Slides - Napa Valley College
... Hypothalamic-Inhibiting Hormones The hypothalamic-inhibiting hormones inhibit the Anterior Pituitary Gland from releasing (secreting) its hormones. ...
... Hypothalamic-Inhibiting Hormones The hypothalamic-inhibiting hormones inhibit the Anterior Pituitary Gland from releasing (secreting) its hormones. ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... response—such as a change in metabolism—only from specific target cells, those that have the matching receptor. Cells lacking a receptor for that particular hormone are unaffected. Chemical signaling by hormones is the function of the endocrine system, one of the two basic systems of communication a ...
... response—such as a change in metabolism—only from specific target cells, those that have the matching receptor. Cells lacking a receptor for that particular hormone are unaffected. Chemical signaling by hormones is the function of the endocrine system, one of the two basic systems of communication a ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... the embryo. Within the larval caterpillar, they are nourished as islands of tissues that will eventually become the eyes, wings, brain, and other structures of the butterfly. Once the plump, crawling caterpillar becomes a stationary pupa, the adult cells take over. They complete their program of deve ...
... the embryo. Within the larval caterpillar, they are nourished as islands of tissues that will eventually become the eyes, wings, brain, and other structures of the butterfly. Once the plump, crawling caterpillar becomes a stationary pupa, the adult cells take over. They complete their program of deve ...
PPT File
... – Local hormones include histamine, which is released as part of the allergic and inflammatory responses, and the cytokines by which cells of the immune system communicate with one another – Local hormones have only short range actions because they are either degraded rapidly or taken up by nearby c ...
... – Local hormones include histamine, which is released as part of the allergic and inflammatory responses, and the cytokines by which cells of the immune system communicate with one another – Local hormones have only short range actions because they are either degraded rapidly or taken up by nearby c ...
Slides 9.1
... Glucagon – allows glucose to enter the blood from alpha cells These hormones are antagonists that maintain blood sugar homeostasis Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Glucagon – allows glucose to enter the blood from alpha cells These hormones are antagonists that maintain blood sugar homeostasis Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
138 Hormones and the Body
... condition in which insufficient thyroid hormone is produced. The two thyroid hormones, T3 and T4 , both contain iodine. (T3 , or triiodothyronine, contains three iodine atoms, while T4 contains four iodine atoms.) If an iodine deficiency occurs, the body cannot make sufficient thyroid hormones, re ...
... condition in which insufficient thyroid hormone is produced. The two thyroid hormones, T3 and T4 , both contain iodine. (T3 , or triiodothyronine, contains three iodine atoms, while T4 contains four iodine atoms.) If an iodine deficiency occurs, the body cannot make sufficient thyroid hormones, re ...
Document
... • All sympathetic preganglionic neurons release acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter (cholinergic) • Sympathetic postganglionic neurons release norepinephrine (adrenergic) with the exception of neurons to blood vessels and sweat glands (cholinergic) ...
... • All sympathetic preganglionic neurons release acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter (cholinergic) • Sympathetic postganglionic neurons release norepinephrine (adrenergic) with the exception of neurons to blood vessels and sweat glands (cholinergic) ...
Chapter 5 → Hormonal Responses to Exercise Objectives Objectives
... Thyroid Gland • Stimulated by TSH • Triiodothyronine (T3) & thyroxine (T4) – Establishment of metabolic rate – Permissive hormones Permit full effect of other hormones ...
... Thyroid Gland • Stimulated by TSH • Triiodothyronine (T3) & thyroxine (T4) – Establishment of metabolic rate – Permissive hormones Permit full effect of other hormones ...
Hormone
... signal transduction pathways and/or effector proteins. Responses of target cells may also differ if they have different receptors for the hormone. ...
... signal transduction pathways and/or effector proteins. Responses of target cells may also differ if they have different receptors for the hormone. ...
Slides 15.1
... glandular region in three layers Medulla – inner neural tissue region Sits on top of the kidneys ...
... glandular region in three layers Medulla – inner neural tissue region Sits on top of the kidneys ...
endocrine part 1
... The Endocrine System Second messenger system of the body Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction Growth and development Mobilization of body defenses Maintenance of much of homeostasis Regulation of met ...
... The Endocrine System Second messenger system of the body Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction Growth and development Mobilization of body defenses Maintenance of much of homeostasis Regulation of met ...
The Living World - Chapter 29 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... A hormone is a chemical signal that is produced in one part of the body and that acts at a distant site Three advantages to using chemical signals 1. Can spread to all tissues via the blood 2. Can persist much longer than electric signals 3. Many can act as hormones Different hormones can target dif ...
... A hormone is a chemical signal that is produced in one part of the body and that acts at a distant site Three advantages to using chemical signals 1. Can spread to all tissues via the blood 2. Can persist much longer than electric signals 3. Many can act as hormones Different hormones can target dif ...
The Endocrine System - Napa Valley College
... Adrenal Medulla - Epinepherine Hormone secreted by adrenal medulla: Epinephrine - prepares the body for quick action. “fight or flight” / short-term response to stress. ...
