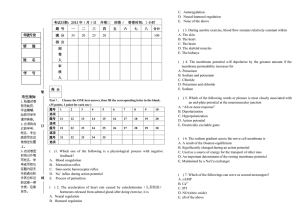
17. Endocrine System
... enlarged and are best called sinusoidal capillaries. They take their origin from capsular arteries (which you can see in the capsule) and run straight through the cortex to the medulla where they become a network of even larger medullary sinusoids. The layers of the cortex can be visually distinguis ...
... enlarged and are best called sinusoidal capillaries. They take their origin from capsular arteries (which you can see in the capsule) and run straight through the cortex to the medulla where they become a network of even larger medullary sinusoids. The layers of the cortex can be visually distinguis ...
NewSChapter18
... Adrenal Glands- sit on the superior border of each kidney. ▪The adrenal gland is divided into two parts: the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. ▫Adrenal Cortex- outer layer of the gland, yellowish in color due to stored lipids. ▫Produces more than two dozen steroid hormones, collectively called ...
... Adrenal Glands- sit on the superior border of each kidney. ▪The adrenal gland is divided into two parts: the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. ▫Adrenal Cortex- outer layer of the gland, yellowish in color due to stored lipids. ▫Produces more than two dozen steroid hormones, collectively called ...
hormones - WordPress.com
... • Soluble in plasma but cannot cross the lipid membrane • Act on cell surface receptors • Binding with the receptor leads to activation of a ‘second messenger’ cascade • May or may not affect transcription in the nucleus ...
... • Soluble in plasma but cannot cross the lipid membrane • Act on cell surface receptors • Binding with the receptor leads to activation of a ‘second messenger’ cascade • May or may not affect transcription in the nucleus ...
Chapter 7 PowerPoint
... funnel or infundibulum, magnum where albumen is secreted, isthmus which secretes the shell membranes, uterus or shell gland, the vagina which connects to the cloaca. ...
... funnel or infundibulum, magnum where albumen is secreted, isthmus which secretes the shell membranes, uterus or shell gland, the vagina which connects to the cloaca. ...
Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Part 3 of 6
... electrolyte and water balance. This in turn, causes the muscles to become weak, and shock is a possibility Hyperaldosteronisim – More water and sodium are retained, leading to high blood pressure and edema – potassium loss may disrupt heart activity and nervous system ...
... electrolyte and water balance. This in turn, causes the muscles to become weak, and shock is a possibility Hyperaldosteronisim – More water and sodium are retained, leading to high blood pressure and edema – potassium loss may disrupt heart activity and nervous system ...
The Endocrine System
... tissue rejection in transplant cases) • Secretion controlled by hypothalamus (corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)) based on cortisol level in blood • Increased release in response to stress, increasing availability of ATP and heightened response to vasoconstrictors • Hyposecretion - Addison’s dise ...
... tissue rejection in transplant cases) • Secretion controlled by hypothalamus (corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)) based on cortisol level in blood • Increased release in response to stress, increasing availability of ATP and heightened response to vasoconstrictors • Hyposecretion - Addison’s dise ...
The Endocrine and Reproductive System
... Uterus- A muscular organ where the egg develops into a baby. • The Cervix- The opening into the Uterus. • The Cervix leads into the Vagina- The birthing tube that leads to outside the body. ...
... Uterus- A muscular organ where the egg develops into a baby. • The Cervix- The opening into the Uterus. • The Cervix leads into the Vagina- The birthing tube that leads to outside the body. ...
Endocrine System
... by specialized cells • Cells secrete hormones into extracellular fluids (blood, lymph) • Blood transfers hormones to target sites • These hormones regulate the activity of other cells! ...
... by specialized cells • Cells secrete hormones into extracellular fluids (blood, lymph) • Blood transfers hormones to target sites • These hormones regulate the activity of other cells! ...
The Encorine System and Homeostasis
... The middle zone, zona fasciculata secrete mainly glucocorticoids hormone because they affect glucose homeostasis. The inner zone, zona reticularis, secretes androgens, which have masculinizing effects. Mineralocorticoids Aldosterone the major mineralocorticoid regulates homeostasis of two mineral io ...
... The middle zone, zona fasciculata secrete mainly glucocorticoids hormone because they affect glucose homeostasis. The inner zone, zona reticularis, secretes androgens, which have masculinizing effects. Mineralocorticoids Aldosterone the major mineralocorticoid regulates homeostasis of two mineral io ...
Hormones
... Hormones: Prostaglandins • Third class of (pseudo)hormones • Derived from arachidonic acid ...
... Hormones: Prostaglandins • Third class of (pseudo)hormones • Derived from arachidonic acid ...
