Chapter 1 - Basic Principles of Endocrine Physiology Mary Zoe
... They are most similar to the steroid hormones and will be discussed below. 1. Four hormones are known – epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin. They are synthesized from tyrosine (first 3) and tryptophan (serotonin). 2. These hormones do not have a hierarchic “feedback system”. Their re ...
... They are most similar to the steroid hormones and will be discussed below. 1. Four hormones are known – epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin. They are synthesized from tyrosine (first 3) and tryptophan (serotonin). 2. These hormones do not have a hierarchic “feedback system”. Their re ...
Endocrine Physiology
... General Organization •Pituitary gland and hypothalamus function in a coordinated manner to integrate many endocrine glands. •Pituitary gland is located just below the hypothalamus at the base of the brain to which it is connected by a short stalk (named the infundibulum,动脉圆锥). •Pituitary is divided ...
... General Organization •Pituitary gland and hypothalamus function in a coordinated manner to integrate many endocrine glands. •Pituitary gland is located just below the hypothalamus at the base of the brain to which it is connected by a short stalk (named the infundibulum,动脉圆锥). •Pituitary is divided ...
Active potential of contractive heart cells Phases of active potential 0
... decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin І. Angiotensin І, by the influences of angiotensin converting enzyme in the vessel of lung, converted in angiotensin II. Angiotensin ІІ has stron ...
... decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin І. Angiotensin І, by the influences of angiotensin converting enzyme in the vessel of lung, converted in angiotensin II. Angiotensin ІІ has stron ...
Lecture 4_Circulation of blood and its regulation. Features of
... decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin І. Angiotensin І, by the influences of angiotensin converting enzyme in the vessel of lung, converted in angiotensin II. Angiotensin ІІ has stron ...
... decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin І. Angiotensin І, by the influences of angiotensin converting enzyme in the vessel of lung, converted in angiotensin II. Angiotensin ІІ has stron ...
Ch 16 - MDC Faculty Web Pages
... (Slide 52) ____________________________ is hypersecretion of aldosterone due to adrenal tumors. (Slide 53) Glucocorticoids keep blood sugar levels relatively constant and maintain blood pressure by increasing the action of ________________________. (Slide 54) ____________________ is the most importa ...
... (Slide 52) ____________________________ is hypersecretion of aldosterone due to adrenal tumors. (Slide 53) Glucocorticoids keep blood sugar levels relatively constant and maintain blood pressure by increasing the action of ________________________. (Slide 54) ____________________ is the most importa ...
Chapter 25 - Las Positas College
... Stimuli received from other glands Certain hormones signal secretion of other hormones Hypothalamus secretes hormones stimulates pituitary stimulates other glands ...
... Stimuli received from other glands Certain hormones signal secretion of other hormones Hypothalamus secretes hormones stimulates pituitary stimulates other glands ...
Target cells
... – Location – on top of the kidney – Structure – outer cortex and inner medulla – Medulla • Secretes epinephrine & norepinephrine • Target – most cells • Effect – Epinephrine – increase cardiac activity, blood pressure, blood glucose; constricts blood vessels in skin, dilates blood vessels in skeleta ...
... – Location – on top of the kidney – Structure – outer cortex and inner medulla – Medulla • Secretes epinephrine & norepinephrine • Target – most cells • Effect – Epinephrine – increase cardiac activity, blood pressure, blood glucose; constricts blood vessels in skin, dilates blood vessels in skeleta ...
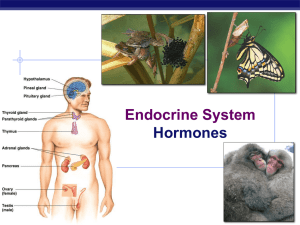
Hormones - Perry Local Schools
... secreted into the circulatory system and communicate regulatory messages within the body. • Hormones reach all parts of the body, but only target cells are equipped to respond. • Insect metamorphosis and many other processes are regulated by hormones. • P.S. – Plants have hormones too ...
... secreted into the circulatory system and communicate regulatory messages within the body. • Hormones reach all parts of the body, but only target cells are equipped to respond. • Insect metamorphosis and many other processes are regulated by hormones. • P.S. – Plants have hormones too ...
The Posterior Pituitary and Hypothalamic Hormones
... Adrenal glands – paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys ...
... Adrenal glands – paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys ...
Chapter 14 Marieb
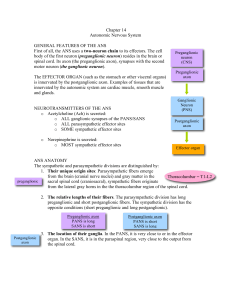
... 1. The preganglionic axon originates at the lateral gray horn and leaves the spinal column via the ventral root and spinal nerves T5-T9 only. It passes through the sympathetic chain via the white ramus, and then passes through the celiac ganglion via the splanchnic nerve. It keeps going! It continue ...
... 1. The preganglionic axon originates at the lateral gray horn and leaves the spinal column via the ventral root and spinal nerves T5-T9 only. It passes through the sympathetic chain via the white ramus, and then passes through the celiac ganglion via the splanchnic nerve. It keeps going! It continue ...
Lecture 4: Endocrine System
... The organs of the body communicate with each other through the nervous and endocrine systems. The nervous system uses neurotransmitters and neurons to convey information to and from the brain. In contrast, the endocrine system uses hormones, which are chemical messengers produced by endocrine organs ...
