The Endocrine Glands
... hormones, which are controlled by the hypothalamus inhibiting or releasing hormones Regulator hormones like ‘thyroid stimulating hormone’ Ex: Growth hormone (GH) GH cell division, protein synthesis, and bone growth GH binds to muscle, causing the release of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) GH also ...
... hormones, which are controlled by the hypothalamus inhibiting or releasing hormones Regulator hormones like ‘thyroid stimulating hormone’ Ex: Growth hormone (GH) GH cell division, protein synthesis, and bone growth GH binds to muscle, causing the release of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) GH also ...
4.03-4.04 Endocrine System PPP
... Overdevelopment of bones in face, hands and feet. Attacks cartilage – so the chin protrudes - lips, nose and extremities ...
... Overdevelopment of bones in face, hands and feet. Attacks cartilage – so the chin protrudes - lips, nose and extremities ...
Chapter one Hormone Chemistry, Synthesis and Elimination
... Steroid hormones are derivatives of cholesterol that are synthesized by a variety of tissues, most prominently the adrenal gland and gonads. The cholesterol precursor comes from cholesterol synthesized within the cell from acetate, from cholesterol ester stores in intracellular lipid droplets or fro ...
... Steroid hormones are derivatives of cholesterol that are synthesized by a variety of tissues, most prominently the adrenal gland and gonads. The cholesterol precursor comes from cholesterol synthesized within the cell from acetate, from cholesterol ester stores in intracellular lipid droplets or fro ...
NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS
... 117. The part of the brain that controls your balance is the a. cerebrum b. cerebellum c. medulla 18. Which gland releases adrenaline, which is released in times of emergency, to increase heart rate? a. thyroid b. adrenal glands c. ovaries d. thymus 19. Which gland secretes growth hormone? a. testes ...
... 117. The part of the brain that controls your balance is the a. cerebrum b. cerebellum c. medulla 18. Which gland releases adrenaline, which is released in times of emergency, to increase heart rate? a. thyroid b. adrenal glands c. ovaries d. thymus 19. Which gland secretes growth hormone? a. testes ...
Notes Chapter 51 Endocrine System
... Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which in turn causes the thyroid to release thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These two hormones are derived from the same amino acid and need iodine to be synthesized. They maintain normal heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature. The thyroid gland also rele ...
... Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which in turn causes the thyroid to release thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These two hormones are derived from the same amino acid and need iodine to be synthesized. They maintain normal heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature. The thyroid gland also rele ...
The Endocrine System
... Produces hormones that maintain the pregnancy Some hormones play a part in the delivery of the baby Produces HCG in addition to estrogen, progesterone, and other hormones ...
... Produces hormones that maintain the pregnancy Some hormones play a part in the delivery of the baby Produces HCG in addition to estrogen, progesterone, and other hormones ...
Thyroid Gland
... decreased digestive and kidney activity 6. Increased metabolic rate © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... decreased digestive and kidney activity 6. Increased metabolic rate © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Releasing Hormones - Dr Kreft`s Human Physiology Class
... blood loss, temp extremes, infection: • Raises blood sugar to make ATP, Depresses all immune responses • Antiinflammatory – inhibits WBCs to slow wound healing, which involves ...
... blood loss, temp extremes, infection: • Raises blood sugar to make ATP, Depresses all immune responses • Antiinflammatory – inhibits WBCs to slow wound healing, which involves ...
Endocrine System
... Non steroids • Water Soluble – can travel through blood freely, but have to interact with membrane receptors (can’t cross lipid bilayer). Once docked, will set cause changes within cell. – Protein is synthesized, packaged into vesicles via golgi bodies – vesicles migrate to and collect at release si ...
... Non steroids • Water Soluble – can travel through blood freely, but have to interact with membrane receptors (can’t cross lipid bilayer). Once docked, will set cause changes within cell. – Protein is synthesized, packaged into vesicles via golgi bodies – vesicles migrate to and collect at release si ...
Chapter 45 - sharpesystems2012
... fluids, and act on specific target cells in other parts of the body to change their functioning Endocrine System - The internal system of communication involving hormones, the ductless glands that secrete hormones, and the molecular receptors on or in target cells that respond to hormones Target Cel ...
... fluids, and act on specific target cells in other parts of the body to change their functioning Endocrine System - The internal system of communication involving hormones, the ductless glands that secrete hormones, and the molecular receptors on or in target cells that respond to hormones Target Cel ...
hormones
... water and mineral balance), glucocorticoids (affect glucose homeostasis, help regulate normal metabolism and stress resistance), and androgens (male sex hormones). • Aldosterone accounts for about 95% of mineralocorticoid activity. It regulates salt excretion by the kidneys and is involved in the us ...
... water and mineral balance), glucocorticoids (affect glucose homeostasis, help regulate normal metabolism and stress resistance), and androgens (male sex hormones). • Aldosterone accounts for about 95% of mineralocorticoid activity. It regulates salt excretion by the kidneys and is involved in the us ...
Central Nervous System Sensory neurons transmit impulses from the
... 1. According to this diagram, a gland secretes a chemical. What is the name of this chemical? Hormone 2. The organs and tissues that the chemical is transported to by the blood is made up of what kind of cells? Target cells 3. What do hormones attach to on these cells? ...
... 1. According to this diagram, a gland secretes a chemical. What is the name of this chemical? Hormone 2. The organs and tissues that the chemical is transported to by the blood is made up of what kind of cells? Target cells 3. What do hormones attach to on these cells? ...
