Skin as a protection against environmental threats
... Lymphocytes in the skin • Professional APC present antigen in the context of MHC II and B7.1/B7.2 to T cells. • (If keratinocytes present antigen, anergy results (no B 7.1/7.2)) ...
... Lymphocytes in the skin • Professional APC present antigen in the context of MHC II and B7.1/B7.2 to T cells. • (If keratinocytes present antigen, anergy results (no B 7.1/7.2)) ...
The Immune System - Watchung Hills Regional High School
... up of proteins -along with antigens which helps the body recognize any foreign substances. -THE JOBS a) Trigger inflammation b) Attract eater cells such as macrophages to the area c) Coat intruders so that eater cells are most likely to devour them d) Kill intruders ...
... up of proteins -along with antigens which helps the body recognize any foreign substances. -THE JOBS a) Trigger inflammation b) Attract eater cells such as macrophages to the area c) Coat intruders so that eater cells are most likely to devour them d) Kill intruders ...
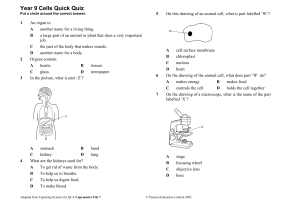
Year 9 Cells Quick Quiz
... An organ system is: A a collection of organs working together to do an important job. B a collection of tissues that do the same job. C a collection of organs that help us breathe. D a way of counting the number of organs in the body. The heart contains: A muscle, fat and nerve tissues. B only muscl ...
... An organ system is: A a collection of organs working together to do an important job. B a collection of tissues that do the same job. C a collection of organs that help us breathe. D a way of counting the number of organs in the body. The heart contains: A muscle, fat and nerve tissues. B only muscl ...
Preventing Communicable Diseases
... After the pathogens are killed and tissue damage is under control, tissue repair can begin. However, regardless of whether pathogens survive the inflammatory response, specific defenses are activated. This activation is an effort to prevent this same infection from occurring again. ...
... After the pathogens are killed and tissue damage is under control, tissue repair can begin. However, regardless of whether pathogens survive the inflammatory response, specific defenses are activated. This activation is an effort to prevent this same infection from occurring again. ...
cell membranes gs
... The membrane that surrounds every cell, forming the selectively permeable boundary between the cell and its environment. It is made up of a double layer of phospholipids with embedded proteins. ...
... The membrane that surrounds every cell, forming the selectively permeable boundary between the cell and its environment. It is made up of a double layer of phospholipids with embedded proteins. ...
Cells and HBS
... • Nervous: receives & sends electrical messages from surroundings (brain) • Lymphatic/ immune: protect against bacteria, viruses, invaders • Respiratory: includes lungs, take in O2 and release CO2 • Skeletal/ muscular: work together to protect organs, create movement ...
... • Nervous: receives & sends electrical messages from surroundings (brain) • Lymphatic/ immune: protect against bacteria, viruses, invaders • Respiratory: includes lungs, take in O2 and release CO2 • Skeletal/ muscular: work together to protect organs, create movement ...
4a Final Exam All
... 12. The cross-linking of antibodies with antigens is called: a. immunization b. transmembrane channels c. agglutination d. production of plasma cells e. desensitization 13. Plasma cells are: a. immature forms of T cells b. the cells which produce large amounts of antibodies c. the cells which are re ...
... 12. The cross-linking of antibodies with antigens is called: a. immunization b. transmembrane channels c. agglutination d. production of plasma cells e. desensitization 13. Plasma cells are: a. immature forms of T cells b. the cells which produce large amounts of antibodies c. the cells which are re ...
DOC - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... Clumping cells together is called agglutination. When soluble antigens form clumps, they often precipitate. Complement activation by antibody can enhance both opsonization and inflammation and can lead directly to cell lysis. Page 11: B Cell Activation: Antigen Encounter A B cell becomes activat ...
... Clumping cells together is called agglutination. When soluble antigens form clumps, they often precipitate. Complement activation by antibody can enhance both opsonization and inflammation and can lead directly to cell lysis. Page 11: B Cell Activation: Antigen Encounter A B cell becomes activat ...
Mary Beth Murphy Ms. Huntemann AP Biology Chapter 31
... Primary immune response- the response the 1st time an immune systems reacts to a pathogen Prostaglandins-Fatty acids that cause inflammation Regulatory T cells (Tregs)- keep immune system from reacting to much Secondary immune system response- the 2nd time an immune system reacts to a previous patho ...
... Primary immune response- the response the 1st time an immune systems reacts to a pathogen Prostaglandins-Fatty acids that cause inflammation Regulatory T cells (Tregs)- keep immune system from reacting to much Secondary immune system response- the 2nd time an immune system reacts to a previous patho ...
Viruses - Ms. Franklin`s Classroom
... Viral DNA/RNA is able to mutate at a quick rate which in turn allows the virus to ‘mask’ itself and enter the host cell. The host’s immune system will not recognize the new protein coat and in turn not attack the viral invasion. ...
... Viral DNA/RNA is able to mutate at a quick rate which in turn allows the virus to ‘mask’ itself and enter the host cell. The host’s immune system will not recognize the new protein coat and in turn not attack the viral invasion. ...
HBImmunity
... ● This type of immunity is usually long-lasting ● It depends on memory B and T cells PASSIVE Immunity ● An individual is given prepared antibodies against a particular antigen ● This type of immunity is short-lived ● This can happen naturally as antibodies are passed from mother to fetus or artifici ...
... ● This type of immunity is usually long-lasting ● It depends on memory B and T cells PASSIVE Immunity ● An individual is given prepared antibodies against a particular antigen ● This type of immunity is short-lived ● This can happen naturally as antibodies are passed from mother to fetus or artifici ...
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY The Lymphatic System
... - the T cell then undergoes proliferation and differentiation to become effector cells that carry out the immune response that results in elimination of the antigen How T Cells recognize antigens - the cell membrane of T Cells have T cell receptors that bind with specific antigens - when this occurs ...
... - the T cell then undergoes proliferation and differentiation to become effector cells that carry out the immune response that results in elimination of the antigen How T Cells recognize antigens - the cell membrane of T Cells have T cell receptors that bind with specific antigens - when this occurs ...
Biology Notes
... reproducing. When lactic acid formed instead of alcohol, he observed small rod-like microbes mixed with the yeast. In this, he discovered that yeast caused the fermentation of sugar into alcohol and that containing microorganisms made the fermentations sour. This went against the simple ‘sugar broke ...
... reproducing. When lactic acid formed instead of alcohol, he observed small rod-like microbes mixed with the yeast. In this, he discovered that yeast caused the fermentation of sugar into alcohol and that containing microorganisms made the fermentations sour. This went against the simple ‘sugar broke ...
Biology
... produce antibodies specific to the antigen. 3. One of these antibody producing B-lymphocytes is fused with a tumour cell forming a hybridoma. 4. The hybridoma divides repeatedly producing many clones which all produce the same antibodies (monoclonal antibodies) 5. These Monoclonal antibodies (MAb ...
... produce antibodies specific to the antigen. 3. One of these antibody producing B-lymphocytes is fused with a tumour cell forming a hybridoma. 4. The hybridoma divides repeatedly producing many clones which all produce the same antibodies (monoclonal antibodies) 5. These Monoclonal antibodies (MAb ...
Specific Cellular Defences - Smithycroft Secondary School
... I can state that one group of T-lymphocytes destroy infected cells by inducing apoptosis. Another group of T-lymphocytes secrete cytokines that activate B lymphocytes and phagocytes. When pathogens infect tissue, some phagocytes capture the pathogen and display fragments of its antigens on their sur ...
... I can state that one group of T-lymphocytes destroy infected cells by inducing apoptosis. Another group of T-lymphocytes secrete cytokines that activate B lymphocytes and phagocytes. When pathogens infect tissue, some phagocytes capture the pathogen and display fragments of its antigens on their sur ...
The Human Immune System
... Macrophage engulfs the pathogen and displays the antigen for a T-cell T-cell learns pathogen and hunts out infected cells Once found, T-cells destroy infected cells (thru a process known as apoptosis) ...
... Macrophage engulfs the pathogen and displays the antigen for a T-cell T-cell learns pathogen and hunts out infected cells Once found, T-cells destroy infected cells (thru a process known as apoptosis) ...
4th European CellAid-Symposium Cell Therapies for a Cure of
... Andreas Grützkau, Berlin To be on the safe side: Multiparametric immunophenotyping of peripheral blood cells for monitoring of cell-based therapies ...
... Andreas Grützkau, Berlin To be on the safe side: Multiparametric immunophenotyping of peripheral blood cells for monitoring of cell-based therapies ...
Immunity and Autoimmune Disease
... www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ www.niaid.nih.gov/publications/autoimmune/autoimmune.html ...
... www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ www.niaid.nih.gov/publications/autoimmune/autoimmune.html ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.