The Endocrine System - Palm Beach State College
... • Has dual nature acting as an endocrine gland and a ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system – Innervated by sympathetic preganglionic fibers – Consists of modified sympathetic postganglionic neurons called chromaffin cells – When stimulated, release catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine ...
... • Has dual nature acting as an endocrine gland and a ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system – Innervated by sympathetic preganglionic fibers – Consists of modified sympathetic postganglionic neurons called chromaffin cells – When stimulated, release catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine ...
Endocrine_System__part_1__Feb_28__studen
... • Can occur at any point in the axis – Hypothalamus – Pituitary gland – Adrenal gland ...
... • Can occur at any point in the axis – Hypothalamus – Pituitary gland – Adrenal gland ...
hormonal
... • hormones and different ways of their transport; • proper organs and target tissues, responding to action of hormones. ...
... • hormones and different ways of their transport; • proper organs and target tissues, responding to action of hormones. ...
Night-Lighting
... Exposure to light at night can inhibit the pineal gland's production of melatonin. The pineal gland directs your body's rhythmic activities--including sleep, appetite, and the onset of puberty--through its production of melatonin. This hormone is primarily secreted at night, and it requires darkness ...
... Exposure to light at night can inhibit the pineal gland's production of melatonin. The pineal gland directs your body's rhythmic activities--including sleep, appetite, and the onset of puberty--through its production of melatonin. This hormone is primarily secreted at night, and it requires darkness ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Signals Maintain Homeostasis
... the endocrine system for control of organs and tissues The nervous system allows the body to adjust quickly to environmental changes The endocrine system is designed to maintain ...
... the endocrine system for control of organs and tissues The nervous system allows the body to adjust quickly to environmental changes The endocrine system is designed to maintain ...
Chapter 1: Animal Agriculture
... • Equine chorionic gonadotropin • Human chorionic gonadotropins ...
... • Equine chorionic gonadotropin • Human chorionic gonadotropins ...
System 2
... Mechanisms of Hormone Action • Target cell receptors show – specificity, high affinity (strength of binding), and low capacity (saturation) for a hormone • Lipophilic hormones – have receptors in target's cytoplasm and/or nucleus – diffuse through plasma membrane – target is the nucleus where they ...
... Mechanisms of Hormone Action • Target cell receptors show – specificity, high affinity (strength of binding), and low capacity (saturation) for a hormone • Lipophilic hormones – have receptors in target's cytoplasm and/or nucleus – diffuse through plasma membrane – target is the nucleus where they ...
Document
... is a form of defence that allows organisms to survive. The endocrine system is a group of specialised tissues (glands) that produce chemicals called hormones, many of which are proteins. ...
... is a form of defence that allows organisms to survive. The endocrine system is a group of specialised tissues (glands) that produce chemicals called hormones, many of which are proteins. ...
Thyroid and its Hormones The normal adults thyroid gland weight
... ACTH is one of the pituitary hormones secreted as a large precursor molecular which is cleaved to give several peptides each with important biological effect . The precursor or polypeptides is known as pro-opio melanocortin (POMC) . The secretion of POMC is under the control of CRF . The active ACTH ...
... ACTH is one of the pituitary hormones secreted as a large precursor molecular which is cleaved to give several peptides each with important biological effect . The precursor or polypeptides is known as pro-opio melanocortin (POMC) . The secretion of POMC is under the control of CRF . The active ACTH ...
The Endocrine System
... reproduction and regulates use of carbs and fats. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) – stimulates the metabolism of ALL tissues in the body. Folicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) – production of reproductive cells Prolactin (PRL) – production of milk in mammals Glands ...
... reproduction and regulates use of carbs and fats. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) – stimulates the metabolism of ALL tissues in the body. Folicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) – production of reproductive cells Prolactin (PRL) – production of milk in mammals Glands ...
Chapter 20 - mwsu-wiki
... 4. Iodide attaches to tyrosine within the thyroglobulin molecule 5. Coupling of iodinated tyrosine forms thyroid hormones - T3 and T4 formation 6. Thyroid hormones are stored attached to thyroglobulin within the colloid until it is released into the circulation - TH affects many body tissues, primar ...
... 4. Iodide attaches to tyrosine within the thyroglobulin molecule 5. Coupling of iodinated tyrosine forms thyroid hormones - T3 and T4 formation 6. Thyroid hormones are stored attached to thyroglobulin within the colloid until it is released into the circulation - TH affects many body tissues, primar ...
Endocrine ,cells are distributed in three different ways
... Endocrine tissue, is made up essentially of cells that synthesize hormones and release them at specific time in small amounts into the connective tissue or vascular system. So the endocrine cells lie near the blood capillaries . Hormones travel through the blood to the target cells, some hormones ac ...
... Endocrine tissue, is made up essentially of cells that synthesize hormones and release them at specific time in small amounts into the connective tissue or vascular system. So the endocrine cells lie near the blood capillaries . Hormones travel through the blood to the target cells, some hormones ac ...
You have completed this lesson regarding the Endocrine System of
... • Although the Pancreas is a very important organ involved in the endocrine system, it only secretes two hormones. • Insulin & Glucagon are secreted by the Pancreas and aid in regulating the body’s blood sugar. ...
... • Although the Pancreas is a very important organ involved in the endocrine system, it only secretes two hormones. • Insulin & Glucagon are secreted by the Pancreas and aid in regulating the body’s blood sugar. ...
