Immunopathology
... The human MHC, known as the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex, consists of a cluster of genes on chromosome 6. -The HLA system is highly polymorphic; that is, there are several alternative forms (alleles) of a gene at each locus ...
... The human MHC, known as the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex, consists of a cluster of genes on chromosome 6. -The HLA system is highly polymorphic; that is, there are several alternative forms (alleles) of a gene at each locus ...
CELLS& ORGANS OF IMMUNE MECHANISM.
... of virtually all nucleated cells. • The complete class 1 protein is highly polymorphic. • The polymorphism of these molecules is important in the recognition of self and nonself. ...
... of virtually all nucleated cells. • The complete class 1 protein is highly polymorphic. • The polymorphism of these molecules is important in the recognition of self and nonself. ...
Name:
... 35. Which of the following properties of the Fc region of human IgG can NOT be mediated by other Ig classes? A. Transplacental transfer B. Complement fixation C. Binding to mast cells D. Secretion across epithelial layers E. Binding J chain 36. The Reticuloendothelial System consists of all EXCEPT: ...
... 35. Which of the following properties of the Fc region of human IgG can NOT be mediated by other Ig classes? A. Transplacental transfer B. Complement fixation C. Binding to mast cells D. Secretion across epithelial layers E. Binding J chain 36. The Reticuloendothelial System consists of all EXCEPT: ...
frans08efi - HLA Matchmaker
... towards which the patient has preformed antibodies. • Problem: it is impossible to determine all antibody specificities in highly sensitized patients ...
... towards which the patient has preformed antibodies. • Problem: it is impossible to determine all antibody specificities in highly sensitized patients ...
Chapter 12 College Prep Biology
... Which one does not belong? Huntingdon’s disease, cystic fibrosis, PKU, taySachs disease. Huntington's disease b/c it is caused by an autosomal dominant allele, whereas the others are the result of autosomal recessive alleles. Huntington’s – lethal disorder-results in a breakdown of certain areas ...
... Which one does not belong? Huntingdon’s disease, cystic fibrosis, PKU, taySachs disease. Huntington's disease b/c it is caused by an autosomal dominant allele, whereas the others are the result of autosomal recessive alleles. Huntington’s – lethal disorder-results in a breakdown of certain areas ...
Introduction to Genetics Notes
... SegregationThe separation of alleles during gamete formation The recessive trait did not disappear!!! When each F1 plant flowers and produces gametes, the 2 alleles segregate from each other. So, each gamete carries only a single copy of each gene. Each F1 plant produces 2 types of gametes: a domina ...
... SegregationThe separation of alleles during gamete formation The recessive trait did not disappear!!! When each F1 plant flowers and produces gametes, the 2 alleles segregate from each other. So, each gamete carries only a single copy of each gene. Each F1 plant produces 2 types of gametes: a domina ...
DNA & RNA
... to genetic drift after a small population inhabits a new region • Bottleneck effect: a small surviving group (near extinction) gives rise to a new population with a dramatically different gene pool ...
... to genetic drift after a small population inhabits a new region • Bottleneck effect: a small surviving group (near extinction) gives rise to a new population with a dramatically different gene pool ...
Patterns of Inheretance
... Ex: Many codominant alleles in human blood types. • The gene encodes an enzyme that adds sugar molecules to the plasma membrane of red blood cells. Act as recognizing markers for the antibodies for the immune system. • Gene is designated I and has 3 possible alleles. • IA, IB, and i • IA and IB are ...
... Ex: Many codominant alleles in human blood types. • The gene encodes an enzyme that adds sugar molecules to the plasma membrane of red blood cells. Act as recognizing markers for the antibodies for the immune system. • Gene is designated I and has 3 possible alleles. • IA, IB, and i • IA and IB are ...
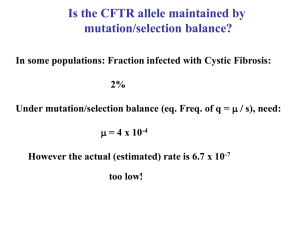
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
... Depends upon: (2Nu) number of mutations arising at locus per generation, and initial frequency of new allele (1/2N) ...
... Depends upon: (2Nu) number of mutations arising at locus per generation, and initial frequency of new allele (1/2N) ...
Foundations in Microbiology
... Classified according to the degree of MHC similarity between donor and host: autograft – recipient also serves as donor isograft – tissue from identical twin is grafted allograft – genetically different individuals but of the same species (humans) xenograft – individuals of different species ...
... Classified according to the degree of MHC similarity between donor and host: autograft – recipient also serves as donor isograft – tissue from identical twin is grafted allograft – genetically different individuals but of the same species (humans) xenograft – individuals of different species ...
Lec.2 Dr.Maysem M.Alwash Hypersensitivity Reaction s (cont.)
... Therefore, these diseases are often referred to as “collagen vascular” or “connective tissue” disorders, even though the immunologic reactions are not specifically directed against constituents of connective tissue or ...
... Therefore, these diseases are often referred to as “collagen vascular” or “connective tissue” disorders, even though the immunologic reactions are not specifically directed against constituents of connective tissue or ...
NGS of Full-length HLA genes of Reference Cell Lines
... NGS of Full-length HLA genes of Reference Cell Lines Cost: participants of this project will be expected to perform NGS typing of a proficiency panel to be provided by the Workshop organizers. Panels consist of 24 DNAs. These will be shipped directly from the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center ...
... NGS of Full-length HLA genes of Reference Cell Lines Cost: participants of this project will be expected to perform NGS typing of a proficiency panel to be provided by the Workshop organizers. Panels consist of 24 DNAs. These will be shipped directly from the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center ...
xiv. hla and transplantation medicine
... 2. The MHC includes several loci closely linked. Each of these loci involves numerous alleles, having at least 10 to 40 alleles per locus that control the production of their corresponding antigens. 3. Some groups of these antigens exhibit cross-reacting characteristics that further increase the co ...
... 2. The MHC includes several loci closely linked. Each of these loci involves numerous alleles, having at least 10 to 40 alleles per locus that control the production of their corresponding antigens. 3. Some groups of these antigens exhibit cross-reacting characteristics that further increase the co ...
Mendel`s Principles
... trait It involves breeding the individual with an individual who expresses the recessive version of the trait If all offspring display the dominant phenotype, the individual is homozygous dominant If the offspring display both phenotypes, the individual is heterozygous ...
... trait It involves breeding the individual with an individual who expresses the recessive version of the trait If all offspring display the dominant phenotype, the individual is homozygous dominant If the offspring display both phenotypes, the individual is heterozygous ...
Biol2250 – Principles of Genetics – Dr Carr Problem solving
... for orange and “B” for black. OB cats are bi-‐colored (“calico”). I have two cats: Jennet is an orange female; Puszek is a black male. Can Jennet be Puszek’s mother? Can Jennet and Puszek be s ...
... for orange and “B” for black. OB cats are bi-‐colored (“calico”). I have two cats: Jennet is an orange female; Puszek is a black male. Can Jennet be Puszek’s mother? Can Jennet and Puszek be s ...
Beyond Dominant and Recessive Alleles
... Multiple Alleles • Many genes have more than two alleles are said to have multiple alleles. • A common example is coat color in rabbits. • Their color is determined by a gene that has at least four different alleles. • Human blood type is also multiple allelic, meaning that there are three possible ...
... Multiple Alleles • Many genes have more than two alleles are said to have multiple alleles. • A common example is coat color in rabbits. • Their color is determined by a gene that has at least four different alleles. • Human blood type is also multiple allelic, meaning that there are three possible ...
Co dominance - The Grange School Blogs
... production of antigen A B - allele I , which leads to the production of antigen B O - allele I , which does not lead to the production of either antigen ...
... production of antigen A B - allele I , which leads to the production of antigen B O - allele I , which does not lead to the production of either antigen ...
Patterns of Inheritance
... In paternity lawsuits, blood typing often is used to provide genetic evidence that the alleged father could not be related to the child. For the following mother-child combinations, indicate which blood types could NOT have been the father’s: (1) Mother with O and child with B; (2) Mother with B and ...
... In paternity lawsuits, blood typing often is used to provide genetic evidence that the alleged father could not be related to the child. For the following mother-child combinations, indicate which blood types could NOT have been the father’s: (1) Mother with O and child with B; (2) Mother with B and ...
Kuby Immunology 6/e - Dr. Jennifer Capers
... with manipulation Rabbits injected with acetylcholine receptors ...
... with manipulation Rabbits injected with acetylcholine receptors ...
5.2 Probability and Heredity
... identical, and one may be dominant in determining the phenotype while the other is ...
... identical, and one may be dominant in determining the phenotype while the other is ...
