Chapter_020
... Specific rates and rhythms of secretion • Diurnal, pulsatile and cyclic, and patterns depending on circulating substances ...
... Specific rates and rhythms of secretion • Diurnal, pulsatile and cyclic, and patterns depending on circulating substances ...
Week14A - UniMAP Portal
... Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction ...
... Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction ...
39-1 The Endocrine System
... secretion. There are two kinds of glands: Exocrine glands release secretions through ducts directly to the organs that use them. Endocrine glands release their secretions directly into the bloodstream. ...
... secretion. There are two kinds of glands: Exocrine glands release secretions through ducts directly to the organs that use them. Endocrine glands release their secretions directly into the bloodstream. ...
39-1 The Endocrine System
... secretion. There are two kinds of glands: Exocrine glands release secretions through ducts directly to the organs that use them. Endocrine glands release their secretions directly into the bloodstream. ...
... secretion. There are two kinds of glands: Exocrine glands release secretions through ducts directly to the organs that use them. Endocrine glands release their secretions directly into the bloodstream. ...
Frontiers in the Use of Biomarkers of Health in Research on Stress
... Psychological Stress and the SAM Axis As previously described, the SAM axis is the body’s primary physiological response to acute stressors (for review, see Klein & Corwin, 2007). Following the experience of a stressor, NE slows digestion and gastrointestinal motility, increases plasma glucose level ...
... Psychological Stress and the SAM Axis As previously described, the SAM axis is the body’s primary physiological response to acute stressors (for review, see Klein & Corwin, 2007). Following the experience of a stressor, NE slows digestion and gastrointestinal motility, increases plasma glucose level ...
Biochemistry of Hormones-A case oriented approach 2012
... Eicosanoids are a large group of molecules derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids. The principal groups of hormones of this class are prostaglandins, prostacyclins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes. Arachadonic acid is the most abundant precursor for these hormones. Stores of arachadonic acid are pre ...
... Eicosanoids are a large group of molecules derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids. The principal groups of hormones of this class are prostaglandins, prostacyclins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes. Arachadonic acid is the most abundant precursor for these hormones. Stores of arachadonic acid are pre ...
MB_50_win
... Adrenal Glands, continued • Adrenal Cortex – In the presence of some stresses the pituitary gland will secrete the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). – This hormone stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce the hormone cortisol. • Cortisol promotes the production of glucose from proteins to help cel ...
... Adrenal Glands, continued • Adrenal Cortex – In the presence of some stresses the pituitary gland will secrete the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). – This hormone stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce the hormone cortisol. • Cortisol promotes the production of glucose from proteins to help cel ...
Frontiers in the Use of Biomarkers of Health in
... Psychological Stress and the SAM Axis As previously described, the SAM axis is the body’s primary physiological response to acute stressors (for review, see Klein & Corwin, 2007). Following the experience of a stressor, NE slows digestion and gastrointestinal motility, increases plasma glucose level ...
... Psychological Stress and the SAM Axis As previously described, the SAM axis is the body’s primary physiological response to acute stressors (for review, see Klein & Corwin, 2007). Following the experience of a stressor, NE slows digestion and gastrointestinal motility, increases plasma glucose level ...
Chapter 14 - Delmar Cengage Learning
... – Also known as suprarenals – Have two distinct parts: • Inner – Medulla releases epinephrine and norepinephrine » Fight or flight hormones ...
... – Also known as suprarenals – Have two distinct parts: • Inner – Medulla releases epinephrine and norepinephrine » Fight or flight hormones ...
Human Physiology - Maryville University
... & releases 2 hormones produced in hypothalamus: Antidiuretic hormone (ADH/vasopressin) which promotes H20 conservation by kidneys Oxytocin which stimulates contractions of uterus during parturition & contractions of mammary gland alveoli for milkejection reflex ...
... & releases 2 hormones produced in hypothalamus: Antidiuretic hormone (ADH/vasopressin) which promotes H20 conservation by kidneys Oxytocin which stimulates contractions of uterus during parturition & contractions of mammary gland alveoli for milkejection reflex ...
chapt11_lecture
... cell receptors show specificity, high affinity, and low capacity for a hormone Lipophilic hormones have receptors in target's cytoplasm and/or nucleus because can diffuse thru plasma membrane Their target is the nucleus where they affect transcription Called genomic action and takes at least 30 ...
... cell receptors show specificity, high affinity, and low capacity for a hormone Lipophilic hormones have receptors in target's cytoplasm and/or nucleus because can diffuse thru plasma membrane Their target is the nucleus where they affect transcription Called genomic action and takes at least 30 ...
Physics - BC Open Textbooks
... The amino acid-derived hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine bind to betaadrenergic receptors on the plasma membrane of cells. Hormone binding to receptor activates a G-protein, which in turn activates adenylyl cyclase, converting ATP to cAMP. cAMP is a second messenger that mediates a cell-specif ...
... The amino acid-derived hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine bind to betaadrenergic receptors on the plasma membrane of cells. Hormone binding to receptor activates a G-protein, which in turn activates adenylyl cyclase, converting ATP to cAMP. cAMP is a second messenger that mediates a cell-specif ...
Chapter 18 PowerPoint
... The amino acid-derived hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine bind to betaadrenergic receptors on the plasma membrane of cells. Hormone binding to receptor activates a G-protein, which in turn activates adenylyl cyclase, converting ATP to cAMP. cAMP is a second messenger that mediates a cell-specif ...
... The amino acid-derived hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine bind to betaadrenergic receptors on the plasma membrane of cells. Hormone binding to receptor activates a G-protein, which in turn activates adenylyl cyclase, converting ATP to cAMP. cAMP is a second messenger that mediates a cell-specif ...
