Anatomical concepts of the musculoskeletal and peripheral nervous
... false ribs as floating ribs that are not directly attached to the sternum or those that lack contact with the sternum in front (Bakhtiar, 1999). Structurally the head of each rib has two articular facets for articulation with demi-facets on the vertebral bones (Bakhtiar, 1999, Gunn, 2012). Avicenna ...
... false ribs as floating ribs that are not directly attached to the sternum or those that lack contact with the sternum in front (Bakhtiar, 1999). Structurally the head of each rib has two articular facets for articulation with demi-facets on the vertebral bones (Bakhtiar, 1999, Gunn, 2012). Avicenna ...
The neurocranium is comprised of eight bones: occipital
... OCCIPITAL BONE The occipital bone is a trapezoidal, curvy-shaped bone located at the rear of the cranium. Like the other cranial bones, this bone protects the brain and supports the head (specifically the back of the head). It also contains a gap that allows the cranial cavity to communicate with th ...
... OCCIPITAL BONE The occipital bone is a trapezoidal, curvy-shaped bone located at the rear of the cranium. Like the other cranial bones, this bone protects the brain and supports the head (specifically the back of the head). It also contains a gap that allows the cranial cavity to communicate with th ...
Musculoskeletal System
... o Pus forming (Gram + Staph/Strep) o Treatment: surgical debridement o Problem due to increased pressure. o Pox Disease- Tuberculosis in the spine Diagnosis of Acute Osteomyelitis o Pus on aspiration o Positive bacterial culture from bone or blood o Presence of classic signs and symptoms of acute ...
... o Pus forming (Gram + Staph/Strep) o Treatment: surgical debridement o Problem due to increased pressure. o Pox Disease- Tuberculosis in the spine Diagnosis of Acute Osteomyelitis o Pus on aspiration o Positive bacterial culture from bone or blood o Presence of classic signs and symptoms of acute ...
THE SHORT DESCRIPTION OF THE JOINTS 1. THE UPPER LIMB
... abduction to about 90 degrees, because of the coracoacromial lig. More elevation of the arm is possible when the scapula rotates on the chest wall, and the glenoid cavity is elevated. The muscle responsible for it is the anterior serrate muscle. - around the transverse axis: anteflexion (60 degrees) ...
... abduction to about 90 degrees, because of the coracoacromial lig. More elevation of the arm is possible when the scapula rotates on the chest wall, and the glenoid cavity is elevated. The muscle responsible for it is the anterior serrate muscle. - around the transverse axis: anteflexion (60 degrees) ...
Emergency Department Radiography
... Take a history and examine before requesting a radiograph Request a radiograph only when necessary Never look at the radiograph without seeing the patient and never see the patient without reviewing the radiograph 5. Look at the radiograph, the whole radiograph and the radiograph as a whole in appro ...
... Take a history and examine before requesting a radiograph Request a radiograph only when necessary Never look at the radiograph without seeing the patient and never see the patient without reviewing the radiograph 5. Look at the radiograph, the whole radiograph and the radiograph as a whole in appro ...
Lecture 8 -Axillary & Median Nerves
... It passes downward and laterally along the posterior wall of the axilla, then it exit the axilla. Then, it passes posteriorly around the surgical neck of the humerus. It is accompanied by the posterior circumflex humeral vessels. Branches: Motor to the: Deltoid and teres minor muscles. Sensory: Supe ...
... It passes downward and laterally along the posterior wall of the axilla, then it exit the axilla. Then, it passes posteriorly around the surgical neck of the humerus. It is accompanied by the posterior circumflex humeral vessels. Branches: Motor to the: Deltoid and teres minor muscles. Sensory: Supe ...
Grip and Pinch
... b. A powerful movement used in many activities of daily living, such as pulling oneself out of a chair. c. requires functioning MCPJs and at least some amputation stumps of the proximal phalanges of the fingers. 2. Full grip a. requires flexion at all the interphalangeal joints, in some instances in ...
... b. A powerful movement used in many activities of daily living, such as pulling oneself out of a chair. c. requires functioning MCPJs and at least some amputation stumps of the proximal phalanges of the fingers. 2. Full grip a. requires flexion at all the interphalangeal joints, in some instances in ...
Spinal Anatomy - Circle of Docs
... c. Astrocytes d. Microglia 47. Which of the following ligaments prevents hyperextension of the back? a. Anterior longitudinal – hyperextension b. Posterior longitudinal – flexion c. Ligamentum flavum – flexion d. Supraspinous ligament – flexion 48. Which of the following ligaments is a continuation ...
