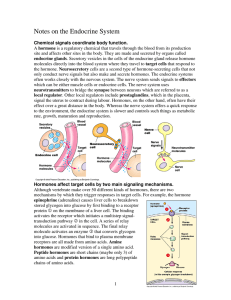
CRITERIOS PARA CLASIFICAR LAS HORMONAS
... Normal levels: 3 - 4.5 mg % adult 5 - 7 mg % children Functions: 1. PH buffer (pk = 6.9) 2. Metabolism 3. Nucleic acids 4. Phspholipids of cell membranes ...
... Normal levels: 3 - 4.5 mg % adult 5 - 7 mg % children Functions: 1. PH buffer (pk = 6.9) 2. Metabolism 3. Nucleic acids 4. Phspholipids of cell membranes ...
Notes on the Endocrine System
... Hormones secreted by the adrenal cortex provide a slower, longer-lasting response to stress. The hypothalamus secretes a releasing hormone that stimulates target cells in the anterior pituitary to secrete the hormone ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone). ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete a ...
... Hormones secreted by the adrenal cortex provide a slower, longer-lasting response to stress. The hypothalamus secretes a releasing hormone that stimulates target cells in the anterior pituitary to secrete the hormone ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone). ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete a ...
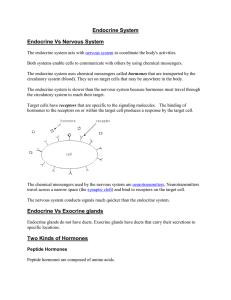
Endocrine System
... Mechanisms of Hormone Action • Hormones and cell membrane receptors; in order to affect a target cell, the hormone must first interact the the appropriate receptor ▫ Each cell has receptors for several different hormones ▫ Lipid based hormones can diffuse across cell membranes ▫ Non-lipid based hor ...
... Mechanisms of Hormone Action • Hormones and cell membrane receptors; in order to affect a target cell, the hormone must first interact the the appropriate receptor ▫ Each cell has receptors for several different hormones ▫ Lipid based hormones can diffuse across cell membranes ▫ Non-lipid based hor ...
Physio Lab 4 Endocrine in PhysioEx
... mechanism would be the endocrine glands of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-X axis (where X- stands for another endocrine gland such as the thyroid, gonads, or adrenal glands). An example of a neural mechanism would be the release of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla: A preganglionic neuron of the symp ...
... mechanism would be the endocrine glands of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-X axis (where X- stands for another endocrine gland such as the thyroid, gonads, or adrenal glands). An example of a neural mechanism would be the release of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla: A preganglionic neuron of the symp ...
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs
... 93) Thyroxine is a peptide hormone, but its mechanism is different from other peptide hormones. Which of the following statements is true concerning this difference? A) It causes positive feedback. B) It is a stimulant of cellular metabolism and targets all cells. C) It does not require a second mes ...
... 93) Thyroxine is a peptide hormone, but its mechanism is different from other peptide hormones. Which of the following statements is true concerning this difference? A) It causes positive feedback. B) It is a stimulant of cellular metabolism and targets all cells. C) It does not require a second mes ...
comp3_unit7_audio_transcript
... hormone disorders. The level of hormones that is secreted into our bloodstream can be affected by factors such as stress, infections, and changes in the levels of our blood’s fluids causing disturbances such as electrolyte imbalances. When your body does not respond to hormones the way it is suppose ...
... hormone disorders. The level of hormones that is secreted into our bloodstream can be affected by factors such as stress, infections, and changes in the levels of our blood’s fluids causing disturbances such as electrolyte imbalances. When your body does not respond to hormones the way it is suppose ...
Endocrine Emergencies
... o “The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis… comprises systems to regulate sodium and water balance, steroid hormone production, glucose metabolism, and thyroid function,” (Atkins, 21). ● Hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) which stimulates the pituitary to release adreno ...
... o “The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis… comprises systems to regulate sodium and water balance, steroid hormone production, glucose metabolism, and thyroid function,” (Atkins, 21). ● Hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) which stimulates the pituitary to release adreno ...
Endocrine System
... • Drop of blood calcium levels triggers a release of PTH which activates osteoclasts and increases the production of calcitriol in the kidneys, this increases the level of Ca2+ and PO43- absorption in the GI tract ...