Ch41_Endocrine Function - University of Perpetual Help System
... Hormones that are released into the bloodstream circulate as either free, unbound molecules or as hormones attached to transport carriers (Fig. 41-1). Peptide hormones and protein hormones usually circulate unbound in the blood. Steroid hormones and thyroid hormone are carried by specific carrier pro ...
... Hormones that are released into the bloodstream circulate as either free, unbound molecules or as hormones attached to transport carriers (Fig. 41-1). Peptide hormones and protein hormones usually circulate unbound in the blood. Steroid hormones and thyroid hormone are carried by specific carrier pro ...
File - Physiology At Large
... Permissiveness – one hormone cannot exert its effects without another hormone being present Synergism – more than one hormone produces the same effects on a target cell Antagonism – one or more hormones opposes the action of another hormone ...
... Permissiveness – one hormone cannot exert its effects without another hormone being present Synergism – more than one hormone produces the same effects on a target cell Antagonism – one or more hormones opposes the action of another hormone ...
chapt09_lecture
... B. Parasympathetic Division 1. Preganglionic neurons come from the brain or sacral region of the spinal cord. a. Also called the craniosacral division b. They synapse on ganglia located near or in effector organs; called terminal ganglia c. Preganglionic neurons do not travel with somatic neurons ( ...
... B. Parasympathetic Division 1. Preganglionic neurons come from the brain or sacral region of the spinal cord. a. Also called the craniosacral division b. They synapse on ganglia located near or in effector organs; called terminal ganglia c. Preganglionic neurons do not travel with somatic neurons ( ...
Thyroid Hormones
... • Concept 45.2: Hormones and other chemical signals bind to target cell receptors, initiating pathways that culminate in specific cell responses • Hormones convey information via the bloodstream – To target cells throughout the body ...
... • Concept 45.2: Hormones and other chemical signals bind to target cell receptors, initiating pathways that culminate in specific cell responses • Hormones convey information via the bloodstream – To target cells throughout the body ...
SECTION 11 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine comes
... Endocrine comes from the word elements end/o which means inside, crin- which means to secrete, and the -e, which is a noun suffix. The hormones produced by the glands included in the endocrine system are released into the bloodstream which then carries these chemical messengers throughout the body. ...
... Endocrine comes from the word elements end/o which means inside, crin- which means to secrete, and the -e, which is a noun suffix. The hormones produced by the glands included in the endocrine system are released into the bloodstream which then carries these chemical messengers throughout the body. ...
The Endocrine System
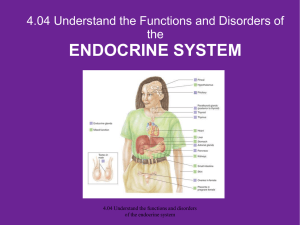
... What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How do you relate the body’s hormones to the endocrine system? ...
... What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How do you relate the body’s hormones to the endocrine system? ...
fd endocrine system
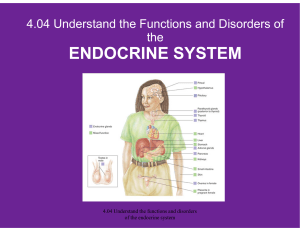
... What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How do you relate the body’s hormones to the endocrine system? ...
... What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How do you relate the body’s hormones to the endocrine system? ...
Structure and Development of the Parotoid Gland in
... the base of the excretory duct. Alcian blue-positive mucous glands also occur in the dermis, and the epidermis is composed of three layers of cuboidal epithelial cells covered by a superficial squamous keratinized layer. The main difference between the granular glands in metamorphosed compared to ne ...
... the base of the excretory duct. Alcian blue-positive mucous glands also occur in the dermis, and the epidermis is composed of three layers of cuboidal epithelial cells covered by a superficial squamous keratinized layer. The main difference between the granular glands in metamorphosed compared to ne ...
Document
... Release of CRF from hypothalamus to anterior pituitary through portal system Negative feedback from adrenal hormones and administered cortisones During sudden stress, ACTH can quickly be released after the hypothalamus is stimulated to send out ACTH- releasing factor (CRF/CRH) to the anterior ...
... Release of CRF from hypothalamus to anterior pituitary through portal system Negative feedback from adrenal hormones and administered cortisones During sudden stress, ACTH can quickly be released after the hypothalamus is stimulated to send out ACTH- releasing factor (CRF/CRH) to the anterior ...
PowerPoint - Pennsylvania Pharmacists Association
... releasing (TRH). The TRH stimulates the pituitary to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The TSH, in turn, stimulates the thyroid to produce thyroid hormone until levels in the blood return to normal. Thyroid hormone exerts negative feedback control over the hypothalamus as well as the pituit ...
... releasing (TRH). The TRH stimulates the pituitary to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The TSH, in turn, stimulates the thyroid to produce thyroid hormone until levels in the blood return to normal. Thyroid hormone exerts negative feedback control over the hypothalamus as well as the pituit ...
The Endocrine System
... •Consists of a group of glands that produce hormones •Works with nervous system to control and coordinate all other body systems •Affects body systems by chemical stimuli ...
... •Consists of a group of glands that produce hormones •Works with nervous system to control and coordinate all other body systems •Affects body systems by chemical stimuli ...
39-1 The Endocrine System
... Sometimes two hormones with opposite effects act to regulate part of the body’s internal environment. Such a complementary system regulates the level of calcium ions in the bloodstream. ...
... Sometimes two hormones with opposite effects act to regulate part of the body’s internal environment. Such a complementary system regulates the level of calcium ions in the bloodstream. ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.