Unit 7 Endocrine
... Caused by the hypersecretion of hGH during adulthood May be caused by steroid and hGH use – Bones of hands, feet, and skull thicken – Eyelids, lips, and tongue enlarge – Skin thickens and develops furrows ...
... Caused by the hypersecretion of hGH during adulthood May be caused by steroid and hGH use – Bones of hands, feet, and skull thicken – Eyelids, lips, and tongue enlarge – Skin thickens and develops furrows ...
Chapter 26
... 7) Endorphins – body’s natural painkillers, like the drug morphine, so called “runner’s high” ...
... 7) Endorphins – body’s natural painkillers, like the drug morphine, so called “runner’s high” ...
Endocrine Disease in Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS)
... hair loss. Girls can have irregular menstrual periods and difficulty becoming pregnant. Hypothyroidism is treated with a once daily pill of thyroid hormone (levothyroxine). Growth Hormone Growth hormone is a hormone that is made in the pituitary gland and is critical for normal growth and adult heig ...
... hair loss. Girls can have irregular menstrual periods and difficulty becoming pregnant. Hypothyroidism is treated with a once daily pill of thyroid hormone (levothyroxine). Growth Hormone Growth hormone is a hormone that is made in the pituitary gland and is critical for normal growth and adult heig ...
SYMPTOMS What are the symptoms?
... • Too much or too little iodine. The thyroid gland must have iodine to make thyroid hormone. Iodine comes into the body in food and travels through the blood to the thyroid. Keeping thyroid hormone production in balance requires the right amount of iodine. Taking in too much iodine can cause or wors ...
... • Too much or too little iodine. The thyroid gland must have iodine to make thyroid hormone. Iodine comes into the body in food and travels through the blood to the thyroid. Keeping thyroid hormone production in balance requires the right amount of iodine. Taking in too much iodine can cause or wors ...
THYROID NODULES – PATIENT INFORMATION
... Your doctor will ask whether thyroid cancer or other thyroid problems run in your family, will ask if you have had radiation therapy involving your neck, will perform a physical examination, and may use the ultrasound machine to evaluate the structure of the thyroid in more detail (this machine us ...
... Your doctor will ask whether thyroid cancer or other thyroid problems run in your family, will ask if you have had radiation therapy involving your neck, will perform a physical examination, and may use the ultrasound machine to evaluate the structure of the thyroid in more detail (this machine us ...
Hypopituitarism Presentation
... tandem with LH, FSH helps stimulate sperm production in men, and egg development and ovulation in women. • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). This hormone stimulates your adrenal glands to produce cortisol and other hormones. Cortisol helps your body deal with stress and influences many body functi ...
... tandem with LH, FSH helps stimulate sperm production in men, and egg development and ovulation in women. • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). This hormone stimulates your adrenal glands to produce cortisol and other hormones. Cortisol helps your body deal with stress and influences many body functi ...
revised set of questions.
... 9. In a normal person, how would plasma cortisol levels be affected following administration of ACTH? What do Oscar's ACTH test results imply? 10. Why is Oscar's endogenous circulating level of ACTH significantly elevated? 11. What is the cause of Oscar's hyperpigmentation? How is this related to hi ...
... 9. In a normal person, how would plasma cortisol levels be affected following administration of ACTH? What do Oscar's ACTH test results imply? 10. Why is Oscar's endogenous circulating level of ACTH significantly elevated? 11. What is the cause of Oscar's hyperpigmentation? How is this related to hi ...
SAP 1 – Students will analyze anatomical structures in
... increase in respiration rate, the pupils to dilate, an increase in blood pressure, restrict blood flow to the skin and digestive system, and stimulate the liver to release glucose, prepares the body for action (fight or flight) ...
... increase in respiration rate, the pupils to dilate, an increase in blood pressure, restrict blood flow to the skin and digestive system, and stimulate the liver to release glucose, prepares the body for action (fight or flight) ...
Human Physiology Unit 3A: Endocrine System
... (Up-regulation, Down-regulation) is where target cells form more receptors in response to a hormone, while (Up-regulation, Down-regulation) is where target cells lose receptors in response to a hormone Hormone Interactions 1. ______________ Effect: 2 hormones required to activate cell, one hormone ...
... (Up-regulation, Down-regulation) is where target cells form more receptors in response to a hormone, while (Up-regulation, Down-regulation) is where target cells lose receptors in response to a hormone Hormone Interactions 1. ______________ Effect: 2 hormones required to activate cell, one hormone ...
CHAPTER 18 STUDY GUIDE
... ADH – antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) causes kidneys to return more water to the blood rather than going to urine output decreases water loss through perspiration raises blood pressure by constricting arterioles ...
