpitations and a high pulse, weight loss despite increased eating, trembling hands, increased sweating, diarrhoea, menstruation disturbances, fatigue and sleeping problems. ...
Full Text
... TSH resistance syndromes (RTSH) can be broadly defined as reduced or absent end-organ responsiveness to thyrotropin or TSH. The other forms of disorders of thyroid may be reduced sensitivity to thyroid hormone which is a process that impairs the effectiveness of thyroid hormone and ersistent elevati ...
... TSH resistance syndromes (RTSH) can be broadly defined as reduced or absent end-organ responsiveness to thyrotropin or TSH. The other forms of disorders of thyroid may be reduced sensitivity to thyroid hormone which is a process that impairs the effectiveness of thyroid hormone and ersistent elevati ...
TSH Testing at LabCorp
... Guidelines from the American Thyroid Association warn that the prevalence of patients with subclinical hypothyroidism (that is defined as elevated TSH and normal FT4) may be as high as 17% in the adult population.6,12 ...
... Guidelines from the American Thyroid Association warn that the prevalence of patients with subclinical hypothyroidism (that is defined as elevated TSH and normal FT4) may be as high as 17% in the adult population.6,12 ...
1 - Lone Star College
... Caused by a lack of iodine Thyroid enlarges in response to constant stimulation by the anterior pituitary ...
... Caused by a lack of iodine Thyroid enlarges in response to constant stimulation by the anterior pituitary ...
Endocrine System
... • Skeleton: stimulates osteoclast activity • Intestine: increases Ca2+ reabsorption (vitamin D) • Kidneys: activates vitamin D and enhances Ca2+ reabsorption in ...
... • Skeleton: stimulates osteoclast activity • Intestine: increases Ca2+ reabsorption (vitamin D) • Kidneys: activates vitamin D and enhances Ca2+ reabsorption in ...
Endocrine Glands and Hormones Hormone
... T4 has 4 iodine atoms. Hypothyroidism, low metabolic rate, overweight, tired. Treated with radioactive iodine, which will kill off the thyroid. 131I has a short half-life. 2) toxic goiter – autoimmune disease; people produce an antibody that acts like TSH, which stimulates the thyroid to grow. Leads ...
... T4 has 4 iodine atoms. Hypothyroidism, low metabolic rate, overweight, tired. Treated with radioactive iodine, which will kill off the thyroid. 131I has a short half-life. 2) toxic goiter – autoimmune disease; people produce an antibody that acts like TSH, which stimulates the thyroid to grow. Leads ...
endocrine system
... hormones directly into the bloodstream • Target Cells – the cells that a hormone directly affects; if a cell does not have receptors or the receptors don’t respond, the hormone has no effect. ...
... hormones directly into the bloodstream • Target Cells – the cells that a hormone directly affects; if a cell does not have receptors or the receptors don’t respond, the hormone has no effect. ...
Thyroid disease and osteoporosis
... People with hypothyroidism are unable to produce enough thyroid hormone. Once again, women are more often affected than men. The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s disease. Iodine treatment or thyroid surgery, often used to treat hyperthyroidism, can also lead to hypothyroidism. On i ...
... People with hypothyroidism are unable to produce enough thyroid hormone. Once again, women are more often affected than men. The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s disease. Iodine treatment or thyroid surgery, often used to treat hyperthyroidism, can also lead to hypothyroidism. On i ...
Histology Hormones
... Hypersecretion of Growth Hormone: Gigantism in children and acromegaly in adults. Hyposecretion of Growth Hormone: Pituitary dwarfism – if the condition occurs during childhood, slows long bone growth. Those with this condition are usually under 4 feet in height but are normally proportioned. Hypose ...
... Hypersecretion of Growth Hormone: Gigantism in children and acromegaly in adults. Hyposecretion of Growth Hormone: Pituitary dwarfism – if the condition occurs during childhood, slows long bone growth. Those with this condition are usually under 4 feet in height but are normally proportioned. Hypose ...
ppt - Stritch School of Medicine
... • List the 2 hormones that are secreted by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary. • Define “Hering Body”. • Explain in general terms the staining patterns of chromophobes, basophils and acidophils of the anterior pituitary. • List the 6 hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary an ...
... • List the 2 hormones that are secreted by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary. • Define “Hering Body”. • Explain in general terms the staining patterns of chromophobes, basophils and acidophils of the anterior pituitary. • List the 6 hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary an ...
10/2 SI A ECL 365 Endocrine The endocrine system works with the
... i. Controls blood glucose, allows body to use glucose ii. Increases glucose storage (less glucose in the blood) b. Glucagon: i. Similar to insulin, but opposite effect ii. Decreases glucose storage, increases glucose in blood 18. ________________ is caused by a lack of insulin. a. Diabetes 19. The _ ...
... i. Controls blood glucose, allows body to use glucose ii. Increases glucose storage (less glucose in the blood) b. Glucagon: i. Similar to insulin, but opposite effect ii. Decreases glucose storage, increases glucose in blood 18. ________________ is caused by a lack of insulin. a. Diabetes 19. The _ ...
