Regents Biology - Magrin Science
... once body is back to normal level, signal is turned off gland ...
... once body is back to normal level, signal is turned off gland ...
Transcripts/3_9 2
... b. We are going to talk about these all at once. c. We have simplified cross sections of the hypothalamic structures we’re talking about. d. So in this case neurons in the arcuate nucleus produce GRH and release it near the portal vessels near the median eminence. Blood vessels convey it to the ante ...
... b. We are going to talk about these all at once. c. We have simplified cross sections of the hypothalamic structures we’re talking about. d. So in this case neurons in the arcuate nucleus produce GRH and release it near the portal vessels near the median eminence. Blood vessels convey it to the ante ...
power pt notes endo - Aurora City School
... activate G proteins. They exert their effects on target cells through a second messenger, such as cAMP, which alters the activity of enzymes present in the cell. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... activate G proteins. They exert their effects on target cells through a second messenger, such as cAMP, which alters the activity of enzymes present in the cell. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
hormones
... endocrine glands and their negative feedback mechanisms – Example: under severe stress, hypothalamus and sympathetic nervous system activated • body glucose levels rise ...
... endocrine glands and their negative feedback mechanisms – Example: under severe stress, hypothalamus and sympathetic nervous system activated • body glucose levels rise ...
Parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone, which
... gland that regulates calcium levels. It does this by removing calcium from its storage sites in bones and releasing it into the bloodstream. It also signals the kidneys to reabsorb more of this mineral, transporting it into the blood. PTH can also signal the small intestine to absorb calcium by tran ...
... gland that regulates calcium levels. It does this by removing calcium from its storage sites in bones and releasing it into the bloodstream. It also signals the kidneys to reabsorb more of this mineral, transporting it into the blood. PTH can also signal the small intestine to absorb calcium by tran ...
ENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY: PITUITARY AND THYROID
... 2. Other mechanisms are paracrine whereby chemical modulators do not enter the circulation but travel a short distance between the secretory cell and the target cell. 3. Neuroendocrine function involves neurones discharging their secretory products directly into the circulation (hypothalmic and post ...
... 2. Other mechanisms are paracrine whereby chemical modulators do not enter the circulation but travel a short distance between the secretory cell and the target cell. 3. Neuroendocrine function involves neurones discharging their secretory products directly into the circulation (hypothalmic and post ...
Marieb Chapter 16: The Endocrine System
... hormones transported in the blood • Responses occur more slowly but tend to last longer than those of the nervous system • Endocrine glands: pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands ...
... hormones transported in the blood • Responses occur more slowly but tend to last longer than those of the nervous system • Endocrine glands: pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands ...
Thyrosyn - New Roots Herbal
... amino acids, minerals, and specific nutrients to strengthen thyroid function. Impaired thyroid function, known as hypothyroidism, impacts the metabolism of every living cell. Symptoms include fatigue, generalized chills, dry skin, slow heart rate, and unexplained weight gain. Hereditary factors, agi ...
... amino acids, minerals, and specific nutrients to strengthen thyroid function. Impaired thyroid function, known as hypothyroidism, impacts the metabolism of every living cell. Symptoms include fatigue, generalized chills, dry skin, slow heart rate, and unexplained weight gain. Hereditary factors, agi ...
The Posterior Pituitary and Hypothalamic Hormones Posterior
... Adrenal glands – paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys ...
... Adrenal glands – paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys ...
Chap 12
... Adrenal Cortex Three cell layers (zones) Outer layer—secretes mineralocorticoids Middle layer—secretes glucocorticoids Inner layer—secretes sex hormones Mineralocorticoids—increase blood sodium and decrease body potassium concentrations by accelerating kidney tubule reabsorption of sodium ...
... Adrenal Cortex Three cell layers (zones) Outer layer—secretes mineralocorticoids Middle layer—secretes glucocorticoids Inner layer—secretes sex hormones Mineralocorticoids—increase blood sodium and decrease body potassium concentrations by accelerating kidney tubule reabsorption of sodium ...
The Peripheral Endocrine Glands
... direct negative-feedback system between pancreatic β cells and concentration of glucose in the blood flowing to them – Glucose stimulates insulin secretion by means of an excitation–secretion coupling ...
