LESSON 14 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM INTRODUCTION The
... They are referred to as endocrine glands because they release their specific chemicals directly into the bloodstream. These chemicals are called hormones because they can regulate many different body functions. Hormones stimulate the growth of bones, cause the maturation of sex organs and reproducti ...
... They are referred to as endocrine glands because they release their specific chemicals directly into the bloodstream. These chemicals are called hormones because they can regulate many different body functions. Hormones stimulate the growth of bones, cause the maturation of sex organs and reproducti ...
Document
... endocrine system when compared with the nervous system? a. relies on release of chemical that bind to specific receptors b. relies primarily on negative feedback mechanisms ...
... endocrine system when compared with the nervous system? a. relies on release of chemical that bind to specific receptors b. relies primarily on negative feedback mechanisms ...
Notes_Endocrine2013
... Some signal molecules act as both neurotransmitters and hormones epinephrine: you know about liver cells’ response to this hormones: break glycogen down into glucose ...
... Some signal molecules act as both neurotransmitters and hormones epinephrine: you know about liver cells’ response to this hormones: break glycogen down into glucose ...
Study Guide for Endocrine
... 50. What precursor is required for the manufacture of all corticoid hormones? 51. What is the principle mineralocorticoid? 52. What are its effects? 53. When would it be released? High or low blood pressure 54. What is the most important glucocorticoid hormone in the body? 55. What is the definition ...
... 50. What precursor is required for the manufacture of all corticoid hormones? 51. What is the principle mineralocorticoid? 52. What are its effects? 53. When would it be released? High or low blood pressure 54. What is the most important glucocorticoid hormone in the body? 55. What is the definition ...
Ch 45 - Phillips Scientific Methods
... • Enters cell & binds to intracellular receptors • Causes change in gene expression (protein synthesis) • Slower response • Longer life • Eg. androgens (testosterone), estrogen, progesterone, cortisol ...
... • Enters cell & binds to intracellular receptors • Causes change in gene expression (protein synthesis) • Slower response • Longer life • Eg. androgens (testosterone), estrogen, progesterone, cortisol ...
Can you help me explain what I have I written below to
... A hormone it is supposed to release, and how the target organs are affected when that specific endocrine process does not function properly. How would you explain the process to a younger patient? Offer at least one analogy and any other means of explanation. ...
... A hormone it is supposed to release, and how the target organs are affected when that specific endocrine process does not function properly. How would you explain the process to a younger patient? Offer at least one analogy and any other means of explanation. ...
Chapter 10 Endocrine System
... o The circulatory system – systemic vasoconstriction o The adrenal cortex – release of aldosterone c. Androgens – derivatives of estrogen and testosterone – produced in minuet quantities – responsible for some male characteristics – increases female sex drive and influences some female characteristi ...
... o The circulatory system – systemic vasoconstriction o The adrenal cortex – release of aldosterone c. Androgens – derivatives of estrogen and testosterone – produced in minuet quantities – responsible for some male characteristics – increases female sex drive and influences some female characteristi ...
Endocrine System and Hormones
... then stimulates the release of more oxytocin. This causes more contractions. The fetus pushes harder on the cervix. More oxytocin is released. The system continues until birth occurs. ...
... then stimulates the release of more oxytocin. This causes more contractions. The fetus pushes harder on the cervix. More oxytocin is released. The system continues until birth occurs. ...
chapt11answers
... complex forms? Generally activates a G-protein, which then activates an enzyme on the inner surface of the cell membrane.. This produces a second messenger inside the cell that then activates prteins to induce changes within the cell What is the name of the second messenger? The most common second m ...
... complex forms? Generally activates a G-protein, which then activates an enzyme on the inner surface of the cell membrane.. This produces a second messenger inside the cell that then activates prteins to induce changes within the cell What is the name of the second messenger? The most common second m ...
Endocrine System
... 1. Paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys 2. Structurally & functionally: Two glands in one (Adrenal Medulla & Adrenal Cortex) 3. Adrenal Cortex: Glandular tissue a. Synthesizes and releases steroid hormones called corticosteroids b. Different corticosteroids are produced in each of the thre ...
... 1. Paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys 2. Structurally & functionally: Two glands in one (Adrenal Medulla & Adrenal Cortex) 3. Adrenal Cortex: Glandular tissue a. Synthesizes and releases steroid hormones called corticosteroids b. Different corticosteroids are produced in each of the thre ...
Ch44
... Prostaglandins are modified fatty acids that have a wide range of activities. Lungs, liver, digestive tract and reproductive organs release prostaglandins. Affect cells in their immediate vicinity. Mimic cyclic AMP and interact with other hormones that regulate many metabolic ...
... Prostaglandins are modified fatty acids that have a wide range of activities. Lungs, liver, digestive tract and reproductive organs release prostaglandins. Affect cells in their immediate vicinity. Mimic cyclic AMP and interact with other hormones that regulate many metabolic ...
Unit 12 Chp 45 Animal Endocrine System Notes
... Estrogen, progesterone, vitamin D, and NO are examples of hormones and regulators that enter target cells and bind to intracellular receptors. ...
... Estrogen, progesterone, vitamin D, and NO are examples of hormones and regulators that enter target cells and bind to intracellular receptors. ...
Endocrine System
... rich network of capillaries, and hormones are carried to target tissues & organs by the blood. ...
... rich network of capillaries, and hormones are carried to target tissues & organs by the blood. ...
The Endocrine System
... Regulate mineral content in blood Regulate water and electrolyte balance Target organ is the kidney Production stimulated by renin and aldosterone Production inhibited by atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) Glucocorticoids (including cortisone and cortisol) Produced in the middle layer of the adrenal c ...
... Regulate mineral content in blood Regulate water and electrolyte balance Target organ is the kidney Production stimulated by renin and aldosterone Production inhibited by atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) Glucocorticoids (including cortisone and cortisol) Produced in the middle layer of the adrenal c ...
Endocrine System
... Adrenaline - “fight or flight” hormone Estrogen -main female hormone Glands -small organs that make chemicals to help your body function in many ways. Growth hormones -chemicals causing bones, muscles and other organs to grow. Hormones-chemicals that tell your body when/how to function. Insulin- hor ...
... Adrenaline - “fight or flight” hormone Estrogen -main female hormone Glands -small organs that make chemicals to help your body function in many ways. Growth hormones -chemicals causing bones, muscles and other organs to grow. Hormones-chemicals that tell your body when/how to function. Insulin- hor ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... amino acids across cell membranes and speeds the rate that cells utilize carbohydrates and fats; two secretions from the hypothalamus (GH releasing hormone and GH release-inhibiting hormone) control the secretion of GH; also influenced by nutritional state; during low blood glucose concentration or ...
... amino acids across cell membranes and speeds the rate that cells utilize carbohydrates and fats; two secretions from the hypothalamus (GH releasing hormone and GH release-inhibiting hormone) control the secretion of GH; also influenced by nutritional state; during low blood glucose concentration or ...
The Nervous System
... Ganglia are near the innervated organ – Long Pre short Post The post innervates only a single organ Reflects function of discretely regulating processes such as digestion ...
... Ganglia are near the innervated organ – Long Pre short Post The post innervates only a single organ Reflects function of discretely regulating processes such as digestion ...
An Introduction to Endocrinology
... Adrenal Glands • Embedded above each kidney in a capsule of fat • Composed of two endocrine organs – Adrenal cortex • Outer portion • Secretes steroid hormones (aldostrone, cortisol) ...
... Adrenal Glands • Embedded above each kidney in a capsule of fat • Composed of two endocrine organs – Adrenal cortex • Outer portion • Secretes steroid hormones (aldostrone, cortisol) ...
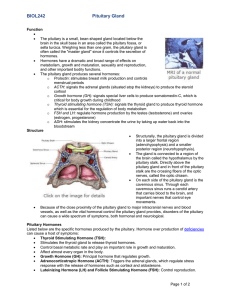
BIOL242pituitaryOCT2012
... Because of the close proximity of the pituitary gland to major intracranial nerves and blood vessels, as well as the vital hormonal control the pituitary gland provides, disorders of the pituitary can cause a wide spectrum of symptoms, both hormonal and neurological. Pituitary Hormones Listed belo ...
... Because of the close proximity of the pituitary gland to major intracranial nerves and blood vessels, as well as the vital hormonal control the pituitary gland provides, disorders of the pituitary can cause a wide spectrum of symptoms, both hormonal and neurological. Pituitary Hormones Listed belo ...
Name - G9Biology
... o If you drink water to replenish blood water levels, the hypothalamus tells the pituitary gland to stop releasing (secreting) ADH, so you go to the bathroom more often (more water in urine) ...
... o If you drink water to replenish blood water levels, the hypothalamus tells the pituitary gland to stop releasing (secreting) ADH, so you go to the bathroom more often (more water in urine) ...
Endocrine Disorders Pituitary Gland Anterior pituitary gland
... Nursing Interventions and Calcium Disorders Monitor calcium levels Warn client to check OTC drugs for calcium content Instruct client to report symptoms of hypo / hypercalcemia For calcitriol do not use other sources of vitamin D ...
... Nursing Interventions and Calcium Disorders Monitor calcium levels Warn client to check OTC drugs for calcium content Instruct client to report symptoms of hypo / hypercalcemia For calcitriol do not use other sources of vitamin D ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.