Basic mechanisms of lung inflammation
... future strategies in treatment of lung disease. In the inflammatory and immune responses, it is the influx of cells as well as local cell division, and apoptosis and luminal clearance that have to be controlled to maintain an appropriate response [25]. Steroids are amongst the major regulators of im ...
... future strategies in treatment of lung disease. In the inflammatory and immune responses, it is the influx of cells as well as local cell division, and apoptosis and luminal clearance that have to be controlled to maintain an appropriate response [25]. Steroids are amongst the major regulators of im ...
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
... • Upset stomach/bloating/gas/loose stools is also fairly common during the first month and for most patients is fairly mild. • HIV levels in the blood will often drop by > 99% in the first month and the CD4 count (marker of immune system function) will often increase providing protection against AID ...
... • Upset stomach/bloating/gas/loose stools is also fairly common during the first month and for most patients is fairly mild. • HIV levels in the blood will often drop by > 99% in the first month and the CD4 count (marker of immune system function) will often increase providing protection against AID ...
Glycogen metabolism supports effector function and energy
... Dendritic cells (DCs), professional antigen presenting cells of the immune system, serve as a bridge between the innate and adaptive immune responses. Activation of DCs by a stimulus through toll-like receptors (TLRs) is coupled with an increase in energy demand fulfilled by a glycolytic burst, whic ...
... Dendritic cells (DCs), professional antigen presenting cells of the immune system, serve as a bridge between the innate and adaptive immune responses. Activation of DCs by a stimulus through toll-like receptors (TLRs) is coupled with an increase in energy demand fulfilled by a glycolytic burst, whic ...
a13 Innate Immunity
... Action of inflammatory chemicals • Dilation of arterioles, resulting in hyperemia • Increased permeability of local capillaries and edema (leakage of exudate) Exudate moves foreign material into lymphatic vessels, delivers clotting proteins to form a scaffold for repair and to isolate the area ...
... Action of inflammatory chemicals • Dilation of arterioles, resulting in hyperemia • Increased permeability of local capillaries and edema (leakage of exudate) Exudate moves foreign material into lymphatic vessels, delivers clotting proteins to form a scaffold for repair and to isolate the area ...
MHC Class II Molecules
... T cells recognize antigens that are presented by antigen presenting cells (APCs) only The way which TCR recognizes antigens is quite different from antigen recognition by antibody (e.g. recognize antigen fragments presented by MHC molecules only) The most important antigen-presenting molecules are c ...
... T cells recognize antigens that are presented by antigen presenting cells (APCs) only The way which TCR recognizes antigens is quite different from antigen recognition by antibody (e.g. recognize antigen fragments presented by MHC molecules only) The most important antigen-presenting molecules are c ...
Structure and Function of Bacterial Cells Part 2
... Why study bacterial cell walls? They are essential structures in bacteria. They are made of chemical components found nowhere else in nature. They may cause symptoms of disease in animals. They are the site of action of some of our most important antibiotics. ...
... Why study bacterial cell walls? They are essential structures in bacteria. They are made of chemical components found nowhere else in nature. They may cause symptoms of disease in animals. They are the site of action of some of our most important antibiotics. ...
Adaptive immunity
... microbes. Another important difference between B and T lymphocytes is that most T cells recognize only microbial protein antigens, whereas antibodies are able to recognize many different types of microbial molecules, including proteins, carbohydrate, and lipids. Immunity may be induced in an individ ...
... microbes. Another important difference between B and T lymphocytes is that most T cells recognize only microbial protein antigens, whereas antibodies are able to recognize many different types of microbial molecules, including proteins, carbohydrate, and lipids. Immunity may be induced in an individ ...
Immunology Basics Biology Lecture PowerPoint
... PowerPoints, video tutorials, sample assignments and course syllabi. New materials are continually being developed, so check back frequently, or follow us on Facebook (Science Prof Online) or Twitter (ScienceProfSPO) for updates. • Many SPO PowerPoints are available in a variety of formats, such as ...
... PowerPoints, video tutorials, sample assignments and course syllabi. New materials are continually being developed, so check back frequently, or follow us on Facebook (Science Prof Online) or Twitter (ScienceProfSPO) for updates. • Many SPO PowerPoints are available in a variety of formats, such as ...
PEGylated IL-10 (AM0010) for advanced solid tumors
... rIL-10 transiently lowered TNFa and IL-1 in patients (-50% only) Signs of efficacy observed but short T1/2 of rHuIL-10 eliminates its therapeutic potency Increased Granzymes and IFNg were observed at higher doses (CD8+ T cell activity) ARMO BioSciences develops AM0010, a PEGylated human IL-10 ...