... direct negative-feedback system between pancreatic β cells and concentration of glucose in the blood flowing to them – Glucose stimulates insulin secretion by means of an excitation–secretion coupling ...
Endocrine Web Practice - Oakland Schools Moodle
... b. result from activation of the endocrine system. c. involve the activity of the nervous system. d. require messages from the pituitary gland. ...
... b. result from activation of the endocrine system. c. involve the activity of the nervous system. d. require messages from the pituitary gland. ...
Chapter 13
... Renin causes angiotensinogen angiotensin I In lungs angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) causes angiotensin I angiotensin II Angiotensin II stimulates aldosterone release Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
... Renin causes angiotensinogen angiotensin I In lungs angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) causes angiotensin I angiotensin II Angiotensin II stimulates aldosterone release Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology II
... Renin causes angiotensinogen angiotensin I In lungs angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) causes angiotensin I angiotensin II Angiotensin II stimulates aldosterone release Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
... Renin causes angiotensinogen angiotensin I In lungs angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) causes angiotensin I angiotensin II Angiotensin II stimulates aldosterone release Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
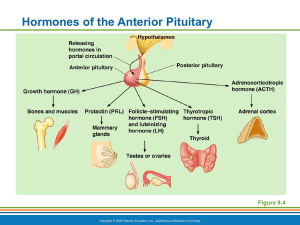
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary 6 Anterior Pituitary Hormones
... of GH during childhood Gigantism results from hypersecretion of GH during childhood Acromegaly results from hypersecretion of GH during adulthood ...
... of GH during childhood Gigantism results from hypersecretion of GH during childhood Acromegaly results from hypersecretion of GH during adulthood ...
The Endocrine System - healingenergies-at
... The physical human body is made up of a multitude of different kinds of cells but can only grow and develop and function properly if there is co-ordinated interaction between these various kinds of cells. One of the ways in which cells communicate with each other is by chemical signals. The chemical ...
... The physical human body is made up of a multitude of different kinds of cells but can only grow and develop and function properly if there is co-ordinated interaction between these various kinds of cells. One of the ways in which cells communicate with each other is by chemical signals. The chemical ...
categories of chemical regulators
... – All steroids are made from cholesterol – Water soluble? • NO • Almost all have binding proteins for transport in blood • They can pass across membranes – No storage – Receptors are intracellular ...
... – All steroids are made from cholesterol – Water soluble? • NO • Almost all have binding proteins for transport in blood • They can pass across membranes – No storage – Receptors are intracellular ...
18-2 Hormones - Anatomy and Physiology
... • Are chains of amino acids • Most are synthesized as prohormones • Inactive molecules converted to active hormones before or after they are secreted ...
... • Are chains of amino acids • Most are synthesized as prohormones • Inactive molecules converted to active hormones before or after they are secreted ...
Lesson Overview
... The heart-pounding, anxious feeling you get when excited or frightened—commonly known as the “fight or flight” response–is produced when impulses from the sympathetic nervous system stimulate the adrenal medulla to release large amounts of epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine. ...
... The heart-pounding, anxious feeling you get when excited or frightened—commonly known as the “fight or flight” response–is produced when impulses from the sympathetic nervous system stimulate the adrenal medulla to release large amounts of epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine. ...
Introduction to Endocrinology
... For certain hormones ,a decreased metabolic clearance rate may cause an excessively high concentration of the hormone in the circulating body fluids . For instance ,this occur for several of the steroid hormones when the liver is diseased , because these hormones are conjugated mainly in the liver a ...
... For certain hormones ,a decreased metabolic clearance rate may cause an excessively high concentration of the hormone in the circulating body fluids . For instance ,this occur for several of the steroid hormones when the liver is diseased , because these hormones are conjugated mainly in the liver a ...
hormones
... surrounding the secretor cells rather than into ducts. From the interstitial fluid, hormones diffuse into blood capillaries and blood carries them to target cells throughout the body. The endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands). In addition,several o ...
... surrounding the secretor cells rather than into ducts. From the interstitial fluid, hormones diffuse into blood capillaries and blood carries them to target cells throughout the body. The endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands). In addition,several o ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.