Disturbance of system level blood pressure
... Products renin cells juxtaglomerular apparatus is also increased by reducing the concentration of sodium ions into the lumen of the distal convoluted tubule. Angiotensin II increases the blood pressure resulting from: 1) A spasm of arterioles and to a lesser extent due to the large veins: - Direct b ...
... Products renin cells juxtaglomerular apparatus is also increased by reducing the concentration of sodium ions into the lumen of the distal convoluted tubule. Angiotensin II increases the blood pressure resulting from: 1) A spasm of arterioles and to a lesser extent due to the large veins: - Direct b ...
Pituitary Hormones and Their Control by the Hypothalamus
... 3-decrease rate of glucose utilization throughout the body Growth hormone promotes protein deposition in tissues: enhancement of amino acid transport through the cell membranes. - enhancement of RNA translation to cause protein synthesis by the ribosomes. - increased nuclear transcription of DNA to ...
... 3-decrease rate of glucose utilization throughout the body Growth hormone promotes protein deposition in tissues: enhancement of amino acid transport through the cell membranes. - enhancement of RNA translation to cause protein synthesis by the ribosomes. - increased nuclear transcription of DNA to ...
39-1 The Endocrine System
... Cells that have receptors for a particular hormone are called target cells. If a cell does not have receptors or the receptors do not respond to a hormone, that hormone has no effect on it. ...
... Cells that have receptors for a particular hormone are called target cells. If a cell does not have receptors or the receptors do not respond to a hormone, that hormone has no effect on it. ...
Diseases and Conditions of the Endocrine System
... promotes the growth of the interstitial cells of the testes and the secretion of testosterone ...
... promotes the growth of the interstitial cells of the testes and the secretion of testosterone ...
Hormones & the Endocrine System
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex – Also function in the body’s response to stress – Fall into three classes of steroid hormones ...
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex – Also function in the body’s response to stress – Fall into three classes of steroid hormones ...
Endocrine PPTC
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex – Also function in the body’s response to stress – Fall into three classes of steroid hormones ...
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex – Also function in the body’s response to stress – Fall into three classes of steroid hormones ...
Animal or Plant Hormone Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH
... bone. T3- active form- increases cellular respiration. T4- inactive formmovement in the blood to the cells & raises blood Ca levels by causing bone cells to break down bone ...
... bone. T3- active form- increases cellular respiration. T4- inactive formmovement in the blood to the cells & raises blood Ca levels by causing bone cells to break down bone ...
The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
... The anterior pituitary produces seven hormones. These hormones are part of the three-level hypothalamicpituitary axis presented in an earlier section. They are the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), gro ...
... The anterior pituitary produces seven hormones. These hormones are part of the three-level hypothalamicpituitary axis presented in an earlier section. They are the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), gro ...
Stress and coping in farm animals
... physical, psychological, or interoeeptive in nature, but usually contains components of all three classifications The adjustment to stress induces a broad ränge of neuroendoerine, physiological and behavioural changes to allow for a rapid recovery or adaptation to the change. The hypothalamic-adrena ...
... physical, psychological, or interoeeptive in nature, but usually contains components of all three classifications The adjustment to stress induces a broad ränge of neuroendoerine, physiological and behavioural changes to allow for a rapid recovery or adaptation to the change. The hypothalamic-adrena ...
140 Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
... An axis of signaling between the hypothalamus, pituitary, and an endocrine gland regulates the secretion of some hormones. An endocrine axis is a group of endocrine glands that signal to one another in sequential order. In an endocrine axis, the hypothalamus secretes releasing hormones that induce t ...
... An axis of signaling between the hypothalamus, pituitary, and an endocrine gland regulates the secretion of some hormones. An endocrine axis is a group of endocrine glands that signal to one another in sequential order. In an endocrine axis, the hypothalamus secretes releasing hormones that induce t ...
Iodination of Tyrosine and Formation of the Thyroid Hormones
... • Interspersed in the interstitial spaces between the follicles is another secretory cell type, the C cells, which secrete the peptide hormone calcitonin. ...
... • Interspersed in the interstitial spaces between the follicles is another secretory cell type, the C cells, which secrete the peptide hormone calcitonin. ...
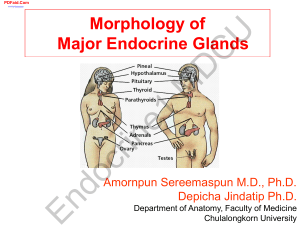
Morphology of Major Endocrine Glands
... • cells have less cytoplasm than the Zona Fasciculata, so appears as a darker layer (at lower powers) • boundaries between zones are indistinct. ...
... • cells have less cytoplasm than the Zona Fasciculata, so appears as a darker layer (at lower powers) • boundaries between zones are indistinct. ...
