Atomic Structure Unit Test 2016
... ____ 41. The change of an atom from an excited state to the ground state always requires a. absorption of energy. b. emission of electromagnetic radiation. c. release of visible light. d. an increase in electron energy. ____ 42. The spin quantum number indicates that the number of possible spin sta ...
... ____ 41. The change of an atom from an excited state to the ground state always requires a. absorption of energy. b. emission of electromagnetic radiation. c. release of visible light. d. an increase in electron energy. ____ 42. The spin quantum number indicates that the number of possible spin sta ...
Chemistry: Introduction to Chemical Reactions Guided Inquiry What
... Why do methane molecules (natural gas) collide with oxygen molecules in the air harmlessly until there is a spark or flame, and then they cause an explosion? Why do iron atoms react with oxygen molecules in the air to form rust, but gold molecules do not react with air? The Collision theory is the b ...
... Why do methane molecules (natural gas) collide with oxygen molecules in the air harmlessly until there is a spark or flame, and then they cause an explosion? Why do iron atoms react with oxygen molecules in the air to form rust, but gold molecules do not react with air? The Collision theory is the b ...
Ch. 3 - My CCSD
... Dalton’s Modern Atomic Theory (experiment based!) 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ...
... Dalton’s Modern Atomic Theory (experiment based!) 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ...
Review for Physical Science Test #2
... To tell a strong acid from a weak acid To tell an acid from a neutral solution To tell a strong base from a weak base To create a temporary tattoo on your little sister’s face right before picture day. ...
... To tell a strong acid from a weak acid To tell an acid from a neutral solution To tell a strong base from a weak base To create a temporary tattoo on your little sister’s face right before picture day. ...
atomic number
... Dalton’s Modern Atomic Theory (experiment based!) 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ...
... Dalton’s Modern Atomic Theory (experiment based!) 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ...
atomic theory webquest[1].
... 1) When did John Dalton originate the idea of an atomic theory? _________________ 2) What are two laws of chemical combination? Law of ____________________________ Law of ____________________________ 3) What were John Dalton’s basic ideas about matter (skip step 4? 1)________________________________ ...
... 1) When did John Dalton originate the idea of an atomic theory? _________________ 2) What are two laws of chemical combination? Law of ____________________________ Law of ____________________________ 3) What were John Dalton’s basic ideas about matter (skip step 4? 1)________________________________ ...
Atomic Structure
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Mass number: the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Isotopes: Atoms of the same element that differ in mass number (differing numbers of neutrons) ...
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Mass number: the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Isotopes: Atoms of the same element that differ in mass number (differing numbers of neutrons) ...
Elements, basic principles, periodic table
... b/c fewer e- feel the "pull" of the positively charged nucleus - ion is larger than the neutral atom Ions behave the same as atoms across the periodic table (row vs column Importance of the radius: molecules can only “fit” certain sizes ...
... b/c fewer e- feel the "pull" of the positively charged nucleus - ion is larger than the neutral atom Ions behave the same as atoms across the periodic table (row vs column Importance of the radius: molecules can only “fit” certain sizes ...
Atoms and Elements Class Notes and Class Work
... 1. What is a definition of “matter” and of “property”? 2. List three properties of matter to explain each of the following: 3. Use the particle theory of matter to explain each of the following: a) Gases have low density (mass/volume) b) Some substances are solids at room temperature. c) Some substa ...
... 1. What is a definition of “matter” and of “property”? 2. List three properties of matter to explain each of the following: 3. Use the particle theory of matter to explain each of the following: a) Gases have low density (mass/volume) b) Some substances are solids at room temperature. c) Some substa ...
IPS Unit 2 Worksheet Packet
... ____ 10. Atoms are indivisible. ____ 11. An atom has a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which scientists can predict where an electron is likely to be found. ____ 12. An atom is made of positively charged, pudding like material through which negatively charged partic ...
... ____ 10. Atoms are indivisible. ____ 11. An atom has a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which scientists can predict where an electron is likely to be found. ____ 12. An atom is made of positively charged, pudding like material through which negatively charged partic ...
isotopes and average atomic mass
... The atomic mass of an element is the sum of all the masses of the sub-atomic particles which comprise the atom. The mass in grams of these particles (protons, neutrons, electrons, et al) are exceptionally small. The mass of the proton is 1.67 X 10-23 grams. The neutron is slightly larger and the ele ...
... The atomic mass of an element is the sum of all the masses of the sub-atomic particles which comprise the atom. The mass in grams of these particles (protons, neutrons, electrons, et al) are exceptionally small. The mass of the proton is 1.67 X 10-23 grams. The neutron is slightly larger and the ele ...
Review
... 5. What is the average atomic mass of silicon if 92.21 % of its atoms have a mass of 27.977 amu, 4.07 % have a mass of 28.976 amu, and 3.09 % have a mass of 29.974 amu? ...
... 5. What is the average atomic mass of silicon if 92.21 % of its atoms have a mass of 27.977 amu, 4.07 % have a mass of 28.976 amu, and 3.09 % have a mass of 29.974 amu? ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... These are topics from a traditional 1st quarter. If you used the thematic approach with me this year, you will notice that the topics are not in order of their presentation throughout the year. The final exam is cumulative so this review will help you with reviewing the concepts and calculations. No ...
