Incomplete Dominance, Codominance, and Multiple Alleles (Fill in
... Stop using the word bank here. If you feel comfortable you can complete Q1 or you can wait until I give you directions. Q1. If you cross a two pink flowers, is it possible to produce a white ...
... Stop using the word bank here. If you feel comfortable you can complete Q1 or you can wait until I give you directions. Q1. If you cross a two pink flowers, is it possible to produce a white ...
Lecture7_8 - Welcome to people.pharmacy.purdue.edu!
... Does Isotype Switching occur in one B cell? 1. Activated B cell resides in the Germinal Center -some individuals will mature directly into plasma cells 2. Some B cells in the germinal center divide and undergo hypermutation and/or isotype switching 3. After this stage they cannot divide and the hig ...
... Does Isotype Switching occur in one B cell? 1. Activated B cell resides in the Germinal Center -some individuals will mature directly into plasma cells 2. Some B cells in the germinal center divide and undergo hypermutation and/or isotype switching 3. After this stage they cannot divide and the hig ...
File
... waxy kernels. If you crossed a waxy kernel plant to a heterozygous normal plant what type of seeds would be produced? ...
... waxy kernels. If you crossed a waxy kernel plant to a heterozygous normal plant what type of seeds would be produced? ...
Lesson Outline continued
... b. When two alleles of a gene are the same, its genotype is homozygous. c. If two alleles of a gene are different, its genotype is heterozygous. B. Modeling Inheritance 1. In a situation based on chance, such as flipping a coin, the chance of getting a certain outcome can be represented by a(n) rati ...
... b. When two alleles of a gene are the same, its genotype is homozygous. c. If two alleles of a gene are different, its genotype is heterozygous. B. Modeling Inheritance 1. In a situation based on chance, such as flipping a coin, the chance of getting a certain outcome can be represented by a(n) rati ...
30.10.2009
... of the immune response The same antigen can induce an active immune response or an active state of tolerance, the result of response depends on many factors: - state of the immune system - characteristics of antigen ...
... of the immune response The same antigen can induce an active immune response or an active state of tolerance, the result of response depends on many factors: - state of the immune system - characteristics of antigen ...
Population Genetics (Chp. 13-15) Allele Frequencies- Chp. 13 pp. 263-276
... Other levels (Human Race) Chapter 13 Population- any group of members of the same species in a given geographical area at a specific time Population genetics – a branch that considers all of the alleles in a population which constitute a gene pool Gene Flow- the movement of alleles due to migration ...
... Other levels (Human Race) Chapter 13 Population- any group of members of the same species in a given geographical area at a specific time Population genetics – a branch that considers all of the alleles in a population which constitute a gene pool Gene Flow- the movement of alleles due to migration ...
08_PopulationGenetics
... 5. The population probably has an equal frequency of A and a alleles. The correct answer is b. The conditions described all contribute to genetic equilibrium, where it would be expected for initial gene frequencies to remain constant generation after generation. 3. Which of the following is NOT a co ...
... 5. The population probably has an equal frequency of A and a alleles. The correct answer is b. The conditions described all contribute to genetic equilibrium, where it would be expected for initial gene frequencies to remain constant generation after generation. 3. Which of the following is NOT a co ...
Histocompatibility
... developed (syngeneic strains). It is now possible to produce mice that only differ by a few genes (congenic strains) or single gene (coisogenic strain). Congenic strains are produced by selective breeding, and repeated back crossing. Congenic strains are designated by the abbreviation of the backgro ...
... developed (syngeneic strains). It is now possible to produce mice that only differ by a few genes (congenic strains) or single gene (coisogenic strain). Congenic strains are produced by selective breeding, and repeated back crossing. Congenic strains are designated by the abbreviation of the backgro ...
Genetics NTK
... 2. Genetics is the field of biology that studies how traits are inherited. 3. Traits are determined by genes that are found in the DNA. 4. Alleles are the various forms of a trait that exist. 5. The dominant allele is the allele that shows. 6. The recessive allele is the allele that is hidden. 7. A ...
... 2. Genetics is the field of biology that studies how traits are inherited. 3. Traits are determined by genes that are found in the DNA. 4. Alleles are the various forms of a trait that exist. 5. The dominant allele is the allele that shows. 6. The recessive allele is the allele that is hidden. 7. A ...
Meiosis - edl.io
... A person inherited from the mother alleles B,D, E and H. And from the father alleles b, d, e, and h. Genes E and H are located on the same chromosome. Genes B and D are each on different chromosomes. Which sets of alleles most likely are found in the gametes of this person? Hint 1: If E and H are lo ...
... A person inherited from the mother alleles B,D, E and H. And from the father alleles b, d, e, and h. Genes E and H are located on the same chromosome. Genes B and D are each on different chromosomes. Which sets of alleles most likely are found in the gametes of this person? Hint 1: If E and H are lo ...
AP Biology Complex Inheritance Incomplete dominance: Pattern of
... Heterozygotes produce equal numbers of normal dysfunctional enzymes. They lack disease symptoms, because half the normal amount of functional enzyme is sufficient to prevent lipid accumulation in the brain. ...
... Heterozygotes produce equal numbers of normal dysfunctional enzymes. They lack disease symptoms, because half the normal amount of functional enzyme is sufficient to prevent lipid accumulation in the brain. ...
Genetics
... and alleles? • Genes are found in the chromosomes and alleles are versions of genes. • For example: Chromosome #3 may contain the DNA code for your legs. The code is the gene. The gene for legs may have two different alleles for length. One allele may code for short legs while the other allele codes ...
