Animals - Petal School District
... Ex: lampreys and hagfishes (are the only ones) Chondrichthyes - Cartilaginous fish Ex: sharks, skates, rays Osteichthyes - Bony fish—Have a swim bladder Ex: Bass, trout, goldfish ...
... Ex: lampreys and hagfishes (are the only ones) Chondrichthyes - Cartilaginous fish Ex: sharks, skates, rays Osteichthyes - Bony fish—Have a swim bladder Ex: Bass, trout, goldfish ...
Some General Features of Animals
... ribcage). • Turtles, lizards and snakes, tuataras, and crocodiles. (pp. 714-718) • What are the components of the amniotic egg? ...
... ribcage). • Turtles, lizards and snakes, tuataras, and crocodiles. (pp. 714-718) • What are the components of the amniotic egg? ...
File
... 5. Do human body systems work independently of each other? Why or why not, explain. No, human body systems work with other systems in order to maintain homeostasis. For example, the skeletal system could not move without the muscles. Muscles help to protect the bones and they connect bones using li ...
... 5. Do human body systems work independently of each other? Why or why not, explain. No, human body systems work with other systems in order to maintain homeostasis. For example, the skeletal system could not move without the muscles. Muscles help to protect the bones and they connect bones using li ...
Introduction to the Body
... body temp. drops sharply (stimulus), detected by your hypothalamus (receptor), your brain (control center) sends nerve impulses (output) to your skeletal muscles (effectors). Results in shivering to generate heat to raise your body temp. ...
... body temp. drops sharply (stimulus), detected by your hypothalamus (receptor), your brain (control center) sends nerve impulses (output) to your skeletal muscles (effectors). Results in shivering to generate heat to raise your body temp. ...
Largest phylum on earth Examples: spiders, ticks
... -Small Intestine – Absorbs nutrients and sends undigested food to LI -Fat Bodies-Fat source for frog during hibernation -Kidney –Produces and excretes Urine -Spleen—Stores and purifies blood -Heart- pumps blood throughout the body -Lungs- Takes in Oxygen and distributes to blood ...
... -Small Intestine – Absorbs nutrients and sends undigested food to LI -Fat Bodies-Fat source for frog during hibernation -Kidney –Produces and excretes Urine -Spleen—Stores and purