Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns, Pattern Recognition Receptors and Pediatric Sepsis Lesley
... cytotoxic NK cells and epithelial cells. PRRs can be expressed on cell surfaces, in the cytoplasm, or in endosomes and have specificity for PAMPs from a variety of sources [12, 13]. The innate immune response can be initiated by PRR-mediated recognition of a vast array of PAMPs expressed or released ...
... cytotoxic NK cells and epithelial cells. PRRs can be expressed on cell surfaces, in the cytoplasm, or in endosomes and have specificity for PAMPs from a variety of sources [12, 13]. The innate immune response can be initiated by PRR-mediated recognition of a vast array of PAMPs expressed or released ...
Hemolytic disease of the newborn - Easymed.club
... • If the mother is RhD negative and the father is RhD positive the baby may inherit the D antigen and express it on fetal RBC. • Fetal red cells (RhD +) enter the maternal circulation as a result of fetomaternal haemorrhage (FMH) at the time of delivery. • The mother immune system reacts and form an ...
... • If the mother is RhD negative and the father is RhD positive the baby may inherit the D antigen and express it on fetal RBC. • Fetal red cells (RhD +) enter the maternal circulation as a result of fetomaternal haemorrhage (FMH) at the time of delivery. • The mother immune system reacts and form an ...
Lytic cycle
... Human Immunodeficiency Virus HIV targets CD4+ cells, mainly helper T cells -Without these cells, the body cannot mount an effective immune response -Host may ultimately die from a variety of opportunistic infections Tests for HIV detect anti-HIV antibodies -Not circulating viruses ...
... Human Immunodeficiency Virus HIV targets CD4+ cells, mainly helper T cells -Without these cells, the body cannot mount an effective immune response -Host may ultimately die from a variety of opportunistic infections Tests for HIV detect anti-HIV antibodies -Not circulating viruses ...
Genetically modified T cells in cancer therapy
... orchestrators and effectors of the adaptive immune response is directed by the specificity of the TCR. Central and peripheral tolerance ...
... orchestrators and effectors of the adaptive immune response is directed by the specificity of the TCR. Central and peripheral tolerance ...
Cytokines and Chemokines
... • Also, multiple cytokines often have overlapping activities • A single cell frequently interacts with multiple cytokines with seemingly identical responses - cross-talk • Many Membrane-bound cytokine forms have been characterized ...
... • Also, multiple cytokines often have overlapping activities • A single cell frequently interacts with multiple cytokines with seemingly identical responses - cross-talk • Many Membrane-bound cytokine forms have been characterized ...
Anatomy of the Brain (seizures)
... • No one knows why allergies develop, but it is known that an allergy can appear, disappear, or reappear at any time and at any age. Allergic reactions rarely occur during the first encounter with the troublesome allergen because the body needs time to accumulate the antibodies. Also, an individual' ...
... • No one knows why allergies develop, but it is known that an allergy can appear, disappear, or reappear at any time and at any age. Allergic reactions rarely occur during the first encounter with the troublesome allergen because the body needs time to accumulate the antibodies. Also, an individual' ...
The nervous system and innate immunity: The neuropeptide
... olfactory bulb42. NPY, secreted by the OECs is believed to act as a growth factor for the olfactory neuron based on in vitro evidence of stimulatory activity and reduced density of olfactory neurons in NPY knockout mice41. Precisely what protects the olfactory epithelium from continuous infection, c ...
... olfactory bulb42. NPY, secreted by the OECs is believed to act as a growth factor for the olfactory neuron based on in vitro evidence of stimulatory activity and reduced density of olfactory neurons in NPY knockout mice41. Precisely what protects the olfactory epithelium from continuous infection, c ...
Protocol S1.
... A total of 50 subjects will be randomized in a 1:1 ratio to Vivotif® or Typherix®. Categorical data will be presented in contingency tables along with frequencies and percentages. Continuous data will be summarized using at least the frequency (n), mean, standard deviation, median and the range. Des ...