... ADH – antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) causes kidneys to return more water to the blood rather than going to urine output decreases water loss through perspiration raises blood pressure by constricting arterioles ...
chapter 18 study guide
... ADH – antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) causes kidneys to return more water to the blood rather than going to urine output decreases water loss through perspiration raises blood pressure by constricting arterioles ...
... ADH – antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) causes kidneys to return more water to the blood rather than going to urine output decreases water loss through perspiration raises blood pressure by constricting arterioles ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Hypothalamopituitary portal vessel • Blood supply to the anterior pituitary is a portal circuit • Releasing hormones from hypothalamus into the first capillary bed (median eminence) • venous drainage transports these neurohormones to a second capillary bed supplying the anterior pituitar ...
... Hypothalamopituitary portal vessel • Blood supply to the anterior pituitary is a portal circuit • Releasing hormones from hypothalamus into the first capillary bed (median eminence) • venous drainage transports these neurohormones to a second capillary bed supplying the anterior pituitar ...
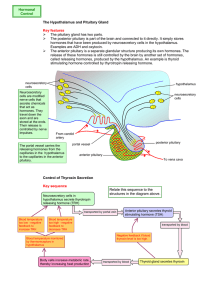
The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Key features The pituitary
... Key features The pituitary gland has two parts. The posterior pituitary is part of the brain and connected to it directly. It simply stores hormones that have been produced by neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus. Examples are ADH and oxytocin. The anterior pituitary is a separate glandular stru ...
... Key features The pituitary gland has two parts. The posterior pituitary is part of the brain and connected to it directly. It simply stores hormones that have been produced by neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus. Examples are ADH and oxytocin. The anterior pituitary is a separate glandular stru ...
Pharmacology Ch 27 480-488 Thyroid Gland Follicular thyroid cells
... -use is uncommon because of potential causing for aplastic anemia Inhibitors of Organification and Hormone Release 1. Iodides – two distinct iodides are used in practice, the first: 131I-, is a radioactive iodide isotope that emits B-particles toxic to cells, and since the Na/I symporter cannot dist ...
... -use is uncommon because of potential causing for aplastic anemia Inhibitors of Organification and Hormone Release 1. Iodides – two distinct iodides are used in practice, the first: 131I-, is a radioactive iodide isotope that emits B-particles toxic to cells, and since the Na/I symporter cannot dist ...
Combined mitral valve replacement and total thyroidectomy: a case
... incident. By the end of the intervention, the cardiovascular team began cardiac surgery using cardiopulmonary bypass. The neck wound was left open during the entire procedure, allowing monitoring for any bleeding from the operative site under the full heparinization (3 mg/kg) that accompanied cardio ...
... incident. By the end of the intervention, the cardiovascular team began cardiac surgery using cardiopulmonary bypass. The neck wound was left open during the entire procedure, allowing monitoring for any bleeding from the operative site under the full heparinization (3 mg/kg) that accompanied cardio ...
Endocrine System - University of Washington
... Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Prolactin (PRL) ...
... Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Prolactin (PRL) ...
Hypothyroidism
... - Usually there is a lack of the other pituitary hormones - low T3 and T4 - TSH low - TRH-test to differentiate between hypothalamic or pituitary etiology ...
... - Usually there is a lack of the other pituitary hormones - low T3 and T4 - TSH low - TRH-test to differentiate between hypothalamic or pituitary etiology ...
Outpatient workup and management of thyroid disorders
... During the first half of pregnancy, there is increased serum thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) and TSH Increased thyroid hormone requirement is due to both increased TBG production and decreased clearance The thyroid gland responds by increasing production of T3 and T4 This change will platea ...
... During the first half of pregnancy, there is increased serum thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) and TSH Increased thyroid hormone requirement is due to both increased TBG production and decreased clearance The thyroid gland responds by increasing production of T3 and T4 This change will platea ...
Study Guide - Belle Vernon Area School District
... _______________________________1. Glands that secrete their chemical signals into the blood, e.g., thyroid gland and adrenal glands. _______________________________2. Glands that secrete their products into ducts, e.g., sweat glands and salivary glands. _______________________________3. Intercellula ...
... _______________________________1. Glands that secrete their chemical signals into the blood, e.g., thyroid gland and adrenal glands. _______________________________2. Glands that secrete their products into ducts, e.g., sweat glands and salivary glands. _______________________________3. Intercellula ...
Application for Thyroid Database - Orthopedic Foundation for Animals
... Note: Please contact the laboratory for information about sample collection and submission. Include OFA form and fee with submission and the lab will forward results to OFA. ...
... Note: Please contact the laboratory for information about sample collection and submission. Include OFA form and fee with submission and the lab will forward results to OFA. ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.