... These are topics from a traditional 1st quarter. If you used the thematic approach with me this year, you will notice that the topics are not in order of their presentation throughout the year. The final exam is cumulative so this review will help you with reviewing the concepts and calculations. No ...
The Building Block of matter What is an atom?
... • Atom has two parts. At the center, there is ______1____charge due to____2_____ which have ____3______ charge. Intense mass at center is due to ____4_______ and _____5____ which are neutral. _____6__ and ___7______ have the same __8______. Negatively charged particles are called ___9_______ and t ...
... • Atom has two parts. At the center, there is ______1____charge due to____2_____ which have ____3______ charge. Intense mass at center is due to ____4_______ and _____5____ which are neutral. _____6__ and ___7______ have the same __8______. Negatively charged particles are called ___9_______ and t ...
Training - Independent School District 196
... Dalton and Atomic Theory – All elements are composed of indivisible particles called atoms. – Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of element are different from others. – Atoms can mix together in whole number ratios – Chemical reactions occur when atoms combine, separate or rearrange ...
... Dalton and Atomic Theory – All elements are composed of indivisible particles called atoms. – Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of element are different from others. – Atoms can mix together in whole number ratios – Chemical reactions occur when atoms combine, separate or rearrange ...
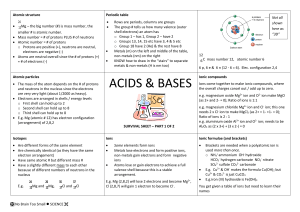
acids and bases - No Brain Too Small
... You get given a table of ions but need to learn their names ...
... You get given a table of ions but need to learn their names ...
Counting Atoms
... • One atomic mass unit, u, is 1/12 mass of carbon12 atom • Average atomic mass is weighted average of naturally occurring isotopes of an element • Number of isotopes • Atomic Mass of each isotope • Relative abundance (usually expressed as %) ...
... • One atomic mass unit, u, is 1/12 mass of carbon12 atom • Average atomic mass is weighted average of naturally occurring isotopes of an element • Number of isotopes • Atomic Mass of each isotope • Relative abundance (usually expressed as %) ...
Chemistry - Rainhill High School
... Describe why the new evidence from the scattering experiment led to a change in the atomic model. ...
... Describe why the new evidence from the scattering experiment led to a change in the atomic model. ...
chem1chapter3fromheisenberg
... Areas of high probability for electrons are orbitals • Each orbital can only have 2 electrons • What do the orbitals look like? ...
... Areas of high probability for electrons are orbitals • Each orbital can only have 2 electrons • What do the orbitals look like? ...
Name ____ Date
... Recognize the origin and distribution of elements in the universe. Summarize the major experimental evidence that led to the development of various atomic models, both historic and current. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, position and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the ...
... Recognize the origin and distribution of elements in the universe. Summarize the major experimental evidence that led to the development of various atomic models, both historic and current. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, position and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the ...
Chemistry: Unit Organizer Name 6-__ Matter has physical properties
... Compounds are substances made of two or more elements chemically combined in a set ratio. made of more than one kind of element. can be broken down during a chemical reaction. represented with elements symbols and subscripts (H20). Subscripts tell how many atoms of each element are in the co ...
... Compounds are substances made of two or more elements chemically combined in a set ratio. made of more than one kind of element. can be broken down during a chemical reaction. represented with elements symbols and subscripts (H20). Subscripts tell how many atoms of each element are in the co ...
The Periodic Table
... An atom isthe smallest the partnucleus of an are element Surrounding a series cloud like energy levelsproperties called shells that of has all the element’s or orbitals ...
... An atom isthe smallest the partnucleus of an are element Surrounding a series cloud like energy levelsproperties called shells that of has all the element’s or orbitals ...
Chap 1.
... Atoms and Photons: Origins of the Quantum Theory Atomic and Subatomic Particles The notion that the building blocks of matter are invisibly tiny particles called atoms is usually traced back to the Greek philosophers Leucippus of Miletus and Democritus of Abdera in the 5th Century BC. The English ch ...
... Atoms and Photons: Origins of the Quantum Theory Atomic and Subatomic Particles The notion that the building blocks of matter are invisibly tiny particles called atoms is usually traced back to the Greek philosophers Leucippus of Miletus and Democritus of Abdera in the 5th Century BC. The English ch ...
Modern Atomic Theory
... Match each name below with the correct term(s) on the right! Greeks (400 BC) Boyle (1627-1691) Dalton (1766-1844) JJ Thomson (1890’s) Lord Kelvin (1824-1907) Rutherford (1910) Chadwick (1932) ...
... Match each name below with the correct term(s) on the right! Greeks (400 BC) Boyle (1627-1691) Dalton (1766-1844) JJ Thomson (1890’s) Lord Kelvin (1824-1907) Rutherford (1910) Chadwick (1932) ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.




![atomic theory webquest[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004106429_1-74fb19df9c1e1b415727097eaedeef12-300x300.png)