* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Polycystic ovary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
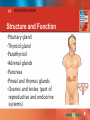
Lecture Notes A PowerPoint Presentation Classroom Activity to Accompany Medical Terminology Systems, Seventh Edition Barbara A. Gylys ∙ Mary Ellen Wedding 14 Endocrine System 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function •Pituitary gland •Thyroid gland •Parathyroid •Adrenal glands •Pancreas •Pineal and thymus glands • Ovaries and testes (part of reproductive and endocrine systems) 2 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Consisting of endocrine (ductless) glands •Secretion of chemicals called hormones directly into the bloodstream •Control and integration of many bodily functions •Action of hormones on target organs to increase or decrease the target’s activity level •Monitoring and interpretation of and reaction to changes in the body and external environment to maintain homeostasis 3 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Pituitary gland (hypophysis) Tiny, pea-shaped structure at the base of the brain Consists of an anterior and posterior lobe Known as the “master gland” of the body Regulation of many body activities Stimulation of other glands to secrete their own specific hormones • Effects of its hormones felt throughout the body • • • • • 4 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Pituitary gland (continued) • Anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) — secretion of six hormones • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which regulates the production of steroid hormones by the adrenal gland • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates egg production in the ovaries or sperm production in the testes • Growth hormone (GH), also called somatotropin, which regulates growth of bones and other tissues 5 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Pituitary gland (continued) • Anterior lobe (adenophypophysis) — secretion of six hormones (continued) • Luteinizing hormone (LH), which stimulates production of sex hormones by the ovaries or testes • Prolactin, which stimulates growth of breast tissue and milk production in females • Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which regulates activity of the thyroid gland 6 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Pituitary gland (continued) • Posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) — secretion of two hormones • Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also called vasopressin • Regulation of urinary output • Role in blood pressure regulation • Oxytocin • Inducement of labor in pregnant women by stimulating contractions in the uterus • Promotion of milk secretion from the mammary glands 7 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Thyroid gland • Two lobes on either side of the trachea • Secretion of three hormones • Calcitonin, which regulates normal blood levels of calcium and phosphate (in conjuction with parathyroid hormone) • Triiodothyronine (T3), which increases the rate of cellular metabolism • Thyroxine (T4), which increases the rate of cellular metabolism after being converted to T3 in the tissues 8 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Parathyroid gland • Two pairs of pea-shaped organs located on the underside of the thyroid gland • Secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) • Regulation of normal blood levels of calcium and phosphate (in conjunction with calcitonin) 9 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Pancreas • Elongated organ located just below the stomach in back of the abdomen • Secretion of two hormones • Insulin, which removes glucose from the blood by promoting storage in tissues as carbohydrates when blood glucose levels are high • Glucagon, which stimulates the release of sugar from storage sites in the liver when blood glucose levels are low 10 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Pineal gland • Small, pinecone–shaped organ located deep within the brain just behind the thalamus • Secretion of melatonin, which influences the maturation of sexual organs during puberty 11 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Thymus gland • Butterfly-shaped organ located between the lungs • Withering away during puberty, leaving adults with fat and connective tissue in its place • Secretion of thymosin, which plays a role in development of the immune response in infants 12 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Ovaries • Functioning in the female reproductive and endocrine systems • Secretion of two female sex hormones • Estrogen (estradiol), which stimulates development of ova (eggs) and secondary sex characteristics • Progesterone, which prepares and maintains the uterus in pregnancy 13 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function (continued) •Testes • Functioning in the male reproductive and endocrine systems • Secretion of male sex hormone testosterone • Responsible for the development of secondary sex characteristics and sex drive • Necessary for sperm production • Maintenance of the reproductive organs in adult males 14 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function Exercise 1. What is a target? 