The Endocrine System
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones and substances directly in the blood stream • These hormones regulate the body's growth, metabolism (the physical and chemical processes of the body), sexual development and function • The hormones are released into the bl ...
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones and substances directly in the blood stream • These hormones regulate the body's growth, metabolism (the physical and chemical processes of the body), sexual development and function • The hormones are released into the bl ...
The Endocrine System
... restst long-term stressors, by increasing blood glucose level -glucocorticoids also depressing the inflammatory response, by decreasing edema and reduce pain by inhibiting pain causing molecules Called prostaglendins , so they used as drugs to suppress inflammation -glucocorticoids are released from ...
... restst long-term stressors, by increasing blood glucose level -glucocorticoids also depressing the inflammatory response, by decreasing edema and reduce pain by inhibiting pain causing molecules Called prostaglendins , so they used as drugs to suppress inflammation -glucocorticoids are released from ...
Glands - cloudfront.net
... Other glands of the endocrine system are described below. You can refer to Figure 1.1 to see where they are located. • The thyroid gland is a large gland in the neck. Thyroid hormones increase the rate of metabolism in cells throughout the body. They control how quickly cells use energy and make pro ...
... Other glands of the endocrine system are described below. You can refer to Figure 1.1 to see where they are located. • The thyroid gland is a large gland in the neck. Thyroid hormones increase the rate of metabolism in cells throughout the body. They control how quickly cells use energy and make pro ...
Introduction to the Endocrine System
... Many hormones are controlled by some form of a negative feedback mechanism. In this type of system, a gland is sensitive to the concentration of a substance that it regulates. A negative feedback system causes a reversal of increases and decreases in body conditions in order to maintain a state of s ...
... Many hormones are controlled by some form of a negative feedback mechanism. In this type of system, a gland is sensitive to the concentration of a substance that it regulates. A negative feedback system causes a reversal of increases and decreases in body conditions in order to maintain a state of s ...
pancreas, in beta-cells of islets of Langerhans general, non
... hyperthyroidism: bulging eyes, increased heart rate, nervousness ...
... hyperthyroidism: bulging eyes, increased heart rate, nervousness ...
Biology 232
... parathyroid hormone (PTH) – major regulator of calcium level in blood increases blood calcium (decreases bone density) stimulates osteoclasts – increases resorption of bone controlled by negative feedback of blood calcium hypocalcemia – low blood calcium; may be caused by low PTH causes nerve depola ...
... parathyroid hormone (PTH) – major regulator of calcium level in blood increases blood calcium (decreases bone density) stimulates osteoclasts – increases resorption of bone controlled by negative feedback of blood calcium hypocalcemia – low blood calcium; may be caused by low PTH causes nerve depola ...
Chapter 13 Endocrine System
... Parathyroid Glands: There are four parathyroid glands, each of which is about the size of a grain of rice. These glands are located on the posterior side of the thyroid gland (para-: near, upon). The function of the hormone released from this gland is to work with calcitonin to control the blood lev ...
... Parathyroid Glands: There are four parathyroid glands, each of which is about the size of a grain of rice. These glands are located on the posterior side of the thyroid gland (para-: near, upon). The function of the hormone released from this gland is to work with calcitonin to control the blood lev ...
Endocrine System Jeopardy - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... Endocrine Thyroid Pituitary Gland Pancreas ...
... Endocrine Thyroid Pituitary Gland Pancreas ...
13 Physiologicoanatomical peculiarities of endocrine system
... The thyroid (from the Greek word for "shield", after its shape) is one of the larger endocrine glands in the body. It is a double-lobed structure located in the neck and produces hormones, principally thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), that regulate the rate of metabolism and affect the growt ...
... The thyroid (from the Greek word for "shield", after its shape) is one of the larger endocrine glands in the body. It is a double-lobed structure located in the neck and produces hormones, principally thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), that regulate the rate of metabolism and affect the growt ...
The Endocrine System
... emergencies. For example, adrenaline increases the amount of oxygen and glucose going to the muscles. You can see an animation of this response at the link below. http://www.abpischools.org.uk/page/modules/hormones/horm8.cfm?coSiteNavigation_allTopic=1 • The gonads secrete sex hormones. The male gon ...
... emergencies. For example, adrenaline increases the amount of oxygen and glucose going to the muscles. You can see an animation of this response at the link below. http://www.abpischools.org.uk/page/modules/hormones/horm8.cfm?coSiteNavigation_allTopic=1 • The gonads secrete sex hormones. The male gon ...
Endocrine System
... Overproduction leads to giantism – height, but also pronounced brow ridges and other effects. Underproduction leads to pituitary dwarfism – all parts in proportion but small. ...
... Overproduction leads to giantism – height, but also pronounced brow ridges and other effects. Underproduction leads to pituitary dwarfism – all parts in proportion but small. ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.