Eugenics and the Hardy-Weinberg equation
... Eugenics and the Hardy-Weinberg equation. The eugenics movement of the early 20th Century promoted the idea that the physiological, mental and moral decline of the human race could be prevented or reversed by promoting marriages between genetically superior specimens and discouraging or preventing r ...
... Eugenics and the Hardy-Weinberg equation. The eugenics movement of the early 20th Century promoted the idea that the physiological, mental and moral decline of the human race could be prevented or reversed by promoting marriages between genetically superior specimens and discouraging or preventing r ...
NK cells Interferons J. Ochotná
... Receptor equipment, containing granules, the mechanisms of stimulation and functions are very similar to mast cells They are responsible for the emergence of anaphylactic shock ...
... Receptor equipment, containing granules, the mechanisms of stimulation and functions are very similar to mast cells They are responsible for the emergence of anaphylactic shock ...
MENDEL AND THE GENE IDEA
... • There is also a law of addition that determines the chances of an event happening in different ways. • For example, there are two ways that F1 gametes can combine to form a heterozygote. • The dominant allele could come from the sperm and the recessive from the ovum (probability = 1/4). • Or, the ...
... • There is also a law of addition that determines the chances of an event happening in different ways. • For example, there are two ways that F1 gametes can combine to form a heterozygote. • The dominant allele could come from the sperm and the recessive from the ovum (probability = 1/4). • Or, the ...
Mendelian Inheritance - Santa Susana High School
... recessive allele - has no noticeable contribution to an organism's appearance if a dominant allele is also present(symbolized by a lower cased letter of the dominant trait) wildtype - the dominant trait expressed in the highest ratio in nature genotype - organisms genetic makeup phenotype - organism ...
... recessive allele - has no noticeable contribution to an organism's appearance if a dominant allele is also present(symbolized by a lower cased letter of the dominant trait) wildtype - the dominant trait expressed in the highest ratio in nature genotype - organisms genetic makeup phenotype - organism ...
Genetics - Georgia Highlands College
... Autosomal Disorders • Dominant – Rare because always expressed embryo/fetal death – Huntington’s disease: impairs motor functioning • Onset after reproductive age, increase probability of passing ...
... Autosomal Disorders • Dominant – Rare because always expressed embryo/fetal death – Huntington’s disease: impairs motor functioning • Onset after reproductive age, increase probability of passing ...
Human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is the locus of genes that encode for proteins on the surface of cells that are responsible for regulation of the immune system in humans. This group of genes resides on chromosome 6 (exception: the gene for β2-microglobulin which is located on chromosome 15), and encodes cell-surface antigen-presenting proteins and has many other functions. The HLA genes are the human versions of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes that are found in most vertebrates (and thus are the most studied of the MHC genes). The proteins encoded by certain genes are also known as antigens, as a result of their historic discovery as factors in organ transplants. The major HLAs are essential elements for immune function. Different classes have different functions:HLAs corresponding to MHC class I (A, B, and C) present peptides from inside the cell. For example, if the cell is infected by a virus, the HLA system brings fragments of the virus to the surface of the cell so that the cell can be destroyed by the immune system. These peptides are produced from digested proteins that are broken down in the proteasomes. In general, these particular peptides are small polymers, about 9 amino acids in length. Foreign antigens presented by MHC class I attract killer T-cells (also called CD8 positive- or cytotoxic T-cells) that destroy cells.HLAs corresponding to MHC class II (DP, DM, DOA, DOB, DQ, and DR) present antigens from outside of the cell to T-lymphocytes. These particular antigens stimulate the multiplication of T-helper cells, which in turn stimulate antibody-producing B-cells to produce antibodies to that specific antigen. Self-antigens are suppressed by regulatory T cells.HLAs corresponding to MHC class III encode components of the complement system.HLAs have other roles. They are important in disease defense. They are the major cause of organ transplant rejections. They may protect against or fail to protect (if down-regulated by an infection) against cancers. Mutations in HLA may be linked to autoimmune disease (examples: type I diabetes, coeliac disease). HLA may also be related to people's perception of the odor of other people, and may be involved in mate selection, as at least one study found a lower-than-expected rate of HLA similarity between spouses in an isolated community.Aside from the genes encoding the 6 major antigen-presenting proteins, there are a large number of other genes, many involved in immune function, located on the HLA complex. Diversity of HLAs in the human population is one aspect of disease defense, and, as a result, the chance of two unrelated individuals with identical HLA molecules on all loci is very low. HLA genes have historically been identified as a result of the ability to successfully transplant organs between HLA-similar individuals.