... Adrenal Medulla - Epinepherine Hormone secreted by adrenal medulla: Epinephrine - prepares the body for quick action. “fight or flight” / short-term response to stress. ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex – Also function in the body’s response to stress – Fall into three classes of steroid hormones ...
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex – Also function in the body’s response to stress – Fall into three classes of steroid hormones ...
Chapter 5
... prolonged exercise and discuss how those changes influence the four mechanisms used to maintain the blood glucose concentration: insulin, glucagon, cortisol, gorwth hormone, epinephrine, and horepinephrine ...
... prolonged exercise and discuss how those changes influence the four mechanisms used to maintain the blood glucose concentration: insulin, glucagon, cortisol, gorwth hormone, epinephrine, and horepinephrine ...
16 The Endocrine System: Part B
... 1. Renin-angiotensin mechanism: decreased blood pressure stimulates kidneys to release renin, triggers formation of angiotensin II, a potent stimulator of aldosterone release 2. Plasma concentration of K+: Increased K+ directly influences the zona glomerulosa cells to release ...
... 1. Renin-angiotensin mechanism: decreased blood pressure stimulates kidneys to release renin, triggers formation of angiotensin II, a potent stimulator of aldosterone release 2. Plasma concentration of K+: Increased K+ directly influences the zona glomerulosa cells to release ...
Part B
... 1. Renin-angiotensin mechanism: decreased blood pressure stimulates kidneys to release renin, triggers formation of angiotensin II, a potent stimulator of aldosterone release 2. Plasma concentration of K+: Increased K+ directly influences the zona glomerulosa cells to release ...
... 1. Renin-angiotensin mechanism: decreased blood pressure stimulates kidneys to release renin, triggers formation of angiotensin II, a potent stimulator of aldosterone release 2. Plasma concentration of K+: Increased K+ directly influences the zona glomerulosa cells to release ...
Part b
... 1. Renin-angiotensin mechanism: decreased blood pressure stimulates kidneys to release renin, triggers formation of angiotensin II, a potent stimulator of aldosterone release 2. Plasma concentration of K+: Increased K+ directly influences the zona glomerulosa cells to release ...
... 1. Renin-angiotensin mechanism: decreased blood pressure stimulates kidneys to release renin, triggers formation of angiotensin II, a potent stimulator of aldosterone release 2. Plasma concentration of K+: Increased K+ directly influences the zona glomerulosa cells to release ...
ch_16_lecture_outline_b
... 1. Renin-angiotensin mechanism: decreased blood pressure stimulates kidneys to release renin, triggers formation of angiotensin II, a potent stimulator of aldosterone release 2. Plasma concentration of K+: Increased K+ directly influences the zona glomerulosa cells to release ...
... 1. Renin-angiotensin mechanism: decreased blood pressure stimulates kidneys to release renin, triggers formation of angiotensin II, a potent stimulator of aldosterone release 2. Plasma concentration of K+: Increased K+ directly influences the zona glomerulosa cells to release ...
16 - PHSchool.com
... Mechanisms of Hormone Action All major hormones circulate to virtually all tissues, but a given hormone influences the activity of only certain tissue cells, referred to as its target cells. Hormones bring about their ...
... Mechanisms of Hormone Action All major hormones circulate to virtually all tissues, but a given hormone influences the activity of only certain tissue cells, referred to as its target cells. Hormones bring about their ...
cells - Anatomy and Physiology
... 1. Renin-angiotensin mechanism: decreased blood pressure stimulates kidneys to release renin, triggers formation of angiotensin II, a potent stimulator of aldosterone release 2. Plasma concentration of K+: Increased K+ directly influences the zona glomerulosa cells to release ...
... 1. Renin-angiotensin mechanism: decreased blood pressure stimulates kidneys to release renin, triggers formation of angiotensin II, a potent stimulator of aldosterone release 2. Plasma concentration of K+: Increased K+ directly influences the zona glomerulosa cells to release ...
Hormone
... • Animal hormones are chemical signals that are secreted into the circulatory system and communicate regulatory messages within the body • Hormones reach all parts of the body, but only target cells are equipped to respond ...
... • Animal hormones are chemical signals that are secreted into the circulatory system and communicate regulatory messages within the body • Hormones reach all parts of the body, but only target cells are equipped to respond ...
Slides 9.1
... Glucagon – allows glucose to enter the blood from alpha cells These hormones are antagonists that maintain blood sugar homeostasis Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Glucagon – allows glucose to enter the blood from alpha cells These hormones are antagonists that maintain blood sugar homeostasis Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
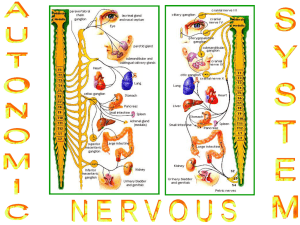
Autonomous nervous systems
... • Preganglionic fibers entering adrenal gland proceed to center (adrenal medulla) • Modified sympathetic ganglion • Preganglionic fibers synapse on neuroendocrine cells • Specialized neurons secrete hormones into bloodstream ...
... • Preganglionic fibers entering adrenal gland proceed to center (adrenal medulla) • Modified sympathetic ganglion • Preganglionic fibers synapse on neuroendocrine cells • Specialized neurons secrete hormones into bloodstream ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.