... A total of 50 subjects will be randomized in a 1:1 ratio to Vivotif® or Typherix®. Categorical data will be presented in contingency tables along with frequencies and percentages. Continuous data will be summarized using at least the frequency (n), mean, standard deviation, median and the range. Des ...
past, present and future - British Society for Immunology
... resolving fact from speculation. The immune system, both in humans and animals, has proved to be immensely more elegant and complex than ever could have been imagined when the BSI was established. Its nature has truly proven fundamental to the way we are made and to how we interact with our environm ...
... resolving fact from speculation. The immune system, both in humans and animals, has proved to be immensely more elegant and complex than ever could have been imagined when the BSI was established. Its nature has truly proven fundamental to the way we are made and to how we interact with our environm ...
B7-1, B7-2 and class II MHC molecules in idiopathic pulmonary
... expression of B7 and class II major histocompatibility complex molecules. The dysregulation of these molecules in epithelial cells may lead to the activation of autoreactive T-lymphocytes, which might contribute to the pathogenesis of fibrosing lung diseases. Eur Respir J 2000; 15: 49±55. ...
... expression of B7 and class II major histocompatibility complex molecules. The dysregulation of these molecules in epithelial cells may lead to the activation of autoreactive T-lymphocytes, which might contribute to the pathogenesis of fibrosing lung diseases. Eur Respir J 2000; 15: 49±55. ...
Herpesvirus Seropositivity in Childhood Monocyte-Induced Associates with Decreased Production
... associated with a bias toward a Th1-type cytokine profile (26). This would suggest that both EBV and CMV could influence the early life development of functionally diverse adaptive immune responses. Innate responses can greatly influence the generation and maintenance of subsequent adaptive effector ...
... associated with a bias toward a Th1-type cytokine profile (26). This would suggest that both EBV and CMV could influence the early life development of functionally diverse adaptive immune responses. Innate responses can greatly influence the generation and maintenance of subsequent adaptive effector ...
nCounter® Vantage 3D™ Protein Immune Cell Signaling Panel for
... Subject to the terms and conditions of sale of the nCounter Analysis System, NanoString grants you a limited, nonexclusive, non-transferable, non-sublicensable, research use only license to use this proprietary nSolver™ software with the nCounter Analysis System only in accordance with this manual, ...
... Subject to the terms and conditions of sale of the nCounter Analysis System, NanoString grants you a limited, nonexclusive, non-transferable, non-sublicensable, research use only license to use this proprietary nSolver™ software with the nCounter Analysis System only in accordance with this manual, ...
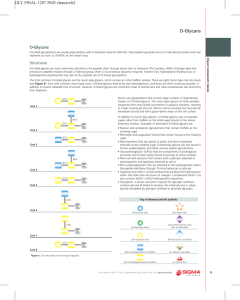
O-Linked Glycoproteins - Sigma
... Proteins that are O-linked with GlcNAc may alternatively be phosphorylated at the same peptide site, and similarly to phosphorylation, O-GlcNAc processing has been associated with cellular signaling events, including insulin signaling and RNA transcription regulation.1,2 ...
... Proteins that are O-linked with GlcNAc may alternatively be phosphorylated at the same peptide site, and similarly to phosphorylation, O-GlcNAc processing has been associated with cellular signaling events, including insulin signaling and RNA transcription regulation.1,2 ...
Elements of the Immune System and their Roles
... immune system. That approach is no longer so successful for developing new vaccines, perhaps because all the easily won vaccines have been made. But deeper understanding of the mechanisms of immunity is spawning new ideas for vaccines against infectious diseases and even against other types of disea ...
... immune system. That approach is no longer so successful for developing new vaccines, perhaps because all the easily won vaccines have been made. But deeper understanding of the mechanisms of immunity is spawning new ideas for vaccines against infectious diseases and even against other types of disea ...
PDF
... corticosteroid-induced cleft palate (Melnick et al. 1981a), corticosteroid treatment does not appear to alter the detectable spatiotemporal distribution of H-2 antigens in developing palates of embryonic BIO.A mice. These data suggest that we should look elsewhere for the mechanism of steroid-induce ...
... corticosteroid-induced cleft palate (Melnick et al. 1981a), corticosteroid treatment does not appear to alter the detectable spatiotemporal distribution of H-2 antigens in developing palates of embryonic BIO.A mice. These data suggest that we should look elsewhere for the mechanism of steroid-induce ...