Topic: Ecological Issues Aim : How do we take part in solving
... Stimulates the release of egg in females; stimulates secretion of sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen and progesterone) ...
... Stimulates the release of egg in females; stimulates secretion of sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen and progesterone) ...
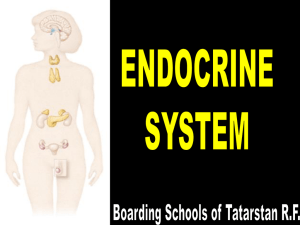
Endocrine System
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex – Also function in the body’s response to stress – Fall into three classes of steroid hormones ...
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex – Also function in the body’s response to stress – Fall into three classes of steroid hormones ...
Thyroid Hormones
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex – Also function in the body’s response to stress – Fall into three classes of steroid hormones ...
... Stress Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex • Hormones from the adrenal cortex – Also function in the body’s response to stress – Fall into three classes of steroid hormones ...
Endocrinolgy - Avian Medicine
... hypothalamic-hypophyseal complex, the gonads, pancreatic islet cells, adrenal glands, thyroid glands, parathyroid glands, ultimobranchial glands and the endocrine cells of the gut. All these organs release hormones into the bloodstream, which act on target tissues by interacting with receptors on th ...
... hypothalamic-hypophyseal complex, the gonads, pancreatic islet cells, adrenal glands, thyroid glands, parathyroid glands, ultimobranchial glands and the endocrine cells of the gut. All these organs release hormones into the bloodstream, which act on target tissues by interacting with receptors on th ...
Mechanisms and Pituitary
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Neuroendocrine presentation
... Hypothalamus Below the thalamus, it caps the brainstem and forms the inferolateral walls of the third ventricle Mammillary bodies - small, small paired nuclei bulging anteriorly from the hypothalamus - relay stations for olfactory pathways Infundibulum – stalk of the hypothalamus connecting to the ...
... Hypothalamus Below the thalamus, it caps the brainstem and forms the inferolateral walls of the third ventricle Mammillary bodies - small, small paired nuclei bulging anteriorly from the hypothalamus - relay stations for olfactory pathways Infundibulum – stalk of the hypothalamus connecting to the ...
Document
... • Elongated organ located just below the stomach in back of the abdomen • Secretion of two hormones • Insulin, which removes glucose from the blood by promoting storage in tissues as carbohydrates when blood glucose levels are high • Glucagon, which stimulates the release of sugar from storage sites ...
... • Elongated organ located just below the stomach in back of the abdomen • Secretion of two hormones • Insulin, which removes glucose from the blood by promoting storage in tissues as carbohydrates when blood glucose levels are high • Glucagon, which stimulates the release of sugar from storage sites ...
Chapter 16: Endocrine System
... Adrenal glands – paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys Structurally and functionally, they are two glands in one Adrenal medulla – nervous tissue that acts as part of the SNS ...
... Adrenal glands – paired, pyramid-shaped organs atop the kidneys Structurally and functionally, they are two glands in one Adrenal medulla – nervous tissue that acts as part of the SNS ...
Document
... secretion of substances needed by the organisms. • Some glands secrete their secretions into some organs by ducts that called EXOCRINE GLANDS. • Other glands release their secretion directly into the bloodstream that called ENDOCRINE GLANDS. ...
... secretion of substances needed by the organisms. • Some glands secrete their secretions into some organs by ducts that called EXOCRINE GLANDS. • Other glands release their secretion directly into the bloodstream that called ENDOCRINE GLANDS. ...
homeostasis
... pituitary releases two hormones produced in the hypothalamus, ADH (restricts water loss) and oxytocin (stimulates contractions in the mammary glands and uterus, and the prostate gland). Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... pituitary releases two hormones produced in the hypothalamus, ADH (restricts water loss) and oxytocin (stimulates contractions in the mammary glands and uterus, and the prostate gland). Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
CASE 33
... corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which is secreted by cells in the paraventricular nucleus. At the level of the adrenal gland, ACTH stimulates growth of the adrenal cortex and the synthesis and secretion of cortisol, corticosterone, and small amounts of adrenal androgens and estrogens. ACTH se ...
... corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which is secreted by cells in the paraventricular nucleus. At the level of the adrenal gland, ACTH stimulates growth of the adrenal cortex and the synthesis and secretion of cortisol, corticosterone, and small amounts of adrenal androgens and estrogens. ACTH se ...
Mammalian Physiology Organization of the Endocrine System
... Neural stimuli – nerve fibers stimulate hormone release – Preganglionic sympathetic nervous system (SNS) fibers stimulate the adrenal medulla to secrete catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) ...
... Neural stimuli – nerve fibers stimulate hormone release – Preganglionic sympathetic nervous system (SNS) fibers stimulate the adrenal medulla to secrete catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.