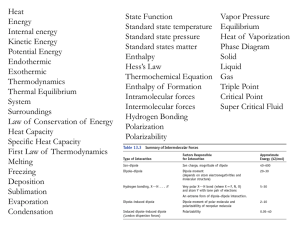
Chem 4B Final Exam Review Sheet Systematic error
... Most proteins function in the body when they are in an aqueous solution, so we will restrict our discussion to water soluble proteins. In this case, perhaps the most important thing occurring is not an interaction, but the lack of an interaction. Water, the solvent, is not able to form hydrogen bond ...
... Most proteins function in the body when they are in an aqueous solution, so we will restrict our discussion to water soluble proteins. In this case, perhaps the most important thing occurring is not an interaction, but the lack of an interaction. Water, the solvent, is not able to form hydrogen bond ...
Document
... Mechanism of Ionization in Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI): How does proton transfer occur Ajax Group Joshua P. Layfield Jordan C. Vincent Desiree M. Bates Ashley K. Tucker Sara E. Ray ...
... Mechanism of Ionization in Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI): How does proton transfer occur Ajax Group Joshua P. Layfield Jordan C. Vincent Desiree M. Bates Ashley K. Tucker Sara E. Ray ...
solution is a solution that contains the maximum amount of solute
... Part A: Fill-in-the-blanks. Choose the word that best completes each statement. [36 points/2 points each] ...
... Part A: Fill-in-the-blanks. Choose the word that best completes each statement. [36 points/2 points each] ...
Ch 2 - Biochemistry
... Directly involved in moving matter. Like riding a bike or the Stomach’s mechanical digestion ...
... Directly involved in moving matter. Like riding a bike or the Stomach’s mechanical digestion ...
43) What are the membrane structures that function in active
... A) It is very rapid over long distances. B) It requires an exPenditure of energy by the cell. of lower C) It is a passive processin which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region concentration. D) It is an active processin which molecules move from a region of lower concentra ...
... A) It is very rapid over long distances. B) It requires an exPenditure of energy by the cell. of lower C) It is a passive processin which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region concentration. D) It is an active processin which molecules move from a region of lower concentra ...
Title: Towards spatial systems biology using imaging mass
... Abstract: Imaging mass spectrometry (imaging MS) has emerged in the last decade as a labelfree, spatially-resolved, and multi-purpose bioanalytical technique for direct analysis of biological samples from animal tissue, plant tissue, biofilms, and polymer films. The impressive technological progress ...
... Abstract: Imaging mass spectrometry (imaging MS) has emerged in the last decade as a labelfree, spatially-resolved, and multi-purpose bioanalytical technique for direct analysis of biological samples from animal tissue, plant tissue, biofilms, and polymer films. The impressive technological progress ...
Analytical Ultracentrifugation
... Analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) has a broad applicability in life sciences and can be used to analyze a variety of molecules in a broad range of solvents. In AUC, molecules are characterized directly in solution, often under biologically relevant conditions. In contrast to many other methods, t ...
... Analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) has a broad applicability in life sciences and can be used to analyze a variety of molecules in a broad range of solvents. In AUC, molecules are characterized directly in solution, often under biologically relevant conditions. In contrast to many other methods, t ...
STUDY GUIDE –Intro to Cell Biology
... The process by which cells change to become different kinds of cells with different functions = DIFFERENTIATION The process by which organisms as a group change over time; Process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms = EVOLUTION What do we call embryonic cells that have th ...
... The process by which cells change to become different kinds of cells with different functions = DIFFERENTIATION The process by which organisms as a group change over time; Process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms = EVOLUTION What do we call embryonic cells that have th ...
I - Decatur ISD
... ____________________________= the building up of large molecules by removing water molecules Enzymes A. Special proteins that speed chemical reactions 1. Chemical reactions require a certain _______________ to get started. 2. Enzymes decrease this energy, making reactions occur faster. B. ...
... ____________________________= the building up of large molecules by removing water molecules Enzymes A. Special proteins that speed chemical reactions 1. Chemical reactions require a certain _______________ to get started. 2. Enzymes decrease this energy, making reactions occur faster. B. ...
dana
... Graphite-furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GF-AAS) is in many respects identical to FAAS but utilizes higher atomization temperatures (up to 3,000 K) which results in LODs that are 10-100 times better than FAAS. The sample is vaporized and atomized on the surface of a heated graphite furnace w ...
... Graphite-furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GF-AAS) is in many respects identical to FAAS but utilizes higher atomization temperatures (up to 3,000 K) which results in LODs that are 10-100 times better than FAAS. The sample is vaporized and atomized on the surface of a heated graphite furnace w ...
Handbook of Protein Sequences: A Compilation of Amino Acid
... During the last few years zonal centrifuges have become more widely and more routinely used in biochemical separations, and many improvements have appeared in apparatus and technique. As the title suggests Volume 3 is to some extent an up-dated version of Volume I-there are a dozen authors in common ...
... During the last few years zonal centrifuges have become more widely and more routinely used in biochemical separations, and many improvements have appeared in apparatus and technique. As the title suggests Volume 3 is to some extent an up-dated version of Volume I-there are a dozen authors in common ...
Biological_Molecules worksheet - answers
... 7. If many simple sugars join together, we call this a polysaccharide. Most of these are insoluble, meaning they don’t dissolve in water. Humans get most of the carbohydrates in our diet from starch, which is found as a storage carbohydrate in many plants. Animal cells contain glycogen, which can be ...
... 7. If many simple sugars join together, we call this a polysaccharide. Most of these are insoluble, meaning they don’t dissolve in water. Humans get most of the carbohydrates in our diet from starch, which is found as a storage carbohydrate in many plants. Animal cells contain glycogen, which can be ...
Course Syllabus - Honors Chemistry
... Absences equate to gaps in one's course work. Since legitimate absences do occur, it is expected that the student will complete missed and/or make-up work. Excessive absences may lead to academic failure. Tardiness disrupts the whole class and will count directly against your class participation gra ...
... Absences equate to gaps in one's course work. Since legitimate absences do occur, it is expected that the student will complete missed and/or make-up work. Excessive absences may lead to academic failure. Tardiness disrupts the whole class and will count directly against your class participation gra ...
Unit One Vocabulary
... de- = without or remove (dehydration is the removal of water) di- = two (disaccharide: a sugar molecule consisting of two monosaccharides) hydr- = water (dehydrate: to remove water from) macro- = large (macromolecule: a giant molecule in a living organism formed by the joining of smaller molecules) ...
... de- = without or remove (dehydration is the removal of water) di- = two (disaccharide: a sugar molecule consisting of two monosaccharides) hydr- = water (dehydrate: to remove water from) macro- = large (macromolecule: a giant molecule in a living organism formed by the joining of smaller molecules) ...
Data Analysis
... using a working curve, and the standard-addition method. Both of these methods require one or more standards of known composition to calibrate the measurement. Instrumental methods are usually calibrated with standards that are prepared (or purchased) using a non-instrumental analysis. There are two ...
... using a working curve, and the standard-addition method. Both of these methods require one or more standards of known composition to calibrate the measurement. Instrumental methods are usually calibrated with standards that are prepared (or purchased) using a non-instrumental analysis. There are two ...
Chapter 5
... Separation of mixture is done by using a stationary solid phase (paper) and moving liquid phase Still based on solubility of each substance in the liquid Substances that are highly soluble move faster ...
... Separation of mixture is done by using a stationary solid phase (paper) and moving liquid phase Still based on solubility of each substance in the liquid Substances that are highly soluble move faster ...
Macromolecules: Building blocks of life
... Today’s notes: • We will be getting information from this power point and putting it into a “foldable”. • We will need four flaps one for each of the macromolecules we will be learning. • You will put the names of the 4 macromolecules on each of the flaps and put some important information about ea ...
... Today’s notes: • We will be getting information from this power point and putting it into a “foldable”. • We will need four flaps one for each of the macromolecules we will be learning. • You will put the names of the 4 macromolecules on each of the flaps and put some important information about ea ...
Ch. 6 Vocabulary
... Covalent Bond – the chemical bond that forms when electrons are shared Molecule – a compound in which the atoms are held together by covalent bonds Ion – an atom that has lost or gained one or more electrons Ionic Bond – an electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or groups of atom ...
... Covalent Bond – the chemical bond that forms when electrons are shared Molecule – a compound in which the atoms are held together by covalent bonds Ion – an atom that has lost or gained one or more electrons Ionic Bond – an electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or groups of atom ...
Ch. 3 Study Guide
... 6. What is the common name for carbohydrates? What suffix is a clue that you are dealing with a carbohydrate? 7. Carbohydrates perform three primary functions for cells. They are: A. B. C. 8. Compare and contrast monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides ...
... 6. What is the common name for carbohydrates? What suffix is a clue that you are dealing with a carbohydrate? 7. Carbohydrates perform three primary functions for cells. They are: A. B. C. 8. Compare and contrast monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides ...
Matter
... • Combo of 2 or more pure substances • Physically combined not chemically combined • Each substance retains its own identity and properties ...
... • Combo of 2 or more pure substances • Physically combined not chemically combined • Each substance retains its own identity and properties ...
Ch.1 Section 1.9 Notes - Effingham County Schools
... substances become gases) of the components. In simple distillation, a mixture is heated in a device and the most volatile component vaporizes (turns into gas) at the lowest temperature, and the vapor (gas) passes through a cooled tube (a condenser) where it condenses back into the liquid state. 2. F ...
... substances become gases) of the components. In simple distillation, a mixture is heated in a device and the most volatile component vaporizes (turns into gas) at the lowest temperature, and the vapor (gas) passes through a cooled tube (a condenser) where it condenses back into the liquid state. 2. F ...
Document
... All the polypeptides have the same charge per unit length All are subject to the same electromotive force in the electric field Separation based on the sieving effect of the polyacrylamide gel Separation is by molecular weight only SDS does not break covalent bonds (i.e., disulfides) (but can treat ...
... All the polypeptides have the same charge per unit length All are subject to the same electromotive force in the electric field Separation based on the sieving effect of the polyacrylamide gel Separation is by molecular weight only SDS does not break covalent bonds (i.e., disulfides) (but can treat ...
Size-exclusion chromatography

Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size, and in some cases molecular weight. It is usually applied to large molecules or macromolecular complexes such as proteins and industrial polymers. Typically, when an aqueous solution is used to transport the sample through the column, the technique is known as gel-filtration chromatography, versus the name gel permeation chromatography, which is used when an organic solvent is used as a mobile phase. SEC is a widely used polymer characterization method because of its ability to provide good molar mass distribution (Mw) results for polymers.