Historical Genetics George Mendel Mendel`s Experiment
... Genes: A heredity factors found on chromosomes Alleles: Two genes associated with a specific characteristic. – Each allele is located on a homologous chromosome ...
... Genes: A heredity factors found on chromosomes Alleles: Two genes associated with a specific characteristic. – Each allele is located on a homologous chromosome ...
The major histocompatibility complex in Old World Camelids: low
... immune responses and mechanisms of disease. Currently, very little is known about the MHC in Old World Camelids. Here, we analyzed MHC genomic sequences of the three species of Old World Camelids, Camelus bactrianus, Camelus dromedarius and Camelus ferus. The three major MHC regions, class I, II and ...
... immune responses and mechanisms of disease. Currently, very little is known about the MHC in Old World Camelids. Here, we analyzed MHC genomic sequences of the three species of Old World Camelids, Camelus bactrianus, Camelus dromedarius and Camelus ferus. The three major MHC regions, class I, II and ...
Document
... •Landsteiner's Rule: If an individual has the antigen, he/she will not have the antibody. This is a universal law with few exceptions. •ABO antigens are glycolipids (on the surface of the RBC) or glycoproteins (in secretions). ABO antigens are found on RBC's , lymphs, platelets, tissue cells, bone m ...
... •Landsteiner's Rule: If an individual has the antigen, he/she will not have the antibody. This is a universal law with few exceptions. •ABO antigens are glycolipids (on the surface of the RBC) or glycoproteins (in secretions). ABO antigens are found on RBC's , lymphs, platelets, tissue cells, bone m ...
NGS Beyond HLA Typing, Marcelo Fernandez-Vina
... Variation in the 3′ untranslated region of HLA-DPB1 is associated with spontaneous clearance of hepatitis B virus in both Japanese and U.S. populations. The mechanism facilitating viral clearance may be related to the A→G single-nucleotide polymorphism rs9277534, which marks HLA-DP cell-surface expr ...
... Variation in the 3′ untranslated region of HLA-DPB1 is associated with spontaneous clearance of hepatitis B virus in both Japanese and U.S. populations. The mechanism facilitating viral clearance may be related to the A→G single-nucleotide polymorphism rs9277534, which marks HLA-DP cell-surface expr ...
Anemia_Pasta_GenTeac..
... The technique used in this activity is based on Pasta Genetics, Developed by Megan Brown and Maureen Munn, The GENETICS Project, University of Washington. The activity itself is based on genotype information found in Verlinsky, V et al, 2001, Preimplantation Diagnosis for Fanconi Anemia Combined wit ...
... The technique used in this activity is based on Pasta Genetics, Developed by Megan Brown and Maureen Munn, The GENETICS Project, University of Washington. The activity itself is based on genotype information found in Verlinsky, V et al, 2001, Preimplantation Diagnosis for Fanconi Anemia Combined wit ...
Patterns of Inheritance - (www.ramsey.k12.nj.us).
... • Dominance: Certain alleles will be expressed over others, the expressed alleles are dominant to the unexpressed recessive alleles • Segregation: Each parent carries two alleles for each gene. During meiosis, the pairs are separated to that only one allele is sent to the offspring in the gamete fro ...
... • Dominance: Certain alleles will be expressed over others, the expressed alleles are dominant to the unexpressed recessive alleles • Segregation: Each parent carries two alleles for each gene. During meiosis, the pairs are separated to that only one allele is sent to the offspring in the gamete fro ...
AAAAI Session 1206 PID-what do I do with my patient
... 91phox Busulfan conditioning Early cell marking was 4-26%, decreased to 0.03-1.1% with partial resolution of infections in 2/3 patients ...
... 91phox Busulfan conditioning Early cell marking was 4-26%, decreased to 0.03-1.1% with partial resolution of infections in 2/3 patients ...
Static
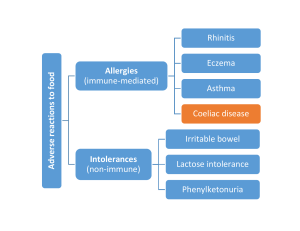
... Immune-mediated reaction to gluten in intestine Most people have no problem with gluten Thus disease attributable mainly to host factors ...
... Immune-mediated reaction to gluten in intestine Most people have no problem with gluten Thus disease attributable mainly to host factors ...
Intensity-Dependent Normalization
... DNA - A nucleic acid that carries the genetic information in the cell. DNA consists of two long chains of nucleotides joined by hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases adenine and thymine or cytosine and guanine. The sequence of nucleotides determines individual hereditary characteristics. ht ...
... DNA - A nucleic acid that carries the genetic information in the cell. DNA consists of two long chains of nucleotides joined by hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases adenine and thymine or cytosine and guanine. The sequence of nucleotides determines individual hereditary characteristics. ht ...
Evolution Practice Questions
... c. Most small anole lizards are between 3 and 6 inches long. STABILIZING 14. Why are zebras and horses considered to be members of two different species if they can interbreed and produce a zorse? In other words, why is the zorse considered to be a hybrid organism? The zorse offspring although possi ...
... c. Most small anole lizards are between 3 and 6 inches long. STABILIZING 14. Why are zebras and horses considered to be members of two different species if they can interbreed and produce a zorse? In other words, why is the zorse considered to be a hybrid organism? The zorse offspring although possi ...
Trait
... Produce many offspring True-breeding – if allowed to self-pollinate they would produce offspring identical to themselves. ...
... Produce many offspring True-breeding – if allowed to self-pollinate they would produce offspring identical to themselves. ...