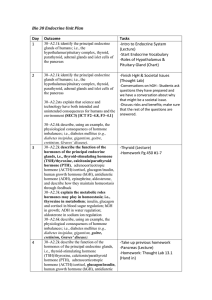
Bio 30 Endocrine Unit Plan Day Outcome Tasks 1 30–A2.1k identify
... 30–A2.2k describe the function of the hormones of the principal endocrine glands, i.e., thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)/thyroxine, calcitonin/parathyroid hormone (PTH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)/cortisol, glucagon/insulin, human growth hormone (hGH), antidiuretic hormone (ADH), epinephrin ...
... 30–A2.2k describe the function of the hormones of the principal endocrine glands, i.e., thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)/thyroxine, calcitonin/parathyroid hormone (PTH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)/cortisol, glucagon/insulin, human growth hormone (hGH), antidiuretic hormone (ADH), epinephrin ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... The endocrine system consists of a number of glands distributed in the head, neck, thorax, and abdomen. They secrete hormones which enter the blood to be distributed throughout the body to regulate growth, metabolism, and the function of many other cells, tissues, and organs. The functions of these ...
... The endocrine system consists of a number of glands distributed in the head, neck, thorax, and abdomen. They secrete hormones which enter the blood to be distributed throughout the body to regulate growth, metabolism, and the function of many other cells, tissues, and organs. The functions of these ...
IHB Endocrine Sys
... Adrenal Glands: Medulla • Adrenal medulla: neuroendocrine organ – Secretion: sympathetic nervous system – Hormones: nonsteroidal • Epinephrine and Norepinephrine secreted in response to emergency (short-term) stress (i.e., fight or flight response) ...
... Adrenal Glands: Medulla • Adrenal medulla: neuroendocrine organ – Secretion: sympathetic nervous system – Hormones: nonsteroidal • Epinephrine and Norepinephrine secreted in response to emergency (short-term) stress (i.e., fight or flight response) ...
EndocrineSystem
... Section of hormones from anterior pituitary controlled by hormones from hypothalamus Section of hormones from posterior pituitary control by action potentions caried by axchy from the hypothalamus. ...
... Section of hormones from anterior pituitary controlled by hormones from hypothalamus Section of hormones from posterior pituitary control by action potentions caried by axchy from the hypothalamus. ...
The Endocrine System
... • a small gland located on a stalk hanging from the base of the brain • “The Master Gland” – Primary function is to control other glands. – Produces many hormones. – Secretion is controlled by the hypothalamus in the base of the brain. ...
... • a small gland located on a stalk hanging from the base of the brain • “The Master Gland” – Primary function is to control other glands. – Produces many hormones. – Secretion is controlled by the hypothalamus in the base of the brain. ...
chapter 1 - Allied Schools
... Prostaglandins are also called tissue hormones because they frequently are produced in a tissue and diffuse only a short distance, acting on cells within that tissue. Typical hormones influence and control activities of widely separated organs. Prostaglandins can influence respiration, blood pressur ...
... Prostaglandins are also called tissue hormones because they frequently are produced in a tissue and diffuse only a short distance, acting on cells within that tissue. Typical hormones influence and control activities of widely separated organs. Prostaglandins can influence respiration, blood pressur ...
Endocrine 112KB 06.09.2016
... The endocrine system relates the most important regulatory systems. It carries out regulatory influence with the help of hormones practically on all functions of an organism – metabolism , growth, reproduction, mental activity, adaptation, functional activity of all organs. The endocrine system cont ...
... The endocrine system relates the most important regulatory systems. It carries out regulatory influence with the help of hormones practically on all functions of an organism – metabolism , growth, reproduction, mental activity, adaptation, functional activity of all organs. The endocrine system cont ...
Endocrine
... responses to stimuli such as stress, dehydration, low protein production, and low blood glucose levels. All of these factors-and many others- must be regulated to keep the internal functioning of the body at a constant and stable state. The Endocrine System not only maintains homeostasis through the ...
... responses to stimuli such as stress, dehydration, low protein production, and low blood glucose levels. All of these factors-and many others- must be regulated to keep the internal functioning of the body at a constant and stable state. The Endocrine System not only maintains homeostasis through the ...
The Endocrine System
... 2. *Medulla – inside – secretes epinephrine (adrenalin), a powerful cardiac stimulant, and norepinephrine. *The adrenal medulla responds to the sympathetic nervous system. The hormones produced are referred to as the “fight-or-flight” hormones, because they prepare the body for an emergency. The adr ...
... 2. *Medulla – inside – secretes epinephrine (adrenalin), a powerful cardiac stimulant, and norepinephrine. *The adrenal medulla responds to the sympathetic nervous system. The hormones produced are referred to as the “fight-or-flight” hormones, because they prepare the body for an emergency. The adr ...
The Endocrine System
... 2. *Medulla – inside – secretes epinephrine (adrenalin), a powerful cardiac stimulant, and norepinephrine. *The adrenal medulla responds to the sympathetic nervous system. The hormones produced are referred to as the “fight-or-flight” hormones, because they prepare the body for an emergency. The adr ...
... 2. *Medulla – inside – secretes epinephrine (adrenalin), a powerful cardiac stimulant, and norepinephrine. *The adrenal medulla responds to the sympathetic nervous system. The hormones produced are referred to as the “fight-or-flight” hormones, because they prepare the body for an emergency. The adr ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.