Anatomy & Physiology
... glucose levels. • Beta cells secrete insulin, which decreases blood glucose levels. • Delta cells secrete somatostatin (identical to growth hormone inhibiting hormone secreted by the hypothalamus), which inhibits insulin release and may slow the absorption of nutrients from the GI tract. • F cells s ...
... glucose levels. • Beta cells secrete insulin, which decreases blood glucose levels. • Delta cells secrete somatostatin (identical to growth hormone inhibiting hormone secreted by the hypothalamus), which inhibits insulin release and may slow the absorption of nutrients from the GI tract. • F cells s ...
Year 12 ATAR Human Biology Unit 3 – Endocrine System
... Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment. Feedback System A situation where the response to a stimulus changes the original stimulus. Negative feedback Where the response changes the original stimulus in an opposite way. Endocrine Gland Glands that secrete hormones d ...
... Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment. Feedback System A situation where the response to a stimulus changes the original stimulus. Negative feedback Where the response changes the original stimulus in an opposite way. Endocrine Gland Glands that secrete hormones d ...
Outline 14
... In the ovaries: It stimulates the development of the eggs in the ____________ that contain them It stimulates secretion of ovarian hormones In the testes, it stimulates the production of sperm o Luteinizing Hormone In females, it stimulates ovulation (the release of the egg) It’s named f ...
... In the ovaries: It stimulates the development of the eggs in the ____________ that contain them It stimulates secretion of ovarian hormones In the testes, it stimulates the production of sperm o Luteinizing Hormone In females, it stimulates ovulation (the release of the egg) It’s named f ...
Chapter 25 Lecture notes
... environment. It signals the pituitary gland, which in turn secretes hormones that influence many body functions, including those of other endocrine glands. B. The posterior pituitary consists of an extension of the hypothalamus. Composed of nervous tissue, it stores and secretes hormones made in the ...
... environment. It signals the pituitary gland, which in turn secretes hormones that influence many body functions, including those of other endocrine glands. B. The posterior pituitary consists of an extension of the hypothalamus. Composed of nervous tissue, it stores and secretes hormones made in the ...
Endocrine System and Puberty
... & FSH into the bloodstream. LH initiates the sex glands to produce the sex hormonesestrogen (Female Ovaries) and testosterone (Male Testicles). These hormones bring about the secondary sex characteristics and are continual produced ...
... & FSH into the bloodstream. LH initiates the sex glands to produce the sex hormonesestrogen (Female Ovaries) and testosterone (Male Testicles). These hormones bring about the secondary sex characteristics and are continual produced ...
Document
... -It also promotes the production of insulinlike growth factors -Stimulate cell division in the epiphyseal growth plates, and thus bone elongation Gigantism is caused by an excessive secretion of growth hormone in a child ...
... -It also promotes the production of insulinlike growth factors -Stimulate cell division in the epiphyseal growth plates, and thus bone elongation Gigantism is caused by an excessive secretion of growth hormone in a child ...
Animal By-Products
... Diagnostic assessment of adrenal gland function; treatment of psoriasis; allergies; mononucleosis and leukemia ...
... Diagnostic assessment of adrenal gland function; treatment of psoriasis; allergies; mononucleosis and leukemia ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... and contribute to the production of peripheral t-cell population. Adrenal glands (cortex & medulla) Cortex secretes glucocorticoids (cortisol), mineralcorticoids (aldosterone) and androgens.Medulla secretes substances that act as neurotransmitters on sympathetic nervous system. Pancreas: endocrine a ...
... and contribute to the production of peripheral t-cell population. Adrenal glands (cortex & medulla) Cortex secretes glucocorticoids (cortisol), mineralcorticoids (aldosterone) and androgens.Medulla secretes substances that act as neurotransmitters on sympathetic nervous system. Pancreas: endocrine a ...
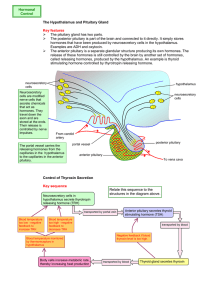
The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Key features The pituitary
... hormones that have been produced by neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus. Examples are ADH and oxytocin. The anterior pituitary is a separate glandular structure producing its own hormones. The release of these hormones is still controlled by the brain by another set of hormones, called releasin ...
... hormones that have been produced by neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus. Examples are ADH and oxytocin. The anterior pituitary is a separate glandular structure producing its own hormones. The release of these hormones is still controlled by the brain by another set of hormones, called releasin ...
endocrine system - Sakshieducation.com
... These two systems co-ordinate and integrate functions of different parts of body in accordance with the changing needs of external and internal environments. Nervous system achieves functional coordination by transmitting information through nerve impulses. The Endocrine system achieves coordination ...
... These two systems co-ordinate and integrate functions of different parts of body in accordance with the changing needs of external and internal environments. Nervous system achieves functional coordination by transmitting information through nerve impulses. The Endocrine system achieves coordination ...
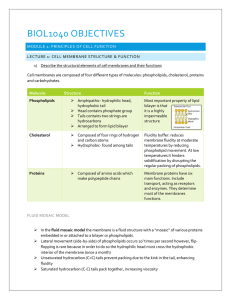
BIOL1040 OBJECTIVES
... ADH makes epithelium more permeable to waterincreased renal absorption of water (retain as much water as possible)reduces urine volumemake urine more concentrated Mechanism via action of aquaporins Hypothalamus also increases feeling of thirst Drinking water decreases blood osmolarity 1) ...
... ADH makes epithelium more permeable to waterincreased renal absorption of water (retain as much water as possible)reduces urine volumemake urine more concentrated Mechanism via action of aquaporins Hypothalamus also increases feeling of thirst Drinking water decreases blood osmolarity 1) ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.