Endocrine System Notes
... 2 main types of hormones Steroid Hormones – are lipid like carbon rings These hormones are able to pass though the cell membrane. ...
... 2 main types of hormones Steroid Hormones – are lipid like carbon rings These hormones are able to pass though the cell membrane. ...
Thyroid Metabolic Hormones
... T4 & T3 receptors are either attached to the DNA genetic strands or located in proximity to them receptors become activated transcription mRNA hundreds of proteins ...
... T4 & T3 receptors are either attached to the DNA genetic strands or located in proximity to them receptors become activated transcription mRNA hundreds of proteins ...
HMC Pulse
... – The Hypothalamus produces hormones that: – Are released by the posterior pituitary – Raise or lower production of anterior pituitary hormones – The pituitary gland: – Produces hormones that regulate other endocrine glands in the body – Each of these hormones has a feedback loop that maintains ...
... – The Hypothalamus produces hormones that: – Are released by the posterior pituitary – Raise or lower production of anterior pituitary hormones – The pituitary gland: – Produces hormones that regulate other endocrine glands in the body – Each of these hormones has a feedback loop that maintains ...
23.2 How Do Animal Hormones Work?
... • The release of thyroxine is under control of the hypothalamus by negative feedback. • Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary stimulates the thyroid to release thyroxine; high thyroxine concentrations in the blood inhibit TSH release from the anterior pituitary. • Iodine in t ...
... • The release of thyroxine is under control of the hypothalamus by negative feedback. • Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary stimulates the thyroid to release thyroxine; high thyroxine concentrations in the blood inhibit TSH release from the anterior pituitary. • Iodine in t ...
Material from all new lectures up to this point
... – (*) Expand story line for each of these hormones following an order such as: origin, stimuli, biosynthesis, release, target, action mechanism, effect, integration, others" ...
... – (*) Expand story line for each of these hormones following an order such as: origin, stimuli, biosynthesis, release, target, action mechanism, effect, integration, others" ...
The Endocrine System - Union County College
... 1. Come from endocrine glands 2. Circulate in the bloodstream 3. Act only upon specific cells in the body • Endocrine glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream; they do not need ducts to help ...
... 1. Come from endocrine glands 2. Circulate in the bloodstream 3. Act only upon specific cells in the body • Endocrine glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream; they do not need ducts to help ...
Chapter 11 - Tribiana.com
... Ranges from mins to hrs for most (days for thyroid hormones) Normal tissue responses are produced only when hormones are in physiological range High (pharmacological) doses can cause # of side effects Probably by binding to receptors of other hormones ...
... Ranges from mins to hrs for most (days for thyroid hormones) Normal tissue responses are produced only when hormones are in physiological range High (pharmacological) doses can cause # of side effects Probably by binding to receptors of other hormones ...
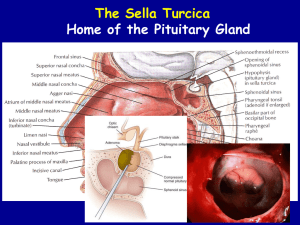
Hypothalamic and Pituitary Hormones
... • Four (4) of these ones are called Tropic Hormones as they stimulate the growth, nutrition and function of : • other endocrine glands • TSH : regulates Thyroid gland secretion • ACTH : controls secretion of Adrenal Cortex • FSH : maintains female sex hormones level and follicle growth • LH : regula ...
... • Four (4) of these ones are called Tropic Hormones as they stimulate the growth, nutrition and function of : • other endocrine glands • TSH : regulates Thyroid gland secretion • ACTH : controls secretion of Adrenal Cortex • FSH : maintains female sex hormones level and follicle growth • LH : regula ...
23 Comp Review 2
... types of lysosome enzymes than neutrophils so they are better at killing difficult pathogens. They also use antibodies for opsonization. When they leave the bloodstream and enter the tissues, they are called MACROPHAGES. ...
... types of lysosome enzymes than neutrophils so they are better at killing difficult pathogens. They also use antibodies for opsonization. When they leave the bloodstream and enter the tissues, they are called MACROPHAGES. ...
6. Physiology of heart. Physiological bases of hemo dynamic
... decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin І. Angiotensin І, by the influences of angiotensin converting enzyme in the vessel of lung, converted in angiotensin II. Angiotensin ІІ has stron ...
... decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin І. Angiotensin І, by the influences of angiotensin converting enzyme in the vessel of lung, converted in angiotensin II. Angiotensin ІІ has stron ...
Lecture 11: Thyroid and Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands: Learning
... Suprarenal Medulla Chromaffin cells secrete catecholamines (mainly epinephrine) into the bloodstream Medullary hormones adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) activate the body to fight-or-flight in response to acute stress Increase heart rate & blood pressure Dilate b ...
... Suprarenal Medulla Chromaffin cells secrete catecholamines (mainly epinephrine) into the bloodstream Medullary hormones adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) activate the body to fight-or-flight in response to acute stress Increase heart rate & blood pressure Dilate b ...
Document
... The purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The Publishers assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages caused by the use of theses programs or from the use of the information herein. ...
... The purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The Publishers assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages caused by the use of theses programs or from the use of the information herein. ...
Hormones
... body’s organs so that they work together. The endocrine system is based on the production of chemical messengers called hormones. Hormones are produced by glands (endocrine glands) in different parts of the body. These chemical messengers are produced in very small quantities and are transported in ...