2. What are common conditions that result in various pathologies of the endocrine system? 3. Why is the pituitary known as a master gland? 15 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Structure and Function Exercise 1. What is a target? Organ or tissue that responds to a hormone 2. What are common conditions that result in various pathologies of the endocrine system? Hypersecretion or hyposecretion of a hormone 3. Why is the pituitary known as a master gland? It regulate many bodily activities and stimulates other glands to secrete specific hormones. 16 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise List the CF(s) for: 1. pancreas: 2. thyroid gland: 3. thymus gland: 4. secrete: 17 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise List the CF(s) for: 1.pancreas: pancreat/o 2.thyroid gland: thyr/o, thyroid/o 3.thymus gland: thym/o 4.secrete: crin/o 18 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise 5. adrenal glands: 6. poison: 7. sugar, sweetness: 8. same, alike: 19 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise 5. adrenal glands: adren/o, adrenal/o 6. poison: toxic/o, tox/o 7. sugar, sweetness: gluc/o, glyc/o, glycos/o 8. same, alike: home/o 20 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise 9. calcium: 10. potassium (an electrolyte): 21 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Combining Forms Exercise 9. calcium: calc/o 10. potassium (an electrolyte): kal/i 22 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Complete the Medical Word Exercise 1. excessive (many, much) thirst: poly/ 2. pertaining to poisonous activity of the thyroid: / /toxic 3. sugar in urine: /uria 4. blood with excessive or abnormal glucose: / /emia 23 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Complete the Medical Word Exercise 1. excessive (many, much) thirst: poly/dipsia 2. pertaining to poisonous activity of the thyroid: thyr/o/toxic 3. sugar in urine: glycos/uria or glucos/uria 4. blood with excessive or abnormal glucose: hyper/glyc/emia 24 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Complete the Medical Word Exercise 5. instrument to measure sugar: /o/ 6. excessive (many, much) urination: poly/ 7. condition of deficient insulin: hypo/ / 8. secrete within (internally): endo/ 25 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Complete the Medical Word Exercise 5. instrument to measure sugar: gluc/o/meter 6. excessive (many, much) urination: poly/uria 7. condition of deficient insulin: hypo/insulin/ism 8. secrete within (internally): endo/crine 26 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Complete the Medical Word Exercise 9. secrete outwardly (outside, outward): /crine 10. enlargement of the thyroid gland: thyr/o/ 27 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Complete the Medical Word Exercise 9. secrete outwardly (outside, outward): exo/crine 10. enlargement of the thyroid gland: thyr/o/megaly 28 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 1. specialist in study of poisons: 2. inflammation of the pancreas: 3. enlargement of extremities: 29 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 1. specialist in study of poisons: toxic/o/logist or toxic/o/log/ist 2. inflammation of the pancreas: pancreat/itis 3. enlargement of extremities: acr/o/megaly 30 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 4. sugar, sweetness (in the) urine: 5. tumor (composed of) insulin: 6. blood condition with potassium (an electrolyte): 31 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 4. sugar, sweetness (in the) urine: glycos/uria or glucos/uria 5. tumor (composed of) insulin: insulin/oma 6. blood condition with potassium (an electrolyte): kal/emia 32 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions Graves Disease •Most common form of hyperthyroidism •Caused by oversecretion of hormones (T4 and T3) by the thyroid gland, in which elevated levels produce profound changes in the body’s physiological processes •More common in women than men 33 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Graves Disease (continued) •Signs and symptoms •Exophthalmos (See illustration.) •Elevated metabolic rate •Heat intolerance •Weight loss, fatigue, and muscle weakness 34 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Graves Disease (continued) •Signs and symptoms (continued) •Enlarged thyroid, also called goiter (See illustration.) •Thyrotoxic crisis (storm), including many cardiac manifestations •Tachycardia •Arrhythmias •Heart murmurs •Cardiomegaly 35 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Graves Disease (continued) •Treatment •Depending on patient’s age and the severity of the disease •Antithyroid agents to block hormone synthesis within the thyroid gland •Alteration in the structure of the thyroid gland through surgery or radioactive iodine therapy •Beta blockers in combination with one of the treatments listed above 36 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mrs. Y., a patient with Graves disease, is concerned about the abnormal protrusion of her eyeballs. The doctor explains that this protrusion is a common symptom of Graves disease, and is called . 2. Ms. M. is scheduled to undergo excision of her thyroid gland, a surgery charted as . 