DM (STZ/N) - Conferences
... More recent clinical study results • ↑TSH leads to worse clinical outcomes in HF. S Chen et al, ...
... More recent clinical study results • ↑TSH leads to worse clinical outcomes in HF. S Chen et al, ...
The Endocrine System - Catherine Huff's Site
... • T4(Tetriodothyronine, thyroxine)-contains four iodine atoms per molecule. • These hormones are produced when TSH from anterior pituitary gland reaches the thyroid gland. • T4 produced in greater abundance than T3 but is mostly converted to T3 before producing effects on target cells • T3 more pote ...
... • T4(Tetriodothyronine, thyroxine)-contains four iodine atoms per molecule. • These hormones are produced when TSH from anterior pituitary gland reaches the thyroid gland. • T4 produced in greater abundance than T3 but is mostly converted to T3 before producing effects on target cells • T3 more pote ...
Endocrine System Wrap-up
... No real cure, only precaution & treatment Gestational diabetes ♦ Develops in some pregnant women • Temporary condition of diabetes • Placental hormone affects insulin levels • ↑ placental hormone, ↓ insulin = diabetes ...
... No real cure, only precaution & treatment Gestational diabetes ♦ Develops in some pregnant women • Temporary condition of diabetes • Placental hormone affects insulin levels • ↑ placental hormone, ↓ insulin = diabetes ...
Introduction to Health Science
... • Type I Diabetes Mellitus is a lifelong disease that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar. • Without insulin, the glucose increases in the bloodstream instead of going into the body cells where it can be used for energy which leads to increased hunger. ...
... • Type I Diabetes Mellitus is a lifelong disease that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar. • Without insulin, the glucose increases in the bloodstream instead of going into the body cells where it can be used for energy which leads to increased hunger. ...
What is hormone sensitivity malignancy status
... on Blood Tests. Thyroid blood tests generally include determination of the levels of circulating thyroid hormones (Free T4. Number: 0501. Policy. Leuprolide. Aetna considers leuprolide (Lupron, Viadur, Eligard) medically necessary for the following indications subject to the specified. The Medical S ...
... on Blood Tests. Thyroid blood tests generally include determination of the levels of circulating thyroid hormones (Free T4. Number: 0501. Policy. Leuprolide. Aetna considers leuprolide (Lupron, Viadur, Eligard) medically necessary for the following indications subject to the specified. The Medical S ...
Endocrine Control of the Lacrimal Gland
... Endocrine Control of the Lacrimal Gland Eduardo M. Rocha Departamento de Oftalmologia, Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia de Cabeça e Pescoço, FMRP-USP Lacrimal gland structure and function are regulated by hormones; therefore hormone dysfunction may affect not just tears production and ocular surface ...
... Endocrine Control of the Lacrimal Gland Eduardo M. Rocha Departamento de Oftalmologia, Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia de Cabeça e Pescoço, FMRP-USP Lacrimal gland structure and function are regulated by hormones; therefore hormone dysfunction may affect not just tears production and ocular surface ...
For Some, L-Thyroxine Replacement Might Not Be Enough: A
... evidence for a physiological role for D2 in the brain includes studies of thyroidectomized rats in which T4 monoreplacement fails to normalize T3 levels in some tissues but the cerebral cortex is spared (14). At the same time, D2 knockout mice exhibit a substantial reduction in brain T3 levels but, ...
... evidence for a physiological role for D2 in the brain includes studies of thyroidectomized rats in which T4 monoreplacement fails to normalize T3 levels in some tissues but the cerebral cortex is spared (14). At the same time, D2 knockout mice exhibit a substantial reduction in brain T3 levels but, ...
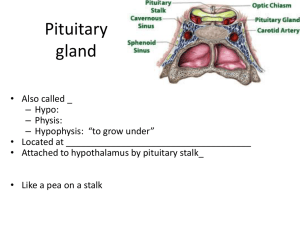
Pituitary gland
... _____ more water moved through kidneys _ • Excess alcohol consumption can _ ...
... _____ more water moved through kidneys _ • Excess alcohol consumption can _ ...
Endocrine Systems - Science Geek.net
... 1. Regulates the level of calcium in the blood a. Stimulates the uptake of calcium by bones b. Inhibits absorption of calcium in the intestine Other Glands and Hormones A. Pineal Gland 1. Secretes hormone melatonin a. Function is not known b. At lowest level after onset of puberty (1) Possible inhib ...
... 1. Regulates the level of calcium in the blood a. Stimulates the uptake of calcium by bones b. Inhibits absorption of calcium in the intestine Other Glands and Hormones A. Pineal Gland 1. Secretes hormone melatonin a. Function is not known b. At lowest level after onset of puberty (1) Possible inhib ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.










![guide2409.ppt [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001502774_1-62a347145ddf836c3494bd6f5c6ae337-300x300.png)