... body’s organs so that they work together. The endocrine system is based on the production of chemical messengers called hormones. Hormones are produced by glands (endocrine glands) in different parts of the body. These chemical messengers are produced in very small quantities and are transported in ...
Hormones
... body’s organs so that they work together. The endocrine system is based on the production of chemical messengers called hormones. Hormones are produced by glands (endocrine glands) in different parts of the body. These chemical messengers are produced in very small quantities and are transported in ...
... body’s organs so that they work together. The endocrine system is based on the production of chemical messengers called hormones. Hormones are produced by glands (endocrine glands) in different parts of the body. These chemical messengers are produced in very small quantities and are transported in ...
topic13 - Bukowian metodyczka - misiek-puchatek
... acetylcholine, released by cholinergic fibers, and nor-epinephrine, released by adrenergic fibers. Neural release of norpinephrine into the plasma produces the same effects as secretion of this substance by the adrenal medulla. This similarity in chemical activity demonstrates the interrelatedness ...
... acetylcholine, released by cholinergic fibers, and nor-epinephrine, released by adrenergic fibers. Neural release of norpinephrine into the plasma produces the same effects as secretion of this substance by the adrenal medulla. This similarity in chemical activity demonstrates the interrelatedness ...
The Endocrine System: Regulating the Body`s
... When a hormone reaches a target cell, it causes the cell to respond in a specific way. The program uses the parathyroid glands as an example. The hormone released by the parathyroids causes target cells in the bones to release calcium, which the body needs. The program shows students in different s ...
... When a hormone reaches a target cell, it causes the cell to respond in a specific way. The program uses the parathyroid glands as an example. The hormone released by the parathyroids causes target cells in the bones to release calcium, which the body needs. The program shows students in different s ...
1. overview of the endocrine system
... The main target of ADH is the renal tubules where they cause increased quantities of water to be reabsorbed from the urine and restored into the blood (hence reducing urine output and increasing blood volume). A drop in blood pressure also stimulates the secretion of ADH. Oxytocin: In females, it ac ...
... The main target of ADH is the renal tubules where they cause increased quantities of water to be reabsorbed from the urine and restored into the blood (hence reducing urine output and increasing blood volume). A drop in blood pressure also stimulates the secretion of ADH. Oxytocin: In females, it ac ...
Endocrine disease
... • An autoimmune disease in which antibodies to the TSH receptor on the surface of the thyroid cells appear to mimic the action of the pituitary hormones. ...
... • An autoimmune disease in which antibodies to the TSH receptor on the surface of the thyroid cells appear to mimic the action of the pituitary hormones. ...
Chapter 18 - Endocrine
... Mineralocorticoids Regulate the electrolyte concentrations of extracellular fluids Aldosterone – most important mineralocorticoid Maintains Na+ balance by reducing excretion of sodium from the body Stimulates reabsorption of Na+ by the kidneys ...
... Mineralocorticoids Regulate the electrolyte concentrations of extracellular fluids Aldosterone – most important mineralocorticoid Maintains Na+ balance by reducing excretion of sodium from the body Stimulates reabsorption of Na+ by the kidneys ...
Hormones
... • What has happened to his cells and their receptors? • The doctor has decided to try giving him an MAO inhibitor along with his dopamine. Why? Copyright © 2009 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... • What has happened to his cells and their receptors? • The doctor has decided to try giving him an MAO inhibitor along with his dopamine. Why? Copyright © 2009 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
L#15 - Dr. Faisal Mohammed - Done by: marah madain
... Eicosanoids: special kind of hormones, they are derivatives of arachidonic acid (a fatty acid composed of 20 cardon atoms, 4 double bonds, exists in the membrane by the action of cyclooxygenaseprostaglandin or eicosanoids) Prostaglandin is responsible for pain sensation, as it synthesizes pain fibe ...
... Eicosanoids: special kind of hormones, they are derivatives of arachidonic acid (a fatty acid composed of 20 cardon atoms, 4 double bonds, exists in the membrane by the action of cyclooxygenaseprostaglandin or eicosanoids) Prostaglandin is responsible for pain sensation, as it synthesizes pain fibe ...
MODULE 8 : Endocrine System - Rajarata University of Sri Lanka
... 2.2.20. Explain how the secretion of thyrotropin is controlled 2.2.21. Recall that prolactin of 23,000 MW is secreted by lactotropes which increase in number and size during pregnancy 2.2.22. Recall that it is involved in initiation and maintenance of lactation 2.2.23. Recall that physiological leve ...
... 2.2.20. Explain how the secretion of thyrotropin is controlled 2.2.21. Recall that prolactin of 23,000 MW is secreted by lactotropes which increase in number and size during pregnancy 2.2.22. Recall that it is involved in initiation and maintenance of lactation 2.2.23. Recall that physiological leve ...
Control and Coordination
... deposition of the proteins in the tissues.Hence there is low excretion of nitrogen. This leads to growth and elongation of the bones by absorption of calcium from blood.It brings about proportionate growth of the muscles and visceral organs. ...
... deposition of the proteins in the tissues.Hence there is low excretion of nitrogen. This leads to growth and elongation of the bones by absorption of calcium from blood.It brings about proportionate growth of the muscles and visceral organs. ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.