21 Endocrine MtSAC
... • The hypothalamus releases its hormone (TSHRH) to the pituitary, telling the pituitary to release its hormone (TSH), which tells the thyroid gland to release thyroid hormone (TH). • When thyroid hormone is released, it will circulate throughout the body, causing an increase in metabolism in all of ...
... • The hypothalamus releases its hormone (TSHRH) to the pituitary, telling the pituitary to release its hormone (TSH), which tells the thyroid gland to release thyroid hormone (TH). • When thyroid hormone is released, it will circulate throughout the body, causing an increase in metabolism in all of ...
Chapter 5: Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes
... from the bloodstream. Iodine in the bloodstream comes from food that has been consumed; iodized salt is the primary source. ...
... from the bloodstream. Iodine in the bloodstream comes from food that has been consumed; iodized salt is the primary source. ...
Endocrine Vs Exocrine glands
... testes. The pancreas is also part of this hormone-secreting system, even though it is also associated with the digestive system because it also produces and secretes digestive enzymes. Although the endocrine glands are the body's main hormone producers, some non-endocrine organs — such as the brain, ...
... testes. The pancreas is also part of this hormone-secreting system, even though it is also associated with the digestive system because it also produces and secretes digestive enzymes. Although the endocrine glands are the body's main hormone producers, some non-endocrine organs — such as the brain, ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • An Adrenal Gland sits above each kidney • Adrenal Cortex secretes steroid hormones for chronic stress • Adrenal Medulla is a modified sympathetic ganglion that secretes neurotransmitters (catecholamine hormones) into the blood in response to acute stress. – catecholamines secreted by the adrenal m ...
... • An Adrenal Gland sits above each kidney • Adrenal Cortex secretes steroid hormones for chronic stress • Adrenal Medulla is a modified sympathetic ganglion that secretes neurotransmitters (catecholamine hormones) into the blood in response to acute stress. – catecholamines secreted by the adrenal m ...
Oxidation of Fat
... 1. Pyruvic acid from glycolysis is converted to acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA). 2. Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle and forms 2 ATP, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen. 3. Hydrogen in the cell combines with two coenzymes that carry it to the electron transport chain.(NADH) 4. Electron transport chain rec ...
... 1. Pyruvic acid from glycolysis is converted to acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA). 2. Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle and forms 2 ATP, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen. 3. Hydrogen in the cell combines with two coenzymes that carry it to the electron transport chain.(NADH) 4. Electron transport chain rec ...
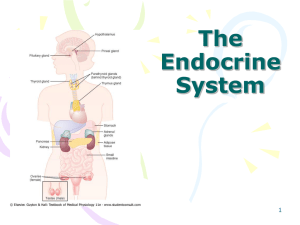
The Endocrine System - Austin Community College
... • Adrenal glands – paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys • Structurally and functionally, they are two glands in one • Adrenal medulla – nervous tissue that acts as part of the SNS • Adrenal cortex – glandular tissue derived from embryonic mesoderm Adrenal Medulla • stimulated by the sympat ...
... • Adrenal glands – paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys • Structurally and functionally, they are two glands in one • Adrenal medulla – nervous tissue that acts as part of the SNS • Adrenal cortex – glandular tissue derived from embryonic mesoderm Adrenal Medulla • stimulated by the sympat ...
1 2 - UMSONPatho
... Description • The hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary are important in the stress response • Cells release releasing factors that travel through the vessels and cause cells in the anterior pituitary to release tropic hormones – Go to target glands to release peripheral hormones • The hormone has ...
... Description • The hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary are important in the stress response • Cells release releasing factors that travel through the vessels and cause cells in the anterior pituitary to release tropic hormones – Go to target glands to release peripheral hormones • The hormone has ...
Endocrine System
... • Gonadocorticoids include both androgens and estrogens. Androgens (which include testosterone) are the primary gonadocorticoids. • Hormones may be involved in outset of puberty • Androgens for females are thought to influence sex drive and may be converted to estrogens after menopause • Hypersecret ...
... • Gonadocorticoids include both androgens and estrogens. Androgens (which include testosterone) are the primary gonadocorticoids. • Hormones may be involved in outset of puberty • Androgens for females are thought to influence sex drive and may be converted to estrogens after menopause • Hypersecret ...
Endocrine System
... 4. Parathyroid hormone and calcitonin balance blood calcium 5. Endocrine tissues of the pancreas secrete insulin and glucagon, antagonistic hormones that regulate blood glucose 6. The adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex help the body manage stress 7. Gonadal steroids regulate growth, development, rep ...
... 4. Parathyroid hormone and calcitonin balance blood calcium 5. Endocrine tissues of the pancreas secrete insulin and glucagon, antagonistic hormones that regulate blood glucose 6. The adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex help the body manage stress 7. Gonadal steroids regulate growth, development, rep ...
SECOND HORMONE(s)
... 14. Which statement(s) is/are true about Thyroid hormone (TH)? a. TH is secreted in response to TSH b. TH has four active forms c. TH lowers basal metabolic rate d. TH decreases body temperature e. TH causes increased lethargy and hypothyroidism 15. Which of the following is not considered to be a m ...
... 14. Which statement(s) is/are true about Thyroid hormone (TH)? a. TH is secreted in response to TSH b. TH has four active forms c. TH lowers basal metabolic rate d. TH decreases body temperature e. TH causes increased lethargy and hypothyroidism 15. Which of the following is not considered to be a m ...
