Endocrine Physiology
... These include epinephrine, and norepinephrine Epinephrine and norepinephrine are produced by the adrenal medulla both are water soluble Secreted like peptide hormones ...
... These include epinephrine, and norepinephrine Epinephrine and norepinephrine are produced by the adrenal medulla both are water soluble Secreted like peptide hormones ...
Ch 5 Cell Signaling and the Hormonal Responses to Exercise
... -Amino Acid uptake and protein synthesis -Promotes long bone growth (femur) 3. Spares plasma glucose -Reduces use of plasma glucose (opposes action of insulin) -Increases gluconeogenesis (creation of new glucose through non-CHO carbon substrates such as pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, and glyco ...
... -Amino Acid uptake and protein synthesis -Promotes long bone growth (femur) 3. Spares plasma glucose -Reduces use of plasma glucose (opposes action of insulin) -Increases gluconeogenesis (creation of new glucose through non-CHO carbon substrates such as pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, and glyco ...
Glands - The Anatomy of Sea Turtles by Jeanette Wyneken
... (Figs. 75 and 173) by tracing along the brachiocephalic trunk where it gives rise to thyroid arteries (soon after its bifurcation to form the subclavian arteries). The thyroid arteries “frame” the single thyroid gland that is encased in connective tissue (Fig. 173). The thyroid is round and is often ...
... (Figs. 75 and 173) by tracing along the brachiocephalic trunk where it gives rise to thyroid arteries (soon after its bifurcation to form the subclavian arteries). The thyroid arteries “frame” the single thyroid gland that is encased in connective tissue (Fig. 173). The thyroid is round and is often ...
Biochemistry of hormones derived from amino acids and proteins
... Contains hormones (ACTH, LPH, MSH) and neurotransmitters Precursor molecule involves 285 amino acids Gene expression in the anterior and intermediary pituitary, but also in other tissues (intestine, placenta, male reproductive system) Cleavage into peptides, further modification (glycosylati ...
... Contains hormones (ACTH, LPH, MSH) and neurotransmitters Precursor molecule involves 285 amino acids Gene expression in the anterior and intermediary pituitary, but also in other tissues (intestine, placenta, male reproductive system) Cleavage into peptides, further modification (glycosylati ...
endocrine system
... – Four glands attached to posterior surface of thyroid – Stimulate an increase in number and size of osteoclasts (specialized bone cells) ...
... – Four glands attached to posterior surface of thyroid – Stimulate an increase in number and size of osteoclasts (specialized bone cells) ...
`Oh no it`s Physio!` - Endocrine and Reproduction Notes
... to discuss the concept of endocrine action via hormones and to compare and contrast it with neural signaling Endocrine action = synthesis and secretion, hormonal transport, receptors, intracellular messaging and regulation. Synthesis and secretion = synthesized as pre/pro hormones by granular endopl ...
... to discuss the concept of endocrine action via hormones and to compare and contrast it with neural signaling Endocrine action = synthesis and secretion, hormonal transport, receptors, intracellular messaging and regulation. Synthesis and secretion = synthesized as pre/pro hormones by granular endopl ...
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System
... Receptors for catecholamines (E, NE, and dopamine), peptide hormones, and eicosanoids are in the cell membranes of target cells. Catecholamines and peptide hormones are not lipid soluble; they are unable to penetrate a cell membrane. Instead, these hormones bind to receptor proteins at the outer sur ...
... Receptors for catecholamines (E, NE, and dopamine), peptide hormones, and eicosanoids are in the cell membranes of target cells. Catecholamines and peptide hormones are not lipid soluble; they are unable to penetrate a cell membrane. Instead, these hormones bind to receptor proteins at the outer sur ...
detailed lecture outline
... Receptors for catecholamines (E, NE, and dopamine), peptide hormones, and eicosanoids are in the cell membranes of target cells. Catecholamines and peptide hormones are not lipid soluble; they are unable to penetrate a cell membrane. Instead, these hormones bind to receptor proteins at the outer sur ...
... Receptors for catecholamines (E, NE, and dopamine), peptide hormones, and eicosanoids are in the cell membranes of target cells. Catecholamines and peptide hormones are not lipid soluble; they are unable to penetrate a cell membrane. Instead, these hormones bind to receptor proteins at the outer sur ...
Principles of Endocrinology
... Growth Hormone • carbohydrate metabolism – by mobilizing fatty acids for energy, GH produces glucose-sparing makes glucose available for glycogen synthesis and storage • electrolyte balance – promotes Na+, K+, & Cl- retention by kidneys, enhances Ca+2 absorption in intestine ...
... Growth Hormone • carbohydrate metabolism – by mobilizing fatty acids for energy, GH produces glucose-sparing makes glucose available for glycogen synthesis and storage • electrolyte balance – promotes Na+, K+, & Cl- retention by kidneys, enhances Ca+2 absorption in intestine ...
Unit 2 Power Point 2.3 and 2.4
... › Thyrotropin-releasing hormone, or TRH (controls TSH release) › Corticoptropin-releasing hormone, or CRH (controls ACTH release) › Another hormone made by the hypothalamus is gonadotropinreleasing hormone (GnRH). It tells the pituitary gland to make luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating ...
... › Thyrotropin-releasing hormone, or TRH (controls TSH release) › Corticoptropin-releasing hormone, or CRH (controls ACTH release) › Another hormone made by the hypothalamus is gonadotropinreleasing hormone (GnRH). It tells the pituitary gland to make luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating ...
EndocrineJS
... – Contains two different glands draped over the superior end of each kidney. – Each gland has an outer layer (cortex) and an inner layer (medulla). – Each layer functions independently of the other and secretes its own hormones. ...
... – Contains two different glands draped over the superior end of each kidney. – Each gland has an outer layer (cortex) and an inner layer (medulla). – Each layer functions independently of the other and secretes its own hormones. ...
The Endocrine System
... (the inner portion of the adrenal gland), known as catecholamines, include epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). These are derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Another hormone derived from tyrosine is thyroxine, secreted by the thyroid gland. The pineal gland secretes a diffe ...
... (the inner portion of the adrenal gland), known as catecholamines, include epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). These are derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Another hormone derived from tyrosine is thyroxine, secreted by the thyroid gland. The pineal gland secretes a diffe ...
Endocrinology-general physiolofy of hormone, hormonal feed
... osteogenic cells (causing specific deposition of new bone) 2 principle mechanisms of bone growth: Growth in length (during development before closing the epiphysal slit) ...
... osteogenic cells (causing specific deposition of new bone) 2 principle mechanisms of bone growth: Growth in length (during development before closing the epiphysal slit) ...
Endocrine System - HCC Learning Web
... functions of the adrenal glands, and discuss the effects of abnormal adrenal hormone production. Describe the location of the pineal gland, and discuss the functions of the hormone it produces. Describe the location, structure, hormones, and functions of the pancreas, and discuss the effects of a ...
... functions of the adrenal glands, and discuss the effects of abnormal adrenal hormone production. Describe the location of the pineal gland, and discuss the functions of the hormone it produces. Describe the location, structure, hormones, and functions of the pancreas, and discuss the effects of a ...
29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones
... • Only cells with certain receptors can receive the signals ...
... • Only cells with certain receptors can receive the signals ...
THE PITUITARY HORMONES AND THEIR CONTROL
... A. weighs about 4 grams B. superior to kidney C. composed of medulla and cortex D. medulla (20% of gland) secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine E. cortex secretes corticosteroids ...
... A. weighs about 4 grams B. superior to kidney C. composed of medulla and cortex D. medulla (20% of gland) secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine E. cortex secretes corticosteroids ...
endocrine_system_edited_3
... • PTH regulates calcium levels in the blood by increasing reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys and by increasing uptake of calcium from the digestive system. • PTH affects other organ systems, promoting proper nerve and muscle function and bone structure. Slide 18 of 50 Copyright Pearson Prentice ...
... • PTH regulates calcium levels in the blood by increasing reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys and by increasing uptake of calcium from the digestive system. • PTH affects other organ systems, promoting proper nerve and muscle function and bone structure. Slide 18 of 50 Copyright Pearson Prentice ...
Sample Chapter
... their products into these ducts. For example, the salivary glands send saliva into the mouth by way of the salivary ducts. Each type of hormone has a unique composition. Even so, hormones can be categorized as either peptide hormones (which include proteins, glycoproteins, and modified amino acids) ...
... their products into these ducts. For example, the salivary glands send saliva into the mouth by way of the salivary ducts. Each type of hormone has a unique composition. Even so, hormones can be categorized as either peptide hormones (which include proteins, glycoproteins, and modified amino acids) ...
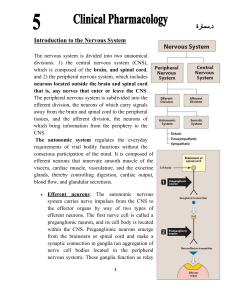
Introduction to the Nervous System
... Fight or flight response: The changes experienced by the body during emergencies have been referred to as the fight or flight response. These reactions are triggered both by direct sympathetic activation of the effector organs and by stimulation of the adrenal medulla to release epinephrine and les ...
... Fight or flight response: The changes experienced by the body during emergencies have been referred to as the fight or flight response. These reactions are triggered both by direct sympathetic activation of the effector organs and by stimulation of the adrenal medulla to release epinephrine and les ...
Physiology Ch 74 p881-892 [4-25
... destruction of receptors, and decreased production of receptors -Up-regulation of receptors and intracellular signaling proteins causes more sensitivity to hormone Intracellular Signaling After Hormone Activation – hormone-receptor complex changes function of receptor to activate hormonal effects 1. ...
... destruction of receptors, and decreased production of receptors -Up-regulation of receptors and intracellular signaling proteins causes more sensitivity to hormone Intracellular Signaling After Hormone Activation – hormone-receptor complex changes function of receptor to activate hormonal effects 1. ...
Endocrine PPT
... CORTISOL helps the body deal with stressful situations like fasting, anxiety, trauma, and infection. It keeps the blood protein and glucose levels high enough to support the brain’s activities and affects the metabolic rate. When the brain perceives a stressful situation, the hypothalamus tells the ...
... CORTISOL helps the body deal with stressful situations like fasting, anxiety, trauma, and infection. It keeps the blood protein and glucose levels high enough to support the brain’s activities and affects the metabolic rate. When the brain perceives a stressful situation, the hypothalamus tells the ...
Adrenal gland

The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys and consist of a series of layers with different structure and functions. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces a class of steroid hormones called corticosteroids, named according to their effects. Mineralocorticoids, produced in the zona glomerulosa, help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of corticosteroid hormones leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.