... and alleles? • Genes are found in the chromosomes and alleles are versions of genes. • For example: Chromosome #3 may contain the DNA code for your legs. The code is the gene. The gene for legs may have two different alleles for length. One allele may code for short legs while the other allele codes ...
CH12Sec3and4
... • Law of Segregation - The two traits for a characteristic separate during the formation of eggs and sperm. Pg 177 ...
... • Law of Segregation - The two traits for a characteristic separate during the formation of eggs and sperm. Pg 177 ...
... presenting the appropriate antigen on class I MHC can activate memory TC cells. Killing of Infected cells by TCTL: Trigger – activation by foreign antigen on class I MHC. Mechanism - identical to NK cells. Perforin & granzymes, FasL Summary: MHC, BCR, TCR. MHC Diversity on a single cell: Diversi ...
Inheritance What Were The Two Ideas Lacking in Darwin`s Natural
... • Some alleles are DOMINANT: F (free earlobes) • Some alleles are recessive: f (attached earlobes) • and some are CO-DOMINANT: A and B blood alleles ...
... • Some alleles are DOMINANT: F (free earlobes) • Some alleles are recessive: f (attached earlobes) • and some are CO-DOMINANT: A and B blood alleles ...
Which best describes the genetics of the afflicting allele in the
... genotypes are known? (i.e., indicate the genotypes on the figure for all known AA, Aa, and aa individuals) 3. Given the following pedigree, would you expect to find more of in Cleopatra-Berenike III compared with the general population? a. Loci which are heterozygous b. Loci which are homozygous for ...
... genotypes are known? (i.e., indicate the genotypes on the figure for all known AA, Aa, and aa individuals) 3. Given the following pedigree, would you expect to find more of in Cleopatra-Berenike III compared with the general population? a. Loci which are heterozygous b. Loci which are homozygous for ...
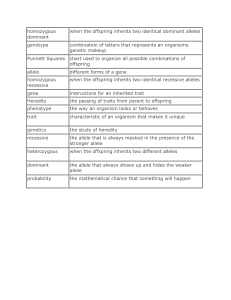
homozygous dominant when the offspring inherits two identical
... combination of letters that represents an organisms genetic makeup ...
... combination of letters that represents an organisms genetic makeup ...
An allele is a segment of a DNA molecule that codes for the
... An allele is a segment of a DNA molecule that codes for the production of a protein. E. What are nucleotides? Sugar+phosphate+base (basic building block of DNA / RNA molecule. What are codons? A linear sequence of three nucleotides (can also say three bases) that specifies (names, stands for, codes ...
... An allele is a segment of a DNA molecule that codes for the production of a protein. E. What are nucleotides? Sugar+phosphate+base (basic building block of DNA / RNA molecule. What are codons? A linear sequence of three nucleotides (can also say three bases) that specifies (names, stands for, codes ...
meiosis_6
... This is because the first gene codes for an intermediate colourless pigment, if the dominant C allele is present The second gene codes for an enzyme that converts the intermediate compound to the purple pigment, if the dominant R allele is present ...
... This is because the first gene codes for an intermediate colourless pigment, if the dominant C allele is present The second gene codes for an enzyme that converts the intermediate compound to the purple pigment, if the dominant R allele is present ...
Human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is the locus of genes that encode for proteins on the surface of cells that are responsible for regulation of the immune system in humans. This group of genes resides on chromosome 6 (exception: the gene for β2-microglobulin which is located on chromosome 15), and encodes cell-surface antigen-presenting proteins and has many other functions. The HLA genes are the human versions of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes that are found in most vertebrates (and thus are the most studied of the MHC genes). The proteins encoded by certain genes are also known as antigens, as a result of their historic discovery as factors in organ transplants. The major HLAs are essential elements for immune function. Different classes have different functions:HLAs corresponding to MHC class I (A, B, and C) present peptides from inside the cell. For example, if the cell is infected by a virus, the HLA system brings fragments of the virus to the surface of the cell so that the cell can be destroyed by the immune system. These peptides are produced from digested proteins that are broken down in the proteasomes. In general, these particular peptides are small polymers, about 9 amino acids in length. Foreign antigens presented by MHC class I attract killer T-cells (also called CD8 positive- or cytotoxic T-cells) that destroy cells.HLAs corresponding to MHC class II (DP, DM, DOA, DOB, DQ, and DR) present antigens from outside of the cell to T-lymphocytes. These particular antigens stimulate the multiplication of T-helper cells, which in turn stimulate antibody-producing B-cells to produce antibodies to that specific antigen. Self-antigens are suppressed by regulatory T cells.HLAs corresponding to MHC class III encode components of the complement system.HLAs have other roles. They are important in disease defense. They are the major cause of organ transplant rejections. They may protect against or fail to protect (if down-regulated by an infection) against cancers. Mutations in HLA may be linked to autoimmune disease (examples: type I diabetes, coeliac disease). HLA may also be related to people's perception of the odor of other people, and may be involved in mate selection, as at least one study found a lower-than-expected rate of HLA similarity between spouses in an isolated community.Aside from the genes encoding the 6 major antigen-presenting proteins, there are a large number of other genes, many involved in immune function, located on the HLA complex. Diversity of HLAs in the human population is one aspect of disease defense, and, as a result, the chance of two unrelated individuals with identical HLA molecules on all loci is very low. HLA genes have historically been identified as a result of the ability to successfully transplant organs between HLA-similar individuals.