... rIL-10 transiently lowered TNFa and IL-1 in patients (-50% only) Signs of efficacy observed but short T1/2 of rHuIL-10 eliminates its therapeutic potency Increased Granzymes and IFNg were observed at higher doses (CD8+ T cell activity) ARMO BioSciences develops AM0010, a PEGylated human IL-10 ...
The lymphoid organs
... of cell adhesion molecules (CD2 and LFA-1, which bind to LFA-3 and ICAMs to allow greater and prolonged interaction with ¾ APCs for CD4+ Th cells ¾ Target cells for CD8+ CTLs. Effector T cells express many membrane-bound (FasL, CD40, and LT-β) and soluble effector molecules that are absent in naïv ...
... of cell adhesion molecules (CD2 and LFA-1, which bind to LFA-3 and ICAMs to allow greater and prolonged interaction with ¾ APCs for CD4+ Th cells ¾ Target cells for CD8+ CTLs. Effector T cells express many membrane-bound (FasL, CD40, and LT-β) and soluble effector molecules that are absent in naïv ...
Cellular Basis of Disease
... These are obviously more common in underprivileged and less well developed areas of the world. Protein and vitamins are the commonest type of the nutritional deficiencies. As important as deficiencies are nutritional excesses, e.g. animal fats taken in excess and the link with atherosclerosis (de ...
... These are obviously more common in underprivileged and less well developed areas of the world. Protein and vitamins are the commonest type of the nutritional deficiencies. As important as deficiencies are nutritional excesses, e.g. animal fats taken in excess and the link with atherosclerosis (de ...
ImmPower - Scientific Bio
... Yes, as long as Avé is consumed two hours before or after taking ImmPower. Many experts recommend using both dietary supplements, because they provide complementary benefits in terms of supporting fundamental aspects of immune health. ImmPower is a pure form of the dietary supplement AHCC® which has ...
... Yes, as long as Avé is consumed two hours before or after taking ImmPower. Many experts recommend using both dietary supplements, because they provide complementary benefits in terms of supporting fundamental aspects of immune health. ImmPower is a pure form of the dietary supplement AHCC® which has ...
raghava_iiita
... • Edward Jenner found that protection against smallpox • Inoculation with material from an individual infected with cowpox • This process was called vaccination (cowpox is vaccina) • Inoculum was termed a vaccine • Protective antibodies was developed ...
... • Edward Jenner found that protection against smallpox • Inoculation with material from an individual infected with cowpox • This process was called vaccination (cowpox is vaccina) • Inoculum was termed a vaccine • Protective antibodies was developed ...
Chapter 17 Active Lecture Questions
... A kidney-transplant patient experienced a cytotoxic rejection of his new kidney. Place the following in order for that rejection: (1) apoptosis occurs; (2) CD8+ T cell becomes CTL; (3) granzymes released; (4) MHC class I activates CD8+ T cell; (5) perforin ...
... A kidney-transplant patient experienced a cytotoxic rejection of his new kidney. Place the following in order for that rejection: (1) apoptosis occurs; (2) CD8+ T cell becomes CTL; (3) granzymes released; (4) MHC class I activates CD8+ T cell; (5) perforin ...
2. Cell-mediated immunity
... Key concepts in NK & CTL in immune defense 1. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity is an essential defense against intracellular pathogens, including viruses, some bacteria and parasites. 2. Cytotoxicity is regulated by celluar interactions, cytokines, and granule exocytosis. 3. CTLs recognize their target c ...
... Key concepts in NK & CTL in immune defense 1. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity is an essential defense against intracellular pathogens, including viruses, some bacteria and parasites. 2. Cytotoxicity is regulated by celluar interactions, cytokines, and granule exocytosis. 3. CTLs recognize their target c ...
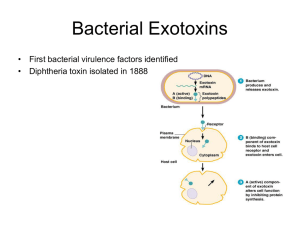
Bacterial Exotoxins
... • They bind to the host cell one specific receptor and are translocated into the cell. – They will become active and modify some proteins or other components of the host cell. ...
... • They bind to the host cell one specific receptor and are translocated into the cell. – They will become active and modify some proteins or other components of the host cell. ...
role of il-23 in crohn`s disease and ulcerative colitis and other
... along with the accumulation of fluid, leukocytes, and inflammatory mediators such as cytokines. In the sub-acute/chronic phase it is characterized by the development of specific humoral and cellular immune responses to the pathogen(s) present at the site of tissue injury.[2] Most cytokines involved ...
... along with the accumulation of fluid, leukocytes, and inflammatory mediators such as cytokines. In the sub-acute/chronic phase it is characterized by the development of specific humoral and cellular immune responses to the pathogen(s) present at the site of tissue injury.[2] Most cytokines involved ...