203.transplantation
... MHC Class I Proteins • They are glycoproteins found on surface of virtually all the nucleated cells • The A locus which have HLA-A genes encode 20 different proteins , B locus having HLA-B genes will encode 40 different proteins and C locus will encode 8 different proteins • So the different protei ...
... MHC Class I Proteins • They are glycoproteins found on surface of virtually all the nucleated cells • The A locus which have HLA-A genes encode 20 different proteins , B locus having HLA-B genes will encode 40 different proteins and C locus will encode 8 different proteins • So the different protei ...
chapter_14_human_heredity
... Pedigree Charts • Pedigree charts show the relationships within a family and can be used to show how traits are passed from one generation to the next. ...
... Pedigree Charts • Pedigree charts show the relationships within a family and can be used to show how traits are passed from one generation to the next. ...
NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS
... 3) Pink snapdragons are heterozygous with one red allele; its expression results in only enough pigment molecules to make flowers pink. ...
... 3) Pink snapdragons are heterozygous with one red allele; its expression results in only enough pigment molecules to make flowers pink. ...
HNA alleles and antigens, up-date 2015 Allele Description
... An allele can encode more than one epitope, e.g. HNA-1b and HNA-1c are encoded by FCGR3B*03 and HNA-1b and HNA-1d are encoded by FCGR3B*02. An antigen can be encoded by more than one allele (e.g. HNA-1a by FCGR3B*01 and FCGR3B*04). ...
... An allele can encode more than one epitope, e.g. HNA-1b and HNA-1c are encoded by FCGR3B*03 and HNA-1b and HNA-1d are encoded by FCGR3B*02. An antigen can be encoded by more than one allele (e.g. HNA-1a by FCGR3B*01 and FCGR3B*04). ...
013368718X_CH11_159
... 12. THINK VISUALLY The capital letter G represents the allele in peas that causes the dominant trait, gray seed coat. The lower-case letter g represents the recessive allele that causes the recessive trait, white seed coat. In the circles, show the alleles in the gametes of the parent generation. Sh ...
... 12. THINK VISUALLY The capital letter G represents the allele in peas that causes the dominant trait, gray seed coat. The lower-case letter g represents the recessive allele that causes the recessive trait, white seed coat. In the circles, show the alleles in the gametes of the parent generation. Sh ...
Probability and Heredity
... • How is probability related to genetics? After mendel’s experiment he realized that the probability of crossing a tall plant was 3 in 4. The probability of crossing a short plant was 1 in 4. Mendel was the first scientist to recognize this. ...
... • How is probability related to genetics? After mendel’s experiment he realized that the probability of crossing a tall plant was 3 in 4. The probability of crossing a short plant was 1 in 4. Mendel was the first scientist to recognize this. ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 1
... Genetic Diagrams. Remember you have two genes for each characteristic and different versions of the same gene are called alleles. ...
... Genetic Diagrams. Remember you have two genes for each characteristic and different versions of the same gene are called alleles. ...
Document
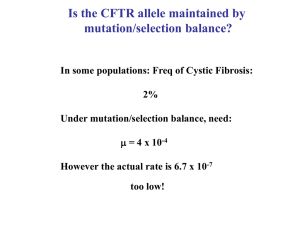
... Depends upon: (2Nu) number of mutations arising at locus per generation, and initial frequency of new allele (1/2N) ...
... Depends upon: (2Nu) number of mutations arising at locus per generation, and initial frequency of new allele (1/2N) ...
Human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is the locus of genes that encode for proteins on the surface of cells that are responsible for regulation of the immune system in humans. This group of genes resides on chromosome 6 (exception: the gene for β2-microglobulin which is located on chromosome 15), and encodes cell-surface antigen-presenting proteins and has many other functions. The HLA genes are the human versions of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes that are found in most vertebrates (and thus are the most studied of the MHC genes). The proteins encoded by certain genes are also known as antigens, as a result of their historic discovery as factors in organ transplants. The major HLAs are essential elements for immune function. Different classes have different functions:HLAs corresponding to MHC class I (A, B, and C) present peptides from inside the cell. For example, if the cell is infected by a virus, the HLA system brings fragments of the virus to the surface of the cell so that the cell can be destroyed by the immune system. These peptides are produced from digested proteins that are broken down in the proteasomes. In general, these particular peptides are small polymers, about 9 amino acids in length. Foreign antigens presented by MHC class I attract killer T-cells (also called CD8 positive- or cytotoxic T-cells) that destroy cells.HLAs corresponding to MHC class II (DP, DM, DOA, DOB, DQ, and DR) present antigens from outside of the cell to T-lymphocytes. These particular antigens stimulate the multiplication of T-helper cells, which in turn stimulate antibody-producing B-cells to produce antibodies to that specific antigen. Self-antigens are suppressed by regulatory T cells.HLAs corresponding to MHC class III encode components of the complement system.HLAs have other roles. They are important in disease defense. They are the major cause of organ transplant rejections. They may protect against or fail to protect (if down-regulated by an infection) against cancers. Mutations in HLA may be linked to autoimmune disease (examples: type I diabetes, coeliac disease). HLA may also be related to people's perception of the odor of other people, and may be involved in mate selection, as at least one study found a lower-than-expected rate of HLA similarity between spouses in an isolated community.Aside from the genes encoding the 6 major antigen-presenting proteins, there are a large number of other genes, many involved in immune function, located on the HLA complex. Diversity of HLAs in the human population is one aspect of disease defense, and, as a result, the chance of two unrelated individuals with identical HLA molecules on all loci is very low. HLA genes have historically been identified as a result of the ability to successfully transplant organs between HLA-similar individuals.