Neurotransmitters, Endocrine System, Synapses
... involved in many neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's, Huntington's, and Tourette's. ➢ High levels also contribute to Depression, OCD, and Autism ...
... involved in many neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's, Huntington's, and Tourette's. ➢ High levels also contribute to Depression, OCD, and Autism ...
Secretsto Exceptional Health
... more. Functioning primarily in the central nervous system (CNS), neurotransmitters facilitate communication between the brain and the body’s glands, organs and muscles. They are released from neurons and travel across a small space, called a synapse, to reach receptors on target cells. Inadequate ne ...
... more. Functioning primarily in the central nervous system (CNS), neurotransmitters facilitate communication between the brain and the body’s glands, organs and muscles. They are released from neurons and travel across a small space, called a synapse, to reach receptors on target cells. Inadequate ne ...
Chapter 45.
... Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large scale changes ...
... Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large scale changes ...
Endocrine System - Biology Junction
... Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large scale changes ...
... Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large scale changes ...
9 - Mr-Js-Science
... • Produced in outer adrenal cortex • Regulate mineral content in blood • Regulate water and electrolyte balance • Target organ is the kidney • Production stimulated by renin and aldosterone • Production inhibited by atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) ...
... • Produced in outer adrenal cortex • Regulate mineral content in blood • Regulate water and electrolyte balance • Target organ is the kidney • Production stimulated by renin and aldosterone • Production inhibited by atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) ...
Pituitary Gland - Meridian Kinesiology
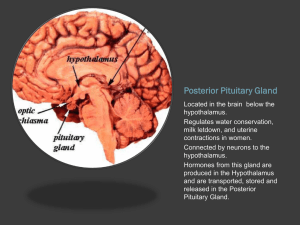
... Endocrine Gland situated at the back of the Brain - often regarded as a component of the Diencephalon of the Brain (the Pituitary does not contain Neurons and is therefore not correctly described as a component of the Nervous System). The Pituitary Gland is under the control of and has physical conn ...
... Endocrine Gland situated at the back of the Brain - often regarded as a component of the Diencephalon of the Brain (the Pituitary does not contain Neurons and is therefore not correctly described as a component of the Nervous System). The Pituitary Gland is under the control of and has physical conn ...
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان
... another membrane-bound protein called a G protein. The G protein activates adenylate cyclase, the enzyme that catalyzes the production of cAMP from ATP. Cyclic AMP then triggers an enzyme that generates specific cellular changes. Inositol triphosphate (IP3) is produced from membrane phospholipids. I ...
... another membrane-bound protein called a G protein. The G protein activates adenylate cyclase, the enzyme that catalyzes the production of cAMP from ATP. Cyclic AMP then triggers an enzyme that generates specific cellular changes. Inositol triphosphate (IP3) is produced from membrane phospholipids. I ...
Hormones - SITH ITB
... Chemical signals coordinate body functions ! Hormones are • chemical signals, • produced by endocrine glands, • usually carried in the blood, and • responsible for specific changes in target cells. ...
... Chemical signals coordinate body functions ! Hormones are • chemical signals, • produced by endocrine glands, • usually carried in the blood, and • responsible for specific changes in target cells. ...
Chapter 2: The Physiology of Stress
... Parasympathetic nervous system maintains homeostasis through the release of acetylcholine (ACh) is responsible for energy conservation and relaxation ...
... Parasympathetic nervous system maintains homeostasis through the release of acetylcholine (ACh) is responsible for energy conservation and relaxation ...
H1 Hormones - TASIS IB Biology
... Peptide and protein hormones • Soluble in plasma but cannot cross the lipid membrane • Act on cell surface receptors • Binding with the receptor leads to activtion of a ‘second messenger’ cascade ...
... Peptide and protein hormones • Soluble in plasma but cannot cross the lipid membrane • Act on cell surface receptors • Binding with the receptor leads to activtion of a ‘second messenger’ cascade ...
Endocrine System
... Diseases of the Endocrine System Diabetes: this disease affects how the body regulates blood glucose levels. It can either make the body not produce enough insulin (type 1) or have the body not respond to insulin properly, causing an imbalance of glucagon. Hypothyroidism: This disease is accumulate ...
... Diseases of the Endocrine System Diabetes: this disease affects how the body regulates blood glucose levels. It can either make the body not produce enough insulin (type 1) or have the body not respond to insulin properly, causing an imbalance of glucagon. Hypothyroidism: This disease is accumulate ...
The Endocrine System - APBIOSTUDENTS
... (ADH) and oxytocin are made in the hypothalamus by secretory neurons (neurons that make hormones rather than neurotransmitters). These hormones are stored in the axon terminals of the secretory hormones and are released when neuron is excited (action potential). Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) affect ...
... (ADH) and oxytocin are made in the hypothalamus by secretory neurons (neurons that make hormones rather than neurotransmitters). These hormones are stored in the axon terminals of the secretory hormones and are released when neuron is excited (action potential). Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) affect ...