... The organs of the body communicate with each other through the nervous and endocrine systems. The nervous system uses neurotransmitters and neurons to convey information to and from the brain. In contrast, the endocrine system uses hormones, which are chemical messengers produced by endocrine organs ...
Hearing - 港九潮州公會中學
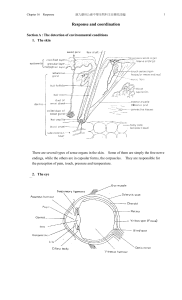
... 1. The nervous system senses changes within the body and in the external environment. 2. It interprets the changes. 3. The nervous system responds to the interpretation by initiating action in the form of muscular contraction or glandular secretions. 4. It integrates body activities in multicellular ...
... 1. The nervous system senses changes within the body and in the external environment. 2. It interprets the changes. 3. The nervous system responds to the interpretation by initiating action in the form of muscular contraction or glandular secretions. 4. It integrates body activities in multicellular ...
Endocrine Disruptors: Atrazine
... ACTH (adrenocorticotrophic hormone) - produced by the pituitary gland to influence the release of corticosteroid hormones from the adrenal glands, ADH (anti-diuretic hormone, vasopressin) - produced by the pituitary gland to stimulate water reabsorption by the kidney tubules Adrenaline (epinephrine) ...
... ACTH (adrenocorticotrophic hormone) - produced by the pituitary gland to influence the release of corticosteroid hormones from the adrenal glands, ADH (anti-diuretic hormone, vasopressin) - produced by the pituitary gland to stimulate water reabsorption by the kidney tubules Adrenaline (epinephrine) ...
The Pathology of Pituitary
... adenohypophysis and/or the neurohypophysis) • (2) Visual problems (from an expanding mass impinging on the optic chiasm, i.e., bitemporal hemianopsia) • (3) Enlarged sella turcica on skull x-rays (due to expanding masses; large pituitary adenomas eventually erode the sella, clinoid processes, diaphr ...
... adenohypophysis and/or the neurohypophysis) • (2) Visual problems (from an expanding mass impinging on the optic chiasm, i.e., bitemporal hemianopsia) • (3) Enlarged sella turcica on skull x-rays (due to expanding masses; large pituitary adenomas eventually erode the sella, clinoid processes, diaphr ...
exocrine glands
... Cells or aggregations of cells that synthesizes a substance to be released ,either in the blood stream or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface ...
... Cells or aggregations of cells that synthesizes a substance to be released ,either in the blood stream or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface ...
File - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... Hormones can be divided into two broad chemical classes. This chemical classification is useful because the two classes exert their effects differently – Lipid soluble hormones bind to receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus of the cell – Water soluble hormones bind to receptors on the surface of the ...
... Hormones can be divided into two broad chemical classes. This chemical classification is useful because the two classes exert their effects differently – Lipid soluble hormones bind to receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus of the cell – Water soluble hormones bind to receptors on the surface of the ...
The Endocrine System
... • Growth hormone (GH; 191 amino acids) and prolactin (PRL; 198 amino acids) • Includes all hormones secreted by: • Hypothalamus, heart, thymus, digestive tract, pancreas, and posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, as well as several hormones produced in other organs © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Growth hormone (GH; 191 amino acids) and prolactin (PRL; 198 amino acids) • Includes all hormones secreted by: • Hypothalamus, heart, thymus, digestive tract, pancreas, and posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, as well as several hormones produced in other organs © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
内分泌学―――Lecture Note
... releasing/inhibitory hormones (or factors). These factors are secreted into the interstitial fluid in median eminence of hypothalamus and absorbed into the capillaries, which is then conducted to the anterior pituitary through the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal vessels. In the anterior pituitary, t ...
... releasing/inhibitory hormones (or factors). These factors are secreted into the interstitial fluid in median eminence of hypothalamus and absorbed into the capillaries, which is then conducted to the anterior pituitary through the hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal vessels. In the anterior pituitary, t ...
LWW PPT Slide Template Master
... Increases muscle protein synthesis when amino acid is adequate ...
... Increases muscle protein synthesis when amino acid is adequate ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Integrates activities of endocrine & nervous system Produces Hormones that regulates Pituitary Gland Pituitary produces other hormones that regulate ...
... Integrates activities of endocrine & nervous system Produces Hormones that regulates Pituitary Gland Pituitary produces other hormones that regulate ...
Endocrine Strachan 14-15
... differ between the sexes, but do not have a direct role in reproduction AP Biology ...
... differ between the sexes, but do not have a direct role in reproduction AP Biology ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Glucagon – allows glucose to enter the blood from alpha cells These hormones are antagonists that maintain blood sugar homeostasis Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Glucagon – allows glucose to enter the blood from alpha cells These hormones are antagonists that maintain blood sugar homeostasis Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
13 Physiologicoanatomical peculiarities of endocrine system in
... It does this in response to releasing hormones produced by the hypothalamus. These travel to the anterior lobe by way of a special capillary system, called the ...
... It does this in response to releasing hormones produced by the hypothalamus. These travel to the anterior lobe by way of a special capillary system, called the ...
File
... release oxytocin, which further stimulates the milk glands. • This is an example of positive feedback, where the stimulus leads to an even greater ...
... release oxytocin, which further stimulates the milk glands. • This is an example of positive feedback, where the stimulus leads to an even greater ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.