FOR THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS ANSWER: A. if choices 1, 2
... SELECT THE ONE BEST ANSWER OR COMPLETION: 22. Which of the following statements is true in relation to the femoral triangle? A. Its medial border is the Sartorius B. The femoral nerve is its most medial structure C. Its upper border is the inguinal ligament D. The femoral canal is its most lateral ...
... SELECT THE ONE BEST ANSWER OR COMPLETION: 22. Which of the following statements is true in relation to the femoral triangle? A. Its medial border is the Sartorius B. The femoral nerve is its most medial structure C. Its upper border is the inguinal ligament D. The femoral canal is its most lateral ...
Stretch
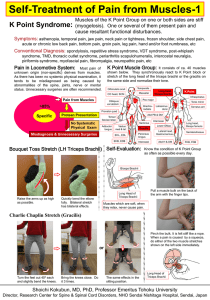
... Muscles of the K Point Group on one or both sides are stiff (myogelosis). One or several of them present pain and cause resultant functional disturbances. ...
... Muscles of the K Point Group on one or both sides are stiff (myogelosis). One or several of them present pain and cause resultant functional disturbances. ...
the shoulder
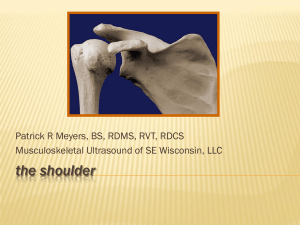
... anatomic structures – spinoglenoid groove Posterior spinoglenoid groove/notch • contains suprascapular nerve, artery and vein • common site for fluid collection or paralabral cyst ...
... anatomic structures – spinoglenoid groove Posterior spinoglenoid groove/notch • contains suprascapular nerve, artery and vein • common site for fluid collection or paralabral cyst ...
The Appendicular Skeleton
... injury can lead to a fractured clavicle The clavicle is weakest at the junction of the two curves Forces are generated through the upper limb to the trunk during a fall Therefore, most breaks occur approximately in the middle of the clavicle Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
... injury can lead to a fractured clavicle The clavicle is weakest at the junction of the two curves Forces are generated through the upper limb to the trunk during a fall Therefore, most breaks occur approximately in the middle of the clavicle Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
Bones
... The jugular foramen is occupied by the jugular bulb (for expansion of the internal jugular vein) in life. The stylomastoid foramen lies between the styloid process and the mastoid process. Anterior to the jugular foramen and in the petrous portion of the temporal bone lies the carotid canal. The for ...
... The jugular foramen is occupied by the jugular bulb (for expansion of the internal jugular vein) in life. The stylomastoid foramen lies between the styloid process and the mastoid process. Anterior to the jugular foramen and in the petrous portion of the temporal bone lies the carotid canal. The for ...
Document
... ◦ The accessory nerve (CN XI) exits the cranial cavity, descends down the neck, innervates sternocleidomastoid and enters the posterior triangle. It crosses the posterior triangle in an oblique, inferoposterior direction, within the investing layer of fascia. It lies relatively superficially in the ...
... ◦ The accessory nerve (CN XI) exits the cranial cavity, descends down the neck, innervates sternocleidomastoid and enters the posterior triangle. It crosses the posterior triangle in an oblique, inferoposterior direction, within the investing layer of fascia. It lies relatively superficially in the ...
review questions
... lies in the median plane of the perineum. consists of two symmetrical parts that are united by a median tendinous raphe. arises in part from the conjoint tendon. functions during micturition and erection. is supplied by the perineal nerve. ...
... lies in the median plane of the perineum. consists of two symmetrical parts that are united by a median tendinous raphe. arises in part from the conjoint tendon. functions during micturition and erection. is supplied by the perineal nerve. ...
Applied anatomy of the thorax and abdomen
... Except for the first and second ribs, all ribs have a groove for the intercostal nerve and blood vessels at their lower margin, which is at the outer aspect confined by a sharp bony edge. All ribs are different from each other in size, width and curvature. The first rib is the shortest. Its anterome ...
... Except for the first and second ribs, all ribs have a groove for the intercostal nerve and blood vessels at their lower margin, which is at the outer aspect confined by a sharp bony edge. All ribs are different from each other in size, width and curvature. The first rib is the shortest. Its anterome ...
ANATOMY OF LUNG & PLEURA
... The borders of the Pleura: The pleura runs close to the lung except at the lower ...
... The borders of the Pleura: The pleura runs close to the lung except at the lower ...
Document
... wall of the axilla, around the lateral thoracic vein and the inferior border of the pectoralis minor. They receive lymph mainly from the anterior thoracic all including the breast. Efferent lymphatic vessels from these nodes pass to the central and apical groups of axillary nodes. ...
... wall of the axilla, around the lateral thoracic vein and the inferior border of the pectoralis minor. They receive lymph mainly from the anterior thoracic all including the breast. Efferent lymphatic vessels from these nodes pass to the central and apical groups of axillary nodes. ...
MS WORD VERSION ()
... 1. pectoral girdle or shoulder girdle-attach bones of upper extremity to the axial skeleton (2 bones) a. clavicle (collar bone)-most commonly broken bone in the body -double curvature -medial end is sternal extremity ...
... 1. pectoral girdle or shoulder girdle-attach bones of upper extremity to the axial skeleton (2 bones) a. clavicle (collar bone)-most commonly broken bone in the body -double curvature -medial end is sternal extremity ...
Ankle power point
... Anterior Tibialis- part of the stirrup of the foot with the peroneus longus. Origin is on the lateral tibia and interosseus membrane and inserts on the 1st cuniform and 1st metatarsal. Very palpatable muscle on anterior lateral foot. Inversion and dorsiflexion are the ...
... Anterior Tibialis- part of the stirrup of the foot with the peroneus longus. Origin is on the lateral tibia and interosseus membrane and inserts on the 1st cuniform and 1st metatarsal. Very palpatable muscle on anterior lateral foot. Inversion and dorsiflexion are the ...
Chapter 1 - UCLA Linguistics
... Without the action of inspiratory forces such as the external intercostals and the diaphragm, the lungs collapse back to their resting state. Normal expiration is entirely passive. The more the lungs are inflated, the greater their tendency to return to the resting position. This restoring force is ...
... Without the action of inspiratory forces such as the external intercostals and the diaphragm, the lungs collapse back to their resting state. Normal expiration is entirely passive. The more the lungs are inflated, the greater their tendency to return to the resting position. This restoring force is ...
Damage To The Plasma Membrane Of Rotator Cuff Muscle Fibers
... original anatomical footprint induces a massive stretch-induced injury to the muscle that could contribute to poor outcomes after repair. Damage to the muscle fiber sarcolemma (the plasma membrane of muscle fibers) results in a persistent influx of calcium molecules, which induce muscle spasm and ac ...
... original anatomical footprint induces a massive stretch-induced injury to the muscle that could contribute to poor outcomes after repair. Damage to the muscle fiber sarcolemma (the plasma membrane of muscle fibers) results in a persistent influx of calcium molecules, which induce muscle spasm and ac ...
Skull
... – Mastoid process prominent lump behind the earlobe • Filled with ear sinuses that communicate with the middle ear cavity • Can become infected (mastoiditis) and possible spread to the brain ...
... – Mastoid process prominent lump behind the earlobe • Filled with ear sinuses that communicate with the middle ear cavity • Can become infected (mastoiditis) and possible spread to the brain ...
The upper limb of Homo naledi (PDF Available)
... The evolutionary transition from an ape-like to human-like upper extremity occurred in the context of a behavioral shift from an upper limb predominantly involved in locomotion to one adapted for manipulation. Selection for overarm throwing and endurance running is thought to have further shaped mod ...
... The evolutionary transition from an ape-like to human-like upper extremity occurred in the context of a behavioral shift from an upper limb predominantly involved in locomotion to one adapted for manipulation. Selection for overarm throwing and endurance running is thought to have further shaped mod ...
The Cubital Fossa Bones of the Forearm
... Fractures of the olecranon process can result from a fall on the flexed elbow or from a direct blow. Depending on the location of the fracture line, the bony fragment may be displaced by the pull of the triceps muscle, which is inserted on the olecranon process (Fig. 9.10). Avulsion fractures of par ...
... Fractures of the olecranon process can result from a fall on the flexed elbow or from a direct blow. Depending on the location of the fracture line, the bony fragment may be displaced by the pull of the triceps muscle, which is inserted on the olecranon process (Fig. 9.10). Avulsion fractures of par ...
PTERYGOP2
... Pterygopalatine fossa. Brief description. The pterygopalatine fossa is a small space below the orbit that is shaped in a form of the inverted cone. It is located inferioly to the apex of the orbit and medial to the infratemporal fossa, between the root of the pterygoid plates and the infratemporal s ...
... Pterygopalatine fossa. Brief description. The pterygopalatine fossa is a small space below the orbit that is shaped in a form of the inverted cone. It is located inferioly to the apex of the orbit and medial to the infratemporal fossa, between the root of the pterygoid plates and the infratemporal s ...
Skeletal System
... • Ossification begins in the middle and radiates out • Ossification not complete at birth • Fontanels (soft spots): molding of head during birth and allow for brain growth ...
... • Ossification begins in the middle and radiates out • Ossification not complete at birth • Fontanels (soft spots): molding of head during birth and allow for brain growth ...
Chapter 11-Part 2-axial muscles
... • rectus abdominis • long, runs vertically entire length of abdominal wall from pubis (origin) to sternum (insertion) • four segments created by three tendinous intersections (form “six pack”) • enclosed in rectus sheath made by • aponeurosis of external oblique • internal oblique • transversus obdo ...
... • rectus abdominis • long, runs vertically entire length of abdominal wall from pubis (origin) to sternum (insertion) • four segments created by three tendinous intersections (form “six pack”) • enclosed in rectus sheath made by • aponeurosis of external oblique • internal oblique • transversus obdo ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.