... c. Astrocytes d. Microglia 47. Which of the following ligaments prevents hyperextension of the back? a. Anterior longitudinal – hyperextension b. Posterior longitudinal – flexion c. Ligamentum flavum – flexion d. Supraspinous ligament – flexion 48. Which of the following ligaments is a continuation ...
Femoral nerve
... Long sensory nerve to the medial knee Also includes the four motor branches to the quadriceps femoris heads Rectus femoris enters on the superior deep surface of the muscle Vastus lateralis enters on the lower part of that muscle with the lateral circumflex femoral artery Vastus medialis branch ...
... Long sensory nerve to the medial knee Also includes the four motor branches to the quadriceps femoris heads Rectus femoris enters on the superior deep surface of the muscle Vastus lateralis enters on the lower part of that muscle with the lateral circumflex femoral artery Vastus medialis branch ...
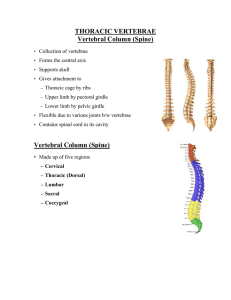
THORACIC VERTEBRAE
... • More or less cylindrical in shape. • Its upper and lower surfaces are flattened and rough • Give attachment to the intervertebral fibrocartilages ...
... • More or less cylindrical in shape. • Its upper and lower surfaces are flattened and rough • Give attachment to the intervertebral fibrocartilages ...
Muscles of the Posterior Compartment of the Forearm cont.
... lateral supracondylar peroneal division of ridge of femur sciatic nerve (L5, S1, and S2) *medial to lateral: semi-membranosis, semi-tendinosis, biceps femoris* Lines on the posterior side of the femus: ...
... lateral supracondylar peroneal division of ridge of femur sciatic nerve (L5, S1, and S2) *medial to lateral: semi-membranosis, semi-tendinosis, biceps femoris* Lines on the posterior side of the femus: ...
Cervical anatomy - Fisiokinesiterapia
... around the lateral mass of the atlas- tortuous course then perforates the dura of the posterior foramen magnum Ascends near falx cerebelli and divides near the torcula into several branches to supply the dura of the posterior part of the posterior fossa, and posterior tentorium, and posterior falx c ...
... around the lateral mass of the atlas- tortuous course then perforates the dura of the posterior foramen magnum Ascends near falx cerebelli and divides near the torcula into several branches to supply the dura of the posterior part of the posterior fossa, and posterior tentorium, and posterior falx c ...
Articulations (Joints) Chapter 8
... Stability is determined by: o Articular surfaces – shape determines what movements are possible o Ligaments – unite bones and prevent excessive or undesirable motion o Labrums and menisci that deepen the articular surface o Muscle tone is accomplished by: Muscle tendons across joints acting as sta ...
... Stability is determined by: o Articular surfaces – shape determines what movements are possible o Ligaments – unite bones and prevent excessive or undesirable motion o Labrums and menisci that deepen the articular surface o Muscle tone is accomplished by: Muscle tendons across joints acting as sta ...
An Introduction to Articulations
... Also called coxal joint Strong ball-and-socket diarthrosis Wide range of motion Structures of the Hip Joint Head of femur fits into it Socket of acetabulum Which is extended by fibrocartilaginous acetabular labrum ...
... Also called coxal joint Strong ball-and-socket diarthrosis Wide range of motion Structures of the Hip Joint Head of femur fits into it Socket of acetabulum Which is extended by fibrocartilaginous acetabular labrum ...
Anatomy of the Head, Neck, Face, and Jaws Lawrence
... fingerlike projection, the zygomatic process, which joins with the zygoma anteriorly to form the zygomatic arch. Immediately posterior to the root of the zygomatic process is a large opening into the depth of the bone. This opening is the entrance to the middle ear and is known as the external audit ...
... fingerlike projection, the zygomatic process, which joins with the zygoma anteriorly to form the zygomatic arch. Immediately posterior to the root of the zygomatic process is a large opening into the depth of the bone. This opening is the entrance to the middle ear and is known as the external audit ...
BIO 218 52999 F 2014 MTX 1 Q 140912.4
... Match the correct anatomical term from Skeleton Appendix of choices for the respective request. Choose the most Appropriate Column for your selection of answers. ...
... Match the correct anatomical term from Skeleton Appendix of choices for the respective request. Choose the most Appropriate Column for your selection of answers. ...
