Immunity and Autoimmune Disease
... www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ www.niaid.nih.gov/publications/autoimmune/autoimmune.html ...
... www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ www.niaid.nih.gov/publications/autoimmune/autoimmune.html ...
File - Pennington AP Biology
... They migrate from the bone marrow to the lymphatic organs. B-cells defend against: Bacteria and viruses outside the cell Toxins produced by bacteria (free antigens) ...
... They migrate from the bone marrow to the lymphatic organs. B-cells defend against: Bacteria and viruses outside the cell Toxins produced by bacteria (free antigens) ...
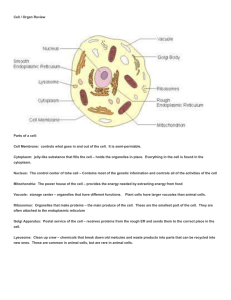
Cell / Organ Review Parts of a cell: Cell Membrane: controls what
... Mitochondria: The power house of the cell – provides the energy needed by extracting energy from food Vacuole: storage center – organelles that have different functions. ...
... Mitochondria: The power house of the cell – provides the energy needed by extracting energy from food Vacuole: storage center – organelles that have different functions. ...
Immune System - Dr. Annette M. Parrott
... Essential knowledge 3.D.2: Cells communicate with each other through direct contact with other cells or from a distance via chemical signaling. • a. Cells communicate by cell-to-cell contact. – Immune cells interact by cell-cell contact, and killer Tcells. Interaction of Antigen Presenting Cells an ...
... Essential knowledge 3.D.2: Cells communicate with each other through direct contact with other cells or from a distance via chemical signaling. • a. Cells communicate by cell-to-cell contact. – Immune cells interact by cell-cell contact, and killer Tcells. Interaction of Antigen Presenting Cells an ...
Regents Biology - Nick Williams` San Marin Science
... don’t get illness long term immunity produce antibodies for life works against many viruses ...
... don’t get illness long term immunity produce antibodies for life works against many viruses ...
Powerpoint - UCSF Immunology Program
... • Adaptive immunity learns from previous experience and hence can protect better upon a second infection by the same agent. • Adaptive immunity has a very large number of distinct “antigen receptors” of T and B lymphocytes; generated by DNA rearrangements in each developing lymphocyte; clonal select ...
... • Adaptive immunity learns from previous experience and hence can protect better upon a second infection by the same agent. • Adaptive immunity has a very large number of distinct “antigen receptors” of T and B lymphocytes; generated by DNA rearrangements in each developing lymphocyte; clonal select ...
Chapter 21 The Genetic Control of Animal Development
... In the immune system, two types of cells participate directly in defense against pathogens. Plasma B cells produce and secrete immunoglobulins (antibodies), and killer T cell produce membranebound proteins that act as receptors for various substances. ...
... In the immune system, two types of cells participate directly in defense against pathogens. Plasma B cells produce and secrete immunoglobulins (antibodies), and killer T cell produce membranebound proteins that act as receptors for various substances. ...
Adverse Immune Reactions and Immune Deficiencies
... There are certain antigens and routes of Ag exposure that favour IgE Ab production Antigens that evoke IgE responses are collectively called allergens The symptomatology is different depending on whether the Ag is injected, inhaled or ingested i.e. depending on the tissue where the pharmacologic med ...
... There are certain antigens and routes of Ag exposure that favour IgE Ab production Antigens that evoke IgE responses are collectively called allergens The symptomatology is different depending on whether the Ag is injected, inhaled or ingested i.e. depending on the tissue where the pharmacologic med ...
After School Physiology review 2013
... pancreas-make chemicals for digestion in small intestine ...
... pancreas-make chemicals for digestion in small intestine ...
Lipoteichoic acid contaminant
... to control infection while the specific immune response develops. ...
... to control infection while the specific immune response develops. ...
Tissue effector memory T cells Lymphoid central memory T cells
... IgG antibody suppresses the activation of naive B cells by cross-linking the B-cell receptor and FcγRIIB1 on the B-cell surface ...
... IgG antibody suppresses the activation of naive B cells by cross-linking the B-cell receptor and FcγRIIB1 on the B-cell surface ...
1. Type I allergy
... In type II allergy, antibodies are produced against the antigen on the cell surface to which complements and cytotoxic T cells have been activated, thereby injuring the cells. Type II allergy induces cutaneous diseases such as autoimmune blistering diseases. In bullous pemphigoid, autoantibodies bin ...
... In type II allergy, antibodies are produced against the antigen on the cell surface to which complements and cytotoxic T cells have been activated, thereby injuring the cells. Type II allergy induces cutaneous diseases such as autoimmune blistering diseases. In bullous pemphigoid, autoantibodies bin ...
Southern Methodist University
... Glatiramer acetate consists of random polymers of 4 amino acids, designed to mimic myelin basic protein, an important component of CNS myelin. Believed to work by activating anti-inflammatory regulatory T cells, which then migrate into the CNS to inhibit local immune rxns. ...
... Glatiramer acetate consists of random polymers of 4 amino acids, designed to mimic myelin basic protein, an important component of CNS myelin. Believed to work by activating anti-inflammatory regulatory T cells, which then migrate into the CNS to inhibit local immune rxns. ...
1st - structure of the immune system 2012-13
... -localization: takes 5-10% of the circulating lymphocytes; migrate from the bone marrow to the secondary lymphatic organs thorugh the circulation - antigen presenting cells (APC) - activation: with antigens, via interaction with macrophages or T lymphocytes, lymphokines, cytokines - upon activation ...
... -localization: takes 5-10% of the circulating lymphocytes; migrate from the bone marrow to the secondary lymphatic organs thorugh the circulation - antigen presenting cells (APC) - activation: with antigens, via interaction with macrophages or T lymphocytes, lymphokines, cytokines - upon activation ...
1. seminar 2012
... -localization: takes 5-10% of the circulating lymphocytes; migrate from the bone marrow to the secondary lymphatic organs thorugh the circulation - antigen presenting cells (APC) - activation: with antigens, via interaction with macrophages or T lymphocytes, lymphokines, cytokines - upon activation ...
... -localization: takes 5-10% of the circulating lymphocytes; migrate from the bone marrow to the secondary lymphatic organs thorugh the circulation - antigen presenting cells (APC) - activation: with antigens, via interaction with macrophages or T lymphocytes, lymphokines, cytokines - upon activation ...
Grade 8 Cell Unit Review What is an organelle? What is the cell
... that carry air from the trachea into the lungs? ...
... that carry air from the trachea into the lungs? ...
Hypersensitivities – 17/03/03
... This is referred to as delayed type hypersensitivity, and these occur as a result of T lymphocytes reacting, usually against self antigens resulting in autoimmune diseases. Most autoimmune diseases are Type IV Hypersensitivity reactions. Mechanisms of Tissue Injury Host is exposed to tissue anti ...
... This is referred to as delayed type hypersensitivity, and these occur as a result of T lymphocytes reacting, usually against self antigens resulting in autoimmune diseases. Most autoimmune diseases are Type IV Hypersensitivity reactions. Mechanisms of Tissue Injury Host is exposed to tissue anti ...
PowerPoint Presentation - I. Introduction to class
... Progressive muscle weakness. Antibodies block acetylcholine receptors at neuromuscular synapse. Affects 25,000 Americans (mainly women). Today most patients survive when treated with drugs or immunosuppressants. ...
... Progressive muscle weakness. Antibodies block acetylcholine receptors at neuromuscular synapse. Affects 25,000 Americans (mainly women). Today most patients survive when treated with drugs or immunosuppressants. ...
EPC (Skin, Fish)
... This cell line known as Epithelioma papulosum cyprini (EPC) was originally reported to be from Carp (Cyprinus carpio) epidermal herpes virus-induced hyperplastic lesions. More recently EPC was found to be derived from Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas) see Winton et al., 2010. This has been confir ...
... This cell line known as Epithelioma papulosum cyprini (EPC) was originally reported to be from Carp (Cyprinus carpio) epidermal herpes virus-induced hyperplastic lesions. More recently EPC was found to be derived from Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas) see Winton et al., 2010. This has been confir ...
Auto-immune diseases – 19/03/03
... Auto-immune diseases – 19/03/03 General information Basically, the immune system does not react to host cells. This is because it exhibits immunologic tolerance. Its ability to discriminate self from non-self is one of its cardinal features. If this is partially/fully lost, then you get self antigen ...
... Auto-immune diseases – 19/03/03 General information Basically, the immune system does not react to host cells. This is because it exhibits immunologic tolerance. Its ability to discriminate self from non-self is one of its cardinal features. If this is partially/fully lost, then you get self antigen ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.