Endocrine System
... hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. • The HPA axis involves the stimulation of hormone release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the pituitary by the hypothalamus. • Adrenal cortex produces three major groups of steroid hormones collectively called CORTICOSTEROIDS. – Mineralocorticoi ...
... hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. • The HPA axis involves the stimulation of hormone release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the pituitary by the hypothalamus. • Adrenal cortex produces three major groups of steroid hormones collectively called CORTICOSTEROIDS. – Mineralocorticoi ...
Endocrine PowerPoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... liver and muscles to glucose so that glucose is readily absorbed by these cells. 2. It promotes the conversion of glucose to glycogen in these cells. ...
... liver and muscles to glucose so that glucose is readily absorbed by these cells. 2. It promotes the conversion of glucose to glycogen in these cells. ...
My Endocrine System Notes - 2014 2015 - Key
... 1. Exocrine glands (not part of the endocrine system): secrete products into ducts which open into cavities in organs (ex: sweat and oil glands, digestive glands) 2. Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Endocrine glands include the hypothalamus (in brain), pituitary (in brain), th ...
... 1. Exocrine glands (not part of the endocrine system): secrete products into ducts which open into cavities in organs (ex: sweat and oil glands, digestive glands) 2. Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Endocrine glands include the hypothalamus (in brain), pituitary (in brain), th ...
Powerpoint lecture
... • Prime metabolic effect is gluconeogenesis formation of glucose from fats and proteins – Promotes rises in blood glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids ...
... • Prime metabolic effect is gluconeogenesis formation of glucose from fats and proteins – Promotes rises in blood glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids ...
Chapter 41 Animal Hormones
... Stressful stimuli cause hypothalamus to secrete releasing hormone that stimulates release of ACTH from anterior pituitary ACTH stimulates release of corticosteriods from adrenal cortex In humans, 2 primary types are glucocorticoids (cortisol) and mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) ...
... Stressful stimuli cause hypothalamus to secrete releasing hormone that stimulates release of ACTH from anterior pituitary ACTH stimulates release of corticosteriods from adrenal cortex In humans, 2 primary types are glucocorticoids (cortisol) and mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) ...
Endocrine and Reproductive System Web Quest Vanessa Cooper
... hypothalamus is located in the brain and is the main connection between the endocrine and nervous system It controls the pituitary gland by telling it when to make more or to stop producing hormones. • The pituitary gland is very important because it makes hormones that controls other endocrine glan ...
... hypothalamus is located in the brain and is the main connection between the endocrine and nervous system It controls the pituitary gland by telling it when to make more or to stop producing hormones. • The pituitary gland is very important because it makes hormones that controls other endocrine glan ...
Hormones - HD Nursing
... • Increases serum calcium levels by: − Stimulating osteoclasts to resorb bone − Reabsorption of Ca++ by kidneys − Blocks reabsorption of phosphate by kidneys − Promotes production of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 ...
... • Increases serum calcium levels by: − Stimulating osteoclasts to resorb bone − Reabsorption of Ca++ by kidneys − Blocks reabsorption of phosphate by kidneys − Promotes production of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 ...
key - Scioly.org
... 32. Since water-soluble hormones are unable to pass through the plasma membrane, the cellular action they initiate results from _____. a. ligand binding b. the activation of a signal transduction pathway c. direct stimulation of the cell’s DNA d. the enzymatic behavior of the signal molecule e. bin ...
... 32. Since water-soluble hormones are unable to pass through the plasma membrane, the cellular action they initiate results from _____. a. ligand binding b. the activation of a signal transduction pathway c. direct stimulation of the cell’s DNA d. the enzymatic behavior of the signal molecule e. bin ...
Z333 Lecture
... Increases blood sugar (cells release glucose) Type I Diabetes: lack β cells Type II Diabetes: low #s insulin receptors ...
... Increases blood sugar (cells release glucose) Type I Diabetes: lack β cells Type II Diabetes: low #s insulin receptors ...
The Endocrine System and Feedback Loops
... Insulin is secreted when high levels of sugar are detected (ex after eating) Glucagon is secreted when low levels of sugar are detected (ex after exercising) ...
... Insulin is secreted when high levels of sugar are detected (ex after eating) Glucagon is secreted when low levels of sugar are detected (ex after exercising) ...
The Blood and Endocrine Systems
... Samuel, Leslie. "Erythropoiesis – Formation of Red Blood Cells - Interactive Biology, with Leslie Samuel." Interactive Biology with Leslie Samuel. Leslie Samuel, 31 July 2012. Web. 26 Feb. 2015.
... Samuel, Leslie. "Erythropoiesis – Formation of Red Blood Cells - Interactive Biology, with Leslie Samuel." Interactive Biology with Leslie Samuel. Leslie Samuel, 31 July 2012. Web. 26 Feb. 2015.
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.