... • Drop of blood calcium levels triggers a release of PTH which activates osteoclasts and increases the production of calcitriol in the kidneys, this increases the level of Ca2+ and PO43- absorption in the GI tract ...
Endocrine System - Dr. Haar
... 3. Cells appear highly vacuolated due to presence of numerous lipid (cholesterol) droplets in the cytoplasm 4. Secretes glucocorticoids: corticosterone, cortisol, androgens and estrogens C. Zona reticularis (about 5%) 1. Occupies deepest layer of the cortex 2. Cells arranged as anastomosing cords 3. ...
... 3. Cells appear highly vacuolated due to presence of numerous lipid (cholesterol) droplets in the cytoplasm 4. Secretes glucocorticoids: corticosterone, cortisol, androgens and estrogens C. Zona reticularis (about 5%) 1. Occupies deepest layer of the cortex 2. Cells arranged as anastomosing cords 3. ...
Name Chapter 18: Alterations of Hormonal Regulation I
... Panhypopituitarism – decreased or absent secretion of all pituitary hormones ACTH deficiency – causes cortisol deficiency (life-threatening). TSH deficiency – causes thyroid hormone deficiency. FSH and LH deficiency – causes gonadal failure and loss of secondary sex characteristics. GH defic ...
... Panhypopituitarism – decreased or absent secretion of all pituitary hormones ACTH deficiency – causes cortisol deficiency (life-threatening). TSH deficiency – causes thyroid hormone deficiency. FSH and LH deficiency – causes gonadal failure and loss of secondary sex characteristics. GH defic ...
in the cell
... – Zona reticularis • gonadocorticoids (mainly androgens (male sex steroid hormones)) –secreted at low levels in males and females and may attribute to the onset of puberty ...
... – Zona reticularis • gonadocorticoids (mainly androgens (male sex steroid hormones)) –secreted at low levels in males and females and may attribute to the onset of puberty ...
video slide - CARNES AP BIO
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex also function in the body’s response to stress and fall into three classes of steroid hormones: • Glucocorticoids, such as cortisol – Influence glucose metabolism and the immune system ...
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex also function in the body’s response to stress and fall into three classes of steroid hormones: • Glucocorticoids, such as cortisol – Influence glucose metabolism and the immune system ...
The Endocrine System
... mineralcorticoids - best known is aldosterone which has already been studied. These are produced mostly by the outer zona glomerulosa layer of the cortex. The mineralcorticoids regulate electrolyte balance by increasing Na+ reabsorption and K+secretion. 2) glucocorticoids - best known is cortisol, a ...
... mineralcorticoids - best known is aldosterone which has already been studied. These are produced mostly by the outer zona glomerulosa layer of the cortex. The mineralcorticoids regulate electrolyte balance by increasing Na+ reabsorption and K+secretion. 2) glucocorticoids - best known is cortisol, a ...
Endocrine System
... mineralcorticoids - best known is aldosterone which has already been studied. These are produced mostly by the outer zona glomerulosa layer of the cortex. The mineralcorticoids regulate electrolyte balance by increasing Na+ reabsorption and K+secretion. 2) glucocorticoids - best known is cortisol, a ...
... mineralcorticoids - best known is aldosterone which has already been studied. These are produced mostly by the outer zona glomerulosa layer of the cortex. The mineralcorticoids regulate electrolyte balance by increasing Na+ reabsorption and K+secretion. 2) glucocorticoids - best known is cortisol, a ...
I. General Characteristics of the Endocrine System
... increased force of cardiac muscle contraction, elevated blood pressure, increased breathing rate and decreased activity of the digestive system 3. The secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine are controlled by the sympathetic nervous system. C. Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex 1. Introduction a. Th ...
... increased force of cardiac muscle contraction, elevated blood pressure, increased breathing rate and decreased activity of the digestive system 3. The secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine are controlled by the sympathetic nervous system. C. Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex 1. Introduction a. Th ...
Hormone review
... Aldosterone secretion is not under the control of the anterior pituitary. It acts primarily on the kidney to promote absorption of sodium and excretion of potassium. Increased sodium levels contributes to the retention of water and thus increased blood volume. In the absence of aldosterone, sodium i ...
... Aldosterone secretion is not under the control of the anterior pituitary. It acts primarily on the kidney to promote absorption of sodium and excretion of potassium. Increased sodium levels contributes to the retention of water and thus increased blood volume. In the absence of aldosterone, sodium i ...
Clues
... 18. Condition that results from the inability to secrete ADH is diabetes _____. 20. The type of feedback that resists deviation from the normal. 23. Neurohormone produced by the adrenal medulla. 25. A hromone acts as a ____ messenger, which carries a signal to the cell membrane. 27. Hormones produce ...
... 18. Condition that results from the inability to secrete ADH is diabetes _____. 20. The type of feedback that resists deviation from the normal. 23. Neurohormone produced by the adrenal medulla. 25. A hromone acts as a ____ messenger, which carries a signal to the cell membrane. 27. Hormones produce ...
from the brain
... It is divided into two halves called the cerebral hemispheres that are connected by a large band of fibers called the corpus callosum They have different tasks (lateralization) ...
... It is divided into two halves called the cerebral hemispheres that are connected by a large band of fibers called the corpus callosum They have different tasks (lateralization) ...
... Describe the anatomy of the adrenal gland and name its parts. Describe the location and the function of the adrenal gland. Where is the thyroid located? How does it control metabolic rate? Is the pancreas an endocrine gland and/or an exocrine gland? Describe the cellular organization of the pancreas ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Hormonal Hormone produced by one endocrine gland (or hypothalamus) affects secretion of hormone by another endocrine gland • hypothalamus acts as overall coordinator releases regulatory hormones (releasing hormones or inhibitory hormones) affects anterior pituitary • anterior pituitary, when sti ...
... Hormonal Hormone produced by one endocrine gland (or hypothalamus) affects secretion of hormone by another endocrine gland • hypothalamus acts as overall coordinator releases regulatory hormones (releasing hormones or inhibitory hormones) affects anterior pituitary • anterior pituitary, when sti ...
physio unit 14 Ch78 Ch79
... Anterior pituitary secretes increasing FSH and LH FSH & LH stimulates follicles to secrete estrogen and inhibin Estrogen up-regulates LH (on thecal cells) and FSH (on granulosa cells) receptors Rapid increase in estrogen by follicle self-stim causes the pituitary to produce an LH surge LH ...
... Anterior pituitary secretes increasing FSH and LH FSH & LH stimulates follicles to secrete estrogen and inhibin Estrogen up-regulates LH (on thecal cells) and FSH (on granulosa cells) receptors Rapid increase in estrogen by follicle self-stim causes the pituitary to produce an LH surge LH ...
Chapter 7
... • Paired organs that cap the kidneys. • Each gland consists of an outer cortex and inner medulla. • Adrenal medulla: – Derived from embryonic neural crest ectoderm (sympathetic ganglia). – Synthesizes and secretes: • Catecholamines (mainly epinephrine but some norepinephrine). ...
... • Paired organs that cap the kidneys. • Each gland consists of an outer cortex and inner medulla. • Adrenal medulla: – Derived from embryonic neural crest ectoderm (sympathetic ganglia). – Synthesizes and secretes: • Catecholamines (mainly epinephrine but some norepinephrine). ...
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System
... - peptides (3-30 amino acids). - amines (modified versions of single amino acids). 固醇類激素(荷爾蒙) (2) The second class of hormones are steroid hormones, which include small, hydrophobic molecules made from cholesterol. 膽固醇 Hormone signaling involves three key events: - reception. - signal transduction ...
... - peptides (3-30 amino acids). - amines (modified versions of single amino acids). 固醇類激素(荷爾蒙) (2) The second class of hormones are steroid hormones, which include small, hydrophobic molecules made from cholesterol. 膽固醇 Hormone signaling involves three key events: - reception. - signal transduction ...
Lecture 1 - Principles of Endocrinology
... Flgure 9-5 Hormonal secretion Irom the primate pituitary gland (hypophysis) is controlled by the hypothalamus. The anterior lobe 01the pituitary gland (adenohypophysis) consists 01 the pars distal is, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis, (The pars tuberalis, not shown, consists 01 a thin layer 01 ce ...
... Flgure 9-5 Hormonal secretion Irom the primate pituitary gland (hypophysis) is controlled by the hypothalamus. The anterior lobe 01the pituitary gland (adenohypophysis) consists 01 the pars distal is, pars intermedia, and pars tuberalis, (The pars tuberalis, not shown, consists 01 a thin layer 01 ce ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.