37 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mrs. Y., a patient with Graves disease, is concerned about the abnormal protrusion of her eyeballs. The doctor explains that this protrusion is a common symptom of Graves disease, and is called exophthalmos or exophthalmia. 2. Ms. M. is scheduled to undergo excision of her thyroid gland, a surgery charted as thyroidectomy. 38 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mrs. N. suffers from hyperthyroidism. She states that her mother had Graves disease and asks about the connection between Graves disease and hyperthyroidism. How should the physician respond? 39 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mrs. N. suffers from hyperthyroidism. She states that her mother had Graves disease and asks about the connection between Graves disease and hyperthyroidism. How should the physician respond? Graves disease is the most common form of hyperthyroidism. 40 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 4. Mr. Z. is diagnosed with Graves disease and asks why his eyes are protruding. How should the physician respond? 41 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 4. Mr. Z. is diagnosed with Graves disease and asks why his eyes are protruding. How should the physician respond? The protrusion is due to an accumulation of cellular material behind the eyeballs, which is stimulated by hypersecretion of thyroidstimulating hormone. 42 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions Cushing Syndrome •Caused by exposure to excess cortisol •Adrenal or pituitary problem •Long-term use of corticosteroids •More common in females 43 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Cushing Syndrome (continued) •Signs and symptoms •Central obesity with thin arms and legs •Fat pad on upper back (buffalo hump) •Round, “moon-shaped” face with acne and facial hair (See illustration.) 44 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Cushing Syndrome (continued) •Signs and symptoms (continued) •Secondary diabetes due to insulin resistance •Glucose intolerance due to stimulation of gluconeogenesis •Muscle wasting and thin skin with purple striae as a result of cortisol’s catabolic effect on tissues •Hypokalemia due to sodium retention and postassium loss in the urine 45 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Cushing Syndrome (continued) •Signs and symptoms (continued) •Catabolic effects on bone leading to osteoporosis, pathological fractures, and back pain from compression fractures of the vertebrae •Risk of infection due to anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive actions of cortisol •Mental status changes in about half of patients, from irritability to psychosis (sometimes referred to as steroid psychosis) 46 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Cushing Syndrome (continued) •Treatment •Restoration of cortisol concentration to normal levels •Varied, according to etiology •Restoration of serum concentration of cortisol to normal levels •Surgery or radiation therapy to remove a tumor •Drugs or radiation to suppress adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion •Discontinuing or reducing corticosteroid drug use •High-potassium or low-sodium diet 47 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Ms. J. is diagnosed with Cushing syndrome. The physician explains that treatment aims to restore the normal levels of the principal steroid hormone produced by the adrenal cortex, which is known as (calcitonin, cortisol, oxytocin). 48 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Ms. J. is diagnosed with Cushing syndrome. The physician explains that treatment aims to restore the normal levels of the principal steroid hormone produced by the adrenal cortex, which is known as (calcitonin, cortisol, oxytocin). 49 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 2. Ms. M. is diagnosed with Cushing syndrome and learns that it is caused by a tumor in her adrenal cortex. The physician recommends surgery followed by chemotherapy. Surgery to remove the adrenal gland(s) is known as . 50 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 2. Ms. M. is diagnosed with Cushing syndrome and learns that it is caused by a tumor in her adrenal cortex. The physician recommends surgery followed by chemotherapy. Surgery to remove the adrenal gland(s) is known as adrenalectomy. 51 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mrs. T. is worried about treating her Cushing syndrome. The physician explains that one of the complications of untreated Cushing syndrome is elevated blood pressure. The medical term for this complication is . 4. Mrs. N. complains of puffiness and water retention. The nurse explains that sodium retention causes increased fluid in tissues, a swelling called . 52 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mrs. T. is worried about treating her Cushing syndrome. The physician explains that one of the complications of untreated Cushing syndrome is elevated blood pressure. The medical term for this complication is hypertension. 4. Mrs. N. complains of puffiness and water retention. The nurse explains that sodium retention causes increased fluid in tissues, a swelling called edema. 