Skeletal System
... Neck – a narrowing that follows a head Tuberosity – point of ligament or muscle attachment, usually rough and convex Tubercle – a small tuberosity Foramen (pl. foramina) – hole Canal – a hole with a long tunnel Meatus – a large hole or gap Fissure – a hole or gap between bones that is elongate on th ...
... Neck – a narrowing that follows a head Tuberosity – point of ligament or muscle attachment, usually rough and convex Tubercle – a small tuberosity Foramen (pl. foramina) – hole Canal – a hole with a long tunnel Meatus – a large hole or gap Fissure – a hole or gap between bones that is elongate on th ...
Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
... Surgical neck – where the tubular shaft begins ; common fracture area Deltoid tuberosity - where the deltoid tendon attaches Capitulum - a round knob-like process on the lateral distal humerus Trochlea - medial to the capitulum, is a spool-shaped projection on the distal humerus Coronoid fossa - ant ...
... Surgical neck – where the tubular shaft begins ; common fracture area Deltoid tuberosity - where the deltoid tendon attaches Capitulum - a round knob-like process on the lateral distal humerus Trochlea - medial to the capitulum, is a spool-shaped projection on the distal humerus Coronoid fossa - ant ...
Anatomic variance of the coracoclavicular ligaments
... conoid ligament differed considerably between specimens. In all cases the conoid inserted at the posteriormost area of the coracoid dorsum, limited anteriorly by the insertion of the trapezoid ligament. Posteriorly, the attachment extended just beyond the angle of the coracoid to the top of the vert ...
... conoid ligament differed considerably between specimens. In all cases the conoid inserted at the posteriormost area of the coracoid dorsum, limited anteriorly by the insertion of the trapezoid ligament. Posteriorly, the attachment extended just beyond the angle of the coracoid to the top of the vert ...
Joints Notes
... 3 general types of movement: (most common types of movement allowed in fig 8.5 gliding movements- occur when relatively flat bone surfaces move back and forth and from side to side with respect to one another (glide or slip over each other, nonaxial) simplest joint motion, no significant alterat ...
... 3 general types of movement: (most common types of movement allowed in fig 8.5 gliding movements- occur when relatively flat bone surfaces move back and forth and from side to side with respect to one another (glide or slip over each other, nonaxial) simplest joint motion, no significant alterat ...
Proximal Humerus Fractures
... » AP: external rotation shows greater tub » AP: internal rotation, greater tub not seen ...
... » AP: external rotation shows greater tub » AP: internal rotation, greater tub not seen ...
Elbow Anatomy - PA
... through its own tunnel as it crosses the elbow. • Because the elbow must bend a great deal, the nerves must bend as well. • Constant bending and straightening can lead to irritation or pressure on the nerves within their tunnels and cause problems such as pain, numbness, and weakness in the arm and ...
... through its own tunnel as it crosses the elbow. • Because the elbow must bend a great deal, the nerves must bend as well. • Constant bending and straightening can lead to irritation or pressure on the nerves within their tunnels and cause problems such as pain, numbness, and weakness in the arm and ...
The Vertebral Column
... The sacral promontory, the anterosuperior margin of the first sacral vertebra, bulges into pelvic cavity. It is used as a landmark for obstetricians and the body’s center of gravity lies about 1 cm posterior to it ...
... The sacral promontory, the anterosuperior margin of the first sacral vertebra, bulges into pelvic cavity. It is used as a landmark for obstetricians and the body’s center of gravity lies about 1 cm posterior to it ...
Respiration: Anatomy
... – lordosis: swayback--caused by TB, poor posture, or prolonged wearing of excessively high heels. – scoliosis: abnormal lateral curvature--caused by muscle imbalance, poor posture, diet, paralysis. ...
... – lordosis: swayback--caused by TB, poor posture, or prolonged wearing of excessively high heels. – scoliosis: abnormal lateral curvature--caused by muscle imbalance, poor posture, diet, paralysis. ...
Skull Base Anatomy
... • Anterior clinoid processes: rounded ends of the lesser wings, serve as a place of attachment for the tentorium cerebelli (a sheet of dura mater that divides the cerebrum from the cerebellum) ...
... • Anterior clinoid processes: rounded ends of the lesser wings, serve as a place of attachment for the tentorium cerebelli (a sheet of dura mater that divides the cerebrum from the cerebellum) ...
Scapula
In anatomy, the scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas) or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones the scapulae are paired, with the scapula on the left side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the right scapula. In early Roman times, people thought the bone resembled a trowel, a small shovel. The shoulder blade is also called omo in Latin medical terminology.The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage.