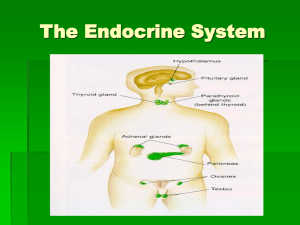
The Endocrine System
... – 2 small glands that sit atop both kidneys. – Each has 2 divisions, each with different functions. ...
... – 2 small glands that sit atop both kidneys. – Each has 2 divisions, each with different functions. ...
The Endocrine System
... – 2 small glands that sit atop both kidneys. – Each has 2 divisions, each with different functions. ...
... – 2 small glands that sit atop both kidneys. – Each has 2 divisions, each with different functions. ...
E-M Timeline - American Physiological Society
... 1902 Ernest Starling and William Bayliss discover that the small intestine produces secretin, a substance that stimulates the pancreas. They introduce the concept of a "hormone" from the Greek word meaning “I excite.” ...
... 1902 Ernest Starling and William Bayliss discover that the small intestine produces secretin, a substance that stimulates the pancreas. They introduce the concept of a "hormone" from the Greek word meaning “I excite.” ...
Classification of Hormones Lecture 1
... Endocrine Glands 6. The Adrenal gland: is composed of A. Adrenal cortex secretes: • Aldosterone which increase blood volume by reabsorption of sodium in kidneys. • Cortisol which affects glucose metabolism and immune status. • Androstenedione which is an anabolic male hormone and/or substrate for e ...
... Endocrine Glands 6. The Adrenal gland: is composed of A. Adrenal cortex secretes: • Aldosterone which increase blood volume by reabsorption of sodium in kidneys. • Cortisol which affects glucose metabolism and immune status. • Androstenedione which is an anabolic male hormone and/or substrate for e ...
Biological influences - Our eclass community
... organs (including brain) When they act on the brain they regulate, influence and affect many different parts of the body, our emotions and even our behaviour Example: our interest in food, the female ovarian and menstrual cycle, our moods, our growth rate, our metabolism Hormones are slow-acting ...
... organs (including brain) When they act on the brain they regulate, influence and affect many different parts of the body, our emotions and even our behaviour Example: our interest in food, the female ovarian and menstrual cycle, our moods, our growth rate, our metabolism Hormones are slow-acting ...
AP Biology Animal Form and Function
... release of insulin to stimulate the uptake of glucose from the blood to the liver to be stored as glycogen. If you go a long time between meals, however, your blood glucose may go below the desired level. This causes glucagon to be released. Glucagon acts on the liver to stimulate the removal of gly ...
... release of insulin to stimulate the uptake of glucose from the blood to the liver to be stored as glycogen. If you go a long time between meals, however, your blood glucose may go below the desired level. This causes glucagon to be released. Glucagon acts on the liver to stimulate the removal of gly ...
Endocrine System
... the level of glucose in the blood. Pineal Glands: A tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleepwake cycles and several other processes. Pituitary Glands: Attached to the hypothalamus by a thin stalk. The posterior (back) lobe stores hor ...
... the level of glucose in the blood. Pineal Glands: A tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleepwake cycles and several other processes. Pituitary Glands: Attached to the hypothalamus by a thin stalk. The posterior (back) lobe stores hor ...
View/Open
... • seasonal variation according to sun light exposure • recommendations for vitamin D supplementation updated in Finland: children in 2011 and over 60-year-old in 2010 ...
... • seasonal variation according to sun light exposure • recommendations for vitamin D supplementation updated in Finland: children in 2011 and over 60-year-old in 2010 ...
A hormone is a chemical substance. It helps different parts of an
... 1. A hormone is a chemical substance. It helps different parts of an organism to function in a coordinated way. 2. The endocrine system works with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis (balance) in the body. The glands and organs regulate and control body functions such a growth and development ...
... 1. A hormone is a chemical substance. It helps different parts of an organism to function in a coordinated way. 2. The endocrine system works with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis (balance) in the body. The glands and organs regulate and control body functions such a growth and development ...
Chapter 11 Efferent Division: Autonomic and Somatic Motor Control
... In response to alarm signals from the CNS, the adrenal medulla releases large amounts of epinephrine as part of the “Fight-or-Flight” response ...
... In response to alarm signals from the CNS, the adrenal medulla releases large amounts of epinephrine as part of the “Fight-or-Flight” response ...
chapter 39 * endocrine and reproductive systems - McGann
... There are two types of diabetes: Type I and Type II • Type I diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that usually develops in people before they turn 15. They’re bodies make little to no insulin. They must follow a strict diet and get daily injections of insulin to keep their blood glucose levels under ...
... There are two types of diabetes: Type I and Type II • Type I diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that usually develops in people before they turn 15. They’re bodies make little to no insulin. They must follow a strict diet and get daily injections of insulin to keep their blood glucose levels under ...
18-1
... Hormone Transport in Blood • Protein hormones circulate in free form in blood • Steroid (lipid) & thyroid hormones must attach to transport proteins synthesized by liver – improve transport by making them water-soluble – slow loss of hormone by filtration within kidney – create reserve of hormone • ...
... Hormone Transport in Blood • Protein hormones circulate in free form in blood • Steroid (lipid) & thyroid hormones must attach to transport proteins synthesized by liver – improve transport by making them water-soluble – slow loss of hormone by filtration within kidney – create reserve of hormone • ...
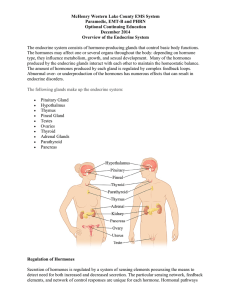
Important Glands of the Endocrine System
... responsibility is to regulate the body’s stress level. The main hormones involved in stress regulation produced here are the protein hormones adrenalin and noradrenalin. Fight or flight response. ...
... responsibility is to regulate the body’s stress level. The main hormones involved in stress regulation produced here are the protein hormones adrenalin and noradrenalin. Fight or flight response. ...
File
... • Acromegaly/Gigantism is a very rare disease and syndrome results from a chronic exposure to GH (Growth Hormone) leading to the classic clinical features that the diagnosis seems to be easy • High exposure to GH produces gigantism in youths prior to epiphyseal fusion and acromegaly in adults. • In ...
... • Acromegaly/Gigantism is a very rare disease and syndrome results from a chronic exposure to GH (Growth Hormone) leading to the classic clinical features that the diagnosis seems to be easy • High exposure to GH produces gigantism in youths prior to epiphyseal fusion and acromegaly in adults. • In ...
Chapter 18- The Endocrine System
... E) All of these are correct. 12) What do T3 and T4 have in common with epinephrine and norepinephrine? A) They are all water-soluble. B) They are all lipid-soluble. C) They are all derived from the amino acid tyrosine. D) They are all made by both the nervous and endocrine systems. E) They are all m ...
... E) All of these are correct. 12) What do T3 and T4 have in common with epinephrine and norepinephrine? A) They are all water-soluble. B) They are all lipid-soluble. C) They are all derived from the amino acid tyrosine. D) They are all made by both the nervous and endocrine systems. E) They are all m ...
Endocrine fill-in guided notes
... Function: Helps the body prepare for and ___________________________ Location: “_______________” glands because found above each kidney Hormones of the Adrenal Gland ___________________ (adrenaline) & Norepinephrine are released in emergency or stress situations to raise _____________________ leve ...
... Function: Helps the body prepare for and ___________________________ Location: “_______________” glands because found above each kidney Hormones of the Adrenal Gland ___________________ (adrenaline) & Norepinephrine are released in emergency or stress situations to raise _____________________ leve ...
The Endocrine System
... The Adrenal Medulla Acts very much like a part of the sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight) Secretes two amines: norepinephrine (20%) epinephrine (80%) Stimulated by preganglionic neurons directly, so controlled by the hypothalamus as if part of the autonomic nervous system, NOT by tropi ...
... The Adrenal Medulla Acts very much like a part of the sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight) Secretes two amines: norepinephrine (20%) epinephrine (80%) Stimulated by preganglionic neurons directly, so controlled by the hypothalamus as if part of the autonomic nervous system, NOT by tropi ...
Biology 30 Notes October 3, 2014 Introduction Endocrine System
... Example: Pancreas, secretes the hormone insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin affects its target cells by making them more permeable to glucose. Homeostasis depends on the close relationship between the nervous system and the endocrine system. Work together and not always easy to distinguish between ...
... Example: Pancreas, secretes the hormone insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin affects its target cells by making them more permeable to glucose. Homeostasis depends on the close relationship between the nervous system and the endocrine system. Work together and not always easy to distinguish between ...
Unit IV: Regulation Endocrine System
... • pores in cell membrane allow signaling chemicals to move from cell to cell – neurotransmitters • released from neurons to travel across gap to 2nd cell – paracrine (local) hormones • secreted into tissue fluids to affect nearby cells – hormones • chemical messengers that travel in the bloodstream ...
... • pores in cell membrane allow signaling chemicals to move from cell to cell – neurotransmitters • released from neurons to travel across gap to 2nd cell – paracrine (local) hormones • secreted into tissue fluids to affect nearby cells – hormones • chemical messengers that travel in the bloodstream ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... - thyroxine: increases the rate of metabolism in cells - triiodothyronine: increases the rate of metabolism in cells - calcitonin: increases the rate at which calcium is deposited in bone 2. What is the function of parathyroid hormone (PTH)? PTH increases calcium levels in blood and tissue fluid by ...
... - thyroxine: increases the rate of metabolism in cells - triiodothyronine: increases the rate of metabolism in cells - calcitonin: increases the rate at which calcium is deposited in bone 2. What is the function of parathyroid hormone (PTH)? PTH increases calcium levels in blood and tissue fluid by ...
Nervous/Endocrine Notes
... The inflammation may be caused by infection, or may be caused by a non infectious irritant to the meninges. The two most common forms of meningitis are Bacterial and Viral. Meningitis should not be confused with encephalitis which is inflammation of the brain itself. ...
... The inflammation may be caused by infection, or may be caused by a non infectious irritant to the meninges. The two most common forms of meningitis are Bacterial and Viral. Meningitis should not be confused with encephalitis which is inflammation of the brain itself. ...
The Endocrine System Chapter 10
... Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) Produced primarily during fetal development; targets melanocytes. No secretion in heathy adults ...
... Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) Produced primarily during fetal development; targets melanocytes. No secretion in heathy adults ...
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT
... gland. The thyroid plays an important role in the body’s metabolis. It secretes thyroxin, triiodothyronine, calcitonin, which affect metabolism, body heat and bone growth. Calcitonin antagonizes the action of parathyroid hormone. ...
... gland. The thyroid plays an important role in the body’s metabolis. It secretes thyroxin, triiodothyronine, calcitonin, which affect metabolism, body heat and bone growth. Calcitonin antagonizes the action of parathyroid hormone. ...
Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
... • Releases hormones that act on the metabolic rate. *T4: thyroxine *T3: triiodothyronine • Also produces the calcitonin. ...
... • Releases hormones that act on the metabolic rate. *T4: thyroxine *T3: triiodothyronine • Also produces the calcitonin. ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.