53 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Growth Hormone (GH) Imbalance •GH (somatropin) responsible for growth of bones, cartilage, and soft tissue •Synthesized and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland •Hypersecretion of GH — two forms • Acromegaly, hypersecretion during adulthood • Gigantism, hypersecretion during childhood •Hyposecretion of GH — one form • Dwarfism, hyposecretion during childhood 54 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) GH Imbalance (continued) •Signs and symptoms •Acromegaly •Hypersecretion of GH during adulthood •Fusion of growth plates at ends of long bones, which prevents person from growing taller •Widening and enlargement of facial features, jaw, hands, and feet 55 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) GH Imbalance (continued) •Signs and symptoms (continued) •Gigantism •Hypersecretion of GH during childhood •Excessive growth of bones and tissues due to high level of GH (See illustration, left.) •Height changes of up to 6″ in 1 year in children •Abrupt development, resulting in abnormally increased height 56 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) GH Imbalance (continued) •Signs and symptoms (continued) •Dwarfism •Hyposecretion of GH during childhood •Lack of growth and short stature but with normal body proportions 57 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) GH Imbalance (continued) •Treatment •Hyposecretion of GH •Drug therapy with growth hormone •Surgery if a tumor is the cause •Hypersecretion of GH •Drug therapy to suppress secretion of growth hormone •Surgery to remove an adenoma or radiation therapy to destroy the adenoma 58 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. The physician explains to Mrs. J. that her son’s short stature is a condition known as dwarfism. This condition is due to (hyposecretion, hypersecretion, hypertrophy) of growth hormone (GH). 59 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. The physician explains to Mrs. J. that her son’s short stature is a condition known as dwarfism. This condition is due to (hyposecretion, hypersecretion, hypertrophy) of growth hormone (GH). 60 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 2. Mr. M. will undergo excision of his pituitary gland. The physician explains that he will require lifelong replacement of thyroid hormone, corticosteroids, and sex hormones in order to maintain a stable internal environment. The regulation required to maintain this stable environment in the body is called (homogenous, homeostasis, homologous). 61 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 2. Mr. M. will undergo excision of his pituitary gland. The physician explains that he will require lifelong replacement of thyroid hormone, corticosteroids, and sex hormones in order to maintain a stable internal environment. The regulation required to maintain this stable environment in the body is called (homogenous, homeostasis, homologous). 62 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mrs. P. is diagnosed with acromegaly caused by a pituitary tumor. The physician explains that surgery to remove the gland is required and can be performed endoscopically (through the nose). This procedure is known as a(n) (hypophysectomy, adenectomy, rhinectomy). 63 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mrs. P. is diagnosed with acromegaly caused by a pituitary tumor. The physician explains that surgery to remove the gland is required and can be performed endoscopically (through the nose). This procedure is known as a (hypophysectomy, adenectomy, rhinectomy). 64 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Diabetes Mellitus •Group of metabolic diseases •Characterized by high glucose levels •Caused by defects in insulin secretion, action, or both •Two primary forms •Type 1 (insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus •Type 2 (non–insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus 65 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Diabetes Mellitus (continued) •Two primary forms •Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus •Chronic metabolic disorder marked by hyperglycemia •Inability of the pancreas to produce enough insulin to properly control blood glucose levels •Most commonly diagnosed in children, adolescents, or young adults 66 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Diabetes Mellitus •Two primary forms (continued) (continued) •Type 2 (non–insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus •Gradual onset that occurs in middle age, commonly in overweight patients (because fat interferes with the body’s ability to use insulin) •Characterized by high blood glucose levels that lead to a chronic, lifelong disease that requires medical management •Insulin resistance and inadequate insulin secretion to sustain normal metabolism 67 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Diabetes Mellitus (continued) •Signs and symptoms •Type 1 •Fatigue •Polyphagia, polyuria, and polydipsia •Unplanned weight loss •Blurred vision (common in hyperglycemic patients with polyphagia) •Diabetic ketoacidosis with loss of metabolic control (such as during periods of infection or noncompliance with therapy) 68 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Diabetes Mellitus (continued) •Signs and symptoms •Type 2 (continued) •Commonly asymptomatic •Polyphagia, polydipsia, and polyuria •Frequent or slow-healing infections •Fatigue •Blurred vision (common in hyperglycemic patients) 69 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diseases and Conditions (continued) Diabetes Mellitus (continued) •Treatment •Type 1 •Specialized diet and regular exercise •Intensive foot and eye care •Medications, including insulin to lower blood glucose levels •Type 2 •Calorie-restricted diet with regular aerobic exercise •Oral drugs • Increase pancreatic secretion of or cellular sensitivity to insulin • Decrease absorption of carbohydrates from the GI tract •Insulin injections (if combinations of oral drugs fail to regulate blood glucose levels) 70 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mrs. Q. has symptoms of polyphagia, polydipsia, and polyuria. The physician explains that these are classic symptoms of (ketosis, diabetes, myxedema). 2. Ms. V. has type 1 diabetes and complains of fluid retention and back pain. The physician explains kidney disease is a complication of untreated DM, and diagnoses her condition as diabetic (nephropathy, cystopathy, uropathy). 71 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mrs. Q. has symptoms of polyphagia, polydipsia, and polyuria. The physician explains that these are classic symptoms of (ketosis, diabetes, myxedema). 2. Ms. V. has type 1 diabetes and complains of fluid retention and back pain. The physician explains kidney disease is a complication of untreated DM, and diagnoses her condition as diabetic (nephropathy, cystopathy, uropathy). 72 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Ms. T.’s fasting blood glucose laboratory result is 150. This abnormally elevated blood glucose level is charted as . 4. During a patient education session about diabetes, the nurse explains that exact insulin measurement is important. Too much insulin will result in an abnormally low blood glucose level, a condition called . 73 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Ms. T.’s fasting blood glucose laboratory result is 150. This abnormally elevated blood glucose level is charted as hyperglycemia. 4. During a patient education session about diabetes, the nurse explains that exact insulin measurement is important. Too much insulin will result in an abnormally low blood glucose level, a condition called hypoglycemia. 74 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Vocabulary Challenge Exercise 1. hormone: 2. exophthalmos: 75 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Vocabulary Challenge Exercise 1. hormone: complex chemical substance produced in one part of the body that regulates the activity of an organ or group of cells in another part of the body 2. exophthalmos: abnormal protrusion of the eyeball caused by tumor (one eye affected) or hyperthyroidism (both eyes affected) 76 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Vocabulary Challenge Exercise 3. glucagon: 4. hirsutism: 77 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Vocabulary Challenge Exercise 3. glucagon: hormone that raises blood glucose levels 4. hirsutism: excessive growth of hair or the presence of hair in unusual places (especially in women) caused by abnormalities in androgen production or adverse effects of medication or hormone therapy 78 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Vocabulary Challenge Exercise 5. myxedema: 79 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Vocabulary Challenge Exercise 5. myxedema: most severe form of hypothyroidism, characterized by swelling of the hands, face, feet, and periorbital tissue and possibly leading to coma and death 80 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Medical and Surgical Procedures •Insulin injection •Rotation of multiple daily injections to several sites (See illustration.) •Absorption and effectiveness determined by injection site •Rapid absorption: abdomen and then upper arm and thigh areas •Slower absorption: subcutaneous fat and hip and buttock areas •No injection within 2″ of the navel 81 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Medical and Surgical Procedures (continued) •Glucose testing with a glucometer •Monitoring test of glucose levels in the blood (glycemia) •Self-monitoring, usually done before meals and at bedtime •Piercing of skin, typically on the finger, to draw blood •Application of blood to a test strip 82 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Medical and Surgical Procedures (continued) •Insulin delivery with an insulin pump •Use of a small pump device that delivers subcutaneous insulin •Typically worn on the abdomen or buttocks •Continuous delivery of insulin in small amounts via a tiny catheter with bolus doses added by pushing a button 83 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Medical and Surgical Procedures (continued) •Hypophysectomy •Minimally invasive endoscopic surgery to excise the pituitary gland (See illustration.) •Transsphenoidal approach via the nose or just under the upper lip •Possible transfrontal craniotomy (entry through the frontal bone of the skull) to remove a large tumor 84 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Medical and Surgical Procedures (continued) •Adrenalectomy •Lobectomy •Thymectomy •Thyroidectomy 85 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mrs. J. is diagnosed with a thymoma. The physician informs her that he must excise it. in a surgical procedure called . 2. Mr. X. is diagnosed with hyperthyroidism. The physician explains that excision of one lobe of the thyroid will stabilize his condition. The surgical procedure to remove a lobe is called . 86 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. Mrs. J. is diagnosed with a thymoma. The physician informs her that he must excise it. in a surgical procedure called thymectomy. 2. Mr. X. is diagnosed with hyperthyroidism. The physician explains that excision of one lobe of the thyroid will stabilize his condition. The surgical procedure to remove a lobe is called lobectomy. 87 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Ms. C. undergoes a biopsy that reveals a malignant tumor of the adrenal gland. The physician charts this malignant tumor as an adrenal . 4. Mr. K.’s MRI reveals a rare tumor of the adrenal glands composed of chromaffin cells. This type of tumor is known as a(n) (cytoma, pheochromocytoma, adrenal sarcoma). 88 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Ms. C. undergoes a biopsy that reveals a malignant tumor of the adrenal gland. The physician charts this malignant tumor as an adrenal carcinoma. 4. Mr. K.’s MRI reveals a rare tumor of the adrenal glands composed of chromaffin cells. This type of tumor is known as a (cytoma, pheochromocytoma, adrenal sarcoma). 89 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 5. Ms. R. will use an insulin pump to replace the multiple insulin injections she takes throughout the day. This pump delivers insulin directly into her bloodstream via a small, hollow tube called a(n) . 6. Ms. D. is diagnosed with diabetes. The nurse demonstrates how to get a blood sample and insert it into a device to measure blood glucose. This device is called a(n) . 90 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 5. Ms. R. will use an insulin pump to replace the multiple insulin injections she takes throughout the day. This pump delivers insulin directly into her bloodstream via a small, hollow tube called a catheter. 6. Ms. D. is diagnosed with diabetes. The nurse demonstrates how to get a blood sample and insert it into a device to measure blood glucose. This device is called a glucometer. 91 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Diagnostic Procedures •Fasting blood glucose (FBG) •Glucose tolerance test (GTT) •Radioactive iodine uptake test (RAIU) •Thyroid function test (TFT) •Total calcium 92 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 1. blood condition of deficient calcium: 2. blood condition of excessive calcium: 3. tumor of the thymus gland: 93 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 1. blood condition of deficient calcium: hypo/calc/emia 2. blood condition of excessive calcium: hyper/calc/emia 3. tumor of the thymus gland: thym/oma 94 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 4. enlargement of the thyroid gland: 5. blood condition of excessive glucose: 6. urine that contains sugar: 95 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Build Medical Words Exercise 4. enlargement of the thyroid gland: thyr/o/megaly 5. blood condition of excessive glucose: hyper/glyc/emia 6. urine that contains sugar: glycos/uria or glucos/uria 96 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pharmacology •Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) •Insulins 97 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. A 10-year-old boy is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. To control his blood glucose levels, the physician prescribes (corticosteroids, insulin, thyroid hormone). 2. Mrs. J. is in menopause. To control her symptoms of hot flashes and vaginal dryness, the physician prescribes an oral synthetic hormone of (calcium, estrogen, testosterone). 98 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 1. A 10-year-old boy is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. To control his blood glucose levels, the physician prescribes (corticosteroids, insulin, thyroid hormone). 2. Mrs. J. is in menopause. To control her symptoms of hot flashes and vaginal dryness, the physician prescribes an oral synthetic hormone of (calcium, estrogen, testosterone). 99 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mr. R. underwent a thyroidectomy. To replace the production of hormones T3 and T4, the physician prescribes (calcium, corticosteroids, thyroid supplements). 4. Ms. S. is postmenopausal and finds she is at risk for osteoporosis. Her physician recommends preventing bone loss by taking a supplement called (calcium, sodium, thyroid). 100 14 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise 3. Mr. R. underwent a thyroidectomy. To replace the production of hormones T3 and T4, the physician prescribes (calcium, corticosteroids, thyroid supplements). 4. Ms. S. is postmenopausal and finds she is at risk for osteoporosis. Her physician recommends preventing bone loss by taking a supplement called (calcium, sodium, thyroid). 101 Copyright © 2013 by F.A. Davis Company. All rights reserved. This product is protected by copyright. No part of it may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means— electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise—without written permission from the publisher. 102