The Language of Chemistry
... • A homogeneous mixture consists of two or more substances in the same phase. No amount of optical magnification will reveal a homogeneous mixture to have different properties in different regions. • A heterogeneous mixture does not have uniform composition. Its components are easily visually distin ...
... • A homogeneous mixture consists of two or more substances in the same phase. No amount of optical magnification will reveal a homogeneous mixture to have different properties in different regions. • A heterogeneous mixture does not have uniform composition. Its components are easily visually distin ...
BTY705 – Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Program
... On completion of the module, students will have achieved the following: A understanding of various molecular biology techniques A knowledge of how these various techniques can be applied in their research programs. Skill in interpreting and recording experiments. An understanding of how to u ...
... On completion of the module, students will have achieved the following: A understanding of various molecular biology techniques A knowledge of how these various techniques can be applied in their research programs. Skill in interpreting and recording experiments. An understanding of how to u ...
Physical Properties
... regular array. The particles vibrate back and forth about their average positions, but seldom does a particle in a solid squeeze past its immediate neighbors to come into contact with a new set of particles. • The atoms or molecules of liquids are arranged randomly rather than in the regular pattern ...
... regular array. The particles vibrate back and forth about their average positions, but seldom does a particle in a solid squeeze past its immediate neighbors to come into contact with a new set of particles. • The atoms or molecules of liquids are arranged randomly rather than in the regular pattern ...
Slide 1
... - 3D quantitative measurements of probe activation and/or retention Provides non-invasive, whole body, deep tissue imaging in small animal models to generate 3D, information-rich results. - Functional imaging of biological and physiological changes Biological targets and pathways can be monitored an ...
... - 3D quantitative measurements of probe activation and/or retention Provides non-invasive, whole body, deep tissue imaging in small animal models to generate 3D, information-rich results. - Functional imaging of biological and physiological changes Biological targets and pathways can be monitored an ...
BIO 330 Cell Biology Spring 2011 Lecture Outline Chemistry of the
... 6 basic principles in polymerization 1 – Macromolecules are synthesized by stepwise polymerization of similar or identical small molecules (monomers) 2 – This occurs by condensation reactions (removal of water) 3 – Monomers must be activated prior to condensation 4 – Activation involves coupling of ...
... 6 basic principles in polymerization 1 – Macromolecules are synthesized by stepwise polymerization of similar or identical small molecules (monomers) 2 – This occurs by condensation reactions (removal of water) 3 – Monomers must be activated prior to condensation 4 – Activation involves coupling of ...
chapter 6 sec 2 resonance structure
... H2O is a molecule which makes H2O a molecular compound and a molecular formula. But H2O is also a chemical formula because we use atomic symbols and subscripts to describe it. ...
... H2O is a molecule which makes H2O a molecular compound and a molecular formula. But H2O is also a chemical formula because we use atomic symbols and subscripts to describe it. ...
Document
... oxidizes glucose. Ribbon model of its aa backbone, portions of which form helices. Note size, complexity relative to glucose, a simple sugar typical of small molecule targets ...
... oxidizes glucose. Ribbon model of its aa backbone, portions of which form helices. Note size, complexity relative to glucose, a simple sugar typical of small molecule targets ...
Bacteria on a leaf... How do they eat? What must they be able to do
... ...all cells re-configure those molecules to make bacterial cell parts There must be different cell types to do different functions-Digestive system to break down food Transport system to move food molecules to other cells Gas exchange system to deal with CO2 and O2 etc ...
... ...all cells re-configure those molecules to make bacterial cell parts There must be different cell types to do different functions-Digestive system to break down food Transport system to move food molecules to other cells Gas exchange system to deal with CO2 and O2 etc ...
Fill-in and matching questions for chapter 2 of Understanding
... The ____________tells you how many protons or electrons the atom has when it is electrically neutral. ...
... The ____________tells you how many protons or electrons the atom has when it is electrically neutral. ...
The basis of specific ligand recognition by proteins
... of active sites) [5]; finally, a growing number of proteins adopt a define 3D structure only when binding to a partner [6]. ...
... of active sites) [5]; finally, a growing number of proteins adopt a define 3D structure only when binding to a partner [6]. ...
What is a Polymer? - Department of Chemistry
... Amino acids are natural monomers, and polymerize to form proteins. Glucose monomers can also polymerize to form starches, amylopectins and glycogen polymers. In this case the polymerization reaction is known as a dehydration or condensation reaction (due to the formation of water as one of the prod ...
... Amino acids are natural monomers, and polymerize to form proteins. Glucose monomers can also polymerize to form starches, amylopectins and glycogen polymers. In this case the polymerization reaction is known as a dehydration or condensation reaction (due to the formation of water as one of the prod ...
2nd Semester Exam Review
... Assumptions of the Kinetic Molecular Theory • Gasses consist of small particles that take up little volume relative to the volume of empty space around them – Gas molecules are very far apart and therefore don’t experience attractive or repulsive forces. ...
... Assumptions of the Kinetic Molecular Theory • Gasses consist of small particles that take up little volume relative to the volume of empty space around them – Gas molecules are very far apart and therefore don’t experience attractive or repulsive forces. ...
biochemistry-tic-tac-toe
... chart. The first column shows the molecule. The second column shows the corresponding item. The third column explains how the two are similar. 10 items minimum. For example: ...
... chart. The first column shows the molecule. The second column shows the corresponding item. The third column explains how the two are similar. 10 items minimum. For example: ...
Molecules to metabolism (2.1)
... Which of the following statements is true about covalent bonds A. ...
... Which of the following statements is true about covalent bonds A. ...
Osmotic forces
... Osmotic forces: Protein solution Concentration difference induces osmotic pressure Semi-permeable membrane (only solvent can penetrate) ...
... Osmotic forces: Protein solution Concentration difference induces osmotic pressure Semi-permeable membrane (only solvent can penetrate) ...
The Origin Of The Earth
... ▫ Disproved in 1668 by Francesco Redi, an Italian physician Used 3 samples of rotting flesh placed in flasks open to air sealed covered with gauze ...
... ▫ Disproved in 1668 by Francesco Redi, an Italian physician Used 3 samples of rotting flesh placed in flasks open to air sealed covered with gauze ...
Headline Text 28 Point Color Text 2
... Chemical informatics and medicinal chemistry databases How molecular motors work Computer modeling in support of chemical and drug design • Polymer delivery systems • Catalysts • Small molecule drugs ...
... Chemical informatics and medicinal chemistry databases How molecular motors work Computer modeling in support of chemical and drug design • Polymer delivery systems • Catalysts • Small molecule drugs ...
Catabolic pathways
... broken down into their component building blocks. For example, proteins are degraded to amino acids, polysaccharides to monosaccharides, and fats (triacyl glycerols) to free fatty acids and glycerol. ...
... broken down into their component building blocks. For example, proteins are degraded to amino acids, polysaccharides to monosaccharides, and fats (triacyl glycerols) to free fatty acids and glycerol. ...
CARBOHYDRATES
... Molecules that contain carbon are called organic compounds. There are over 2 million known organic compounds. ...
... Molecules that contain carbon are called organic compounds. There are over 2 million known organic compounds. ...
Document
... = partial specific volume of the solute (units: cm3/g) One rough estimation of the partial specific volume of a protein, which may be used if the sequence of the protein is not known, is: average partial specific volume of proteins = 0.725 cm^3/g Because the average of experimentally determined p ...
... = partial specific volume of the solute (units: cm3/g) One rough estimation of the partial specific volume of a protein, which may be used if the sequence of the protein is not known, is: average partial specific volume of proteins = 0.725 cm^3/g Because the average of experimentally determined p ...
Ch 8 AP Practice
... (a) Write the equation for the ionization of atomic fluorine that requires 1,681.0 kJ mol-1. (b) Account for the fact that the first ionization energy of atomic fluorine is greater than that of atomic oxygen. (You must discuss both atoms in your response.) (c) Predict whether the first ionization en ...
... (a) Write the equation for the ionization of atomic fluorine that requires 1,681.0 kJ mol-1. (b) Account for the fact that the first ionization energy of atomic fluorine is greater than that of atomic oxygen. (You must discuss both atoms in your response.) (c) Predict whether the first ionization en ...
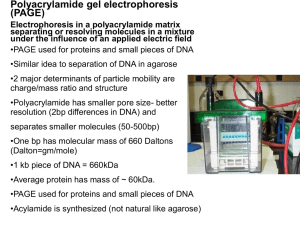
Polyacrylamide gels
... •Similar idea to separation of DNA in agarose •2 major determinants of particle mobility are charge/mass ratio and structure •Polyacrylamide has smaller pore size- better resolution (2bp differences in DNA) and separates smaller molecules (50-500bp) •One bp has molecular mass of 660 Daltons (Dalton= ...
... •Similar idea to separation of DNA in agarose •2 major determinants of particle mobility are charge/mass ratio and structure •Polyacrylamide has smaller pore size- better resolution (2bp differences in DNA) and separates smaller molecules (50-500bp) •One bp has molecular mass of 660 Daltons (Dalton= ...
Size-exclusion chromatography

Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size, and in some cases molecular weight. It is usually applied to large molecules or macromolecular complexes such as proteins and industrial polymers. Typically, when an aqueous solution is used to transport the sample through the column, the technique is known as gel-filtration chromatography, versus the name gel permeation chromatography, which is used when an organic solvent is used as a mobile phase. SEC is a widely used polymer characterization method because of its ability to provide good molar mass distribution (Mw) results for polymers.