FINAL EXAMINATION hormone
... (5 points) 1. (√)Calcitonin is an antagonistic hormone to parathyroid hormone. 2. (X) Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates T3 and T4 secretions. ...
... (5 points) 1. (√)Calcitonin is an antagonistic hormone to parathyroid hormone. 2. (X) Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates T3 and T4 secretions. ...
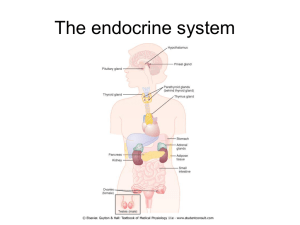
endocrine system
... growth and/or abnormal distribution of hair), poor wound healing, bruise easily, “moon face”, fatty hump between the shoulders, and obesity ...
... growth and/or abnormal distribution of hair), poor wound healing, bruise easily, “moon face”, fatty hump between the shoulders, and obesity ...
Chapter 26
... increased blood glucose 2. Increased blood pressure 3. Increased breathing rate 4. Increased metabolic rate 5. Change in blood-flow patterns, leading to increased alertness and decreased digestive and kidney activity ...
... increased blood glucose 2. Increased blood pressure 3. Increased breathing rate 4. Increased metabolic rate 5. Change in blood-flow patterns, leading to increased alertness and decreased digestive and kidney activity ...
9 Endocrine physiology
... pregnancy hormone. The substrate, when cleaved, precipitates out of solution; it gives you a color, and a new line appears, turning the negative into a plus sign. If no hormone is present, there is no second set of antibodies, the enzyme is not cleaved, no color change. Is she a little or a lot preg ...
... pregnancy hormone. The substrate, when cleaved, precipitates out of solution; it gives you a color, and a new line appears, turning the negative into a plus sign. If no hormone is present, there is no second set of antibodies, the enzyme is not cleaved, no color change. Is she a little or a lot preg ...
Hormones and Young Living Essential Oils
... Sometimes called the “master gland” because of its great influence on the other body organs. Its function is complex and important for overall well-being. Connected to the nervous system through the hypothalamus. Produces hormones that act directly on the body and that stimulate other endocrine glan ...
... Sometimes called the “master gland” because of its great influence on the other body organs. Its function is complex and important for overall well-being. Connected to the nervous system through the hypothalamus. Produces hormones that act directly on the body and that stimulate other endocrine glan ...
Instructor`s Guide
... islets of Langerhans: Clusters of cells in the pancreas that produce glucagon (secreted by alpha cells) and insulin (secreted by beta cells). kidneys: Two organs of the endocrine system, located at the back of the abdominal cavity, that produce renin, a hormone that ultimately helps regulate blood p ...
... islets of Langerhans: Clusters of cells in the pancreas that produce glucagon (secreted by alpha cells) and insulin (secreted by beta cells). kidneys: Two organs of the endocrine system, located at the back of the abdominal cavity, that produce renin, a hormone that ultimately helps regulate blood p ...
Chapter 9
... Releasing hormones: GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. TRH. Thyroid-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone. Causes anterior pituitary to pr ...
... Releasing hormones: GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. TRH. Thyroid-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone. Causes anterior pituitary to pr ...
Chapter 17 Endocrine System
... – histamine from mast cells in connective tissue causes relaxation of blood vessel smooth muscle – nitric oxide from endothelium of blood vessels causes vasodilation – somatostatin from gamma cells inhibits secretion of alpha and beta cells in pancreas – catecholamines diffuse from adrenal medulla t ...
... – histamine from mast cells in connective tissue causes relaxation of blood vessel smooth muscle – nitric oxide from endothelium of blood vessels causes vasodilation – somatostatin from gamma cells inhibits secretion of alpha and beta cells in pancreas – catecholamines diffuse from adrenal medulla t ...
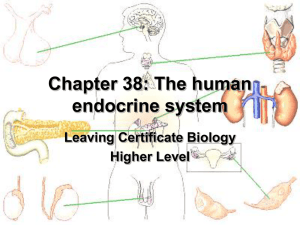
The Endocrine System - Leaving Cert Biology
... The Endocrine System • The basis of the endocrine system is the action of hormones – A hormone is a chemical messenger secreted by an endocrine gland directly into the bloodstream where it is carried to its target organ or tissue where it exerts a specific effect • Most hormones are protein in natu ...
... The Endocrine System • The basis of the endocrine system is the action of hormones – A hormone is a chemical messenger secreted by an endocrine gland directly into the bloodstream where it is carried to its target organ or tissue where it exerts a specific effect • Most hormones are protein in natu ...
Adrenocortical Modulation Following ACTH, Corticoid, and
... Prajna P. Ray, Santasri Chaudhuri-Sengupta and Biswa R. Maiti (2003) Adrenocortical modulation following ACTH, corticoid, and medullary hormone administration in the soft-shelled turtle Lissemys punctata punctata (Bonnoterre)(Family:Trionychidae). Zoological Studies 42 (1): 165-172. Our aim was to s ...
... Prajna P. Ray, Santasri Chaudhuri-Sengupta and Biswa R. Maiti (2003) Adrenocortical modulation following ACTH, corticoid, and medullary hormone administration in the soft-shelled turtle Lissemys punctata punctata (Bonnoterre)(Family:Trionychidae). Zoological Studies 42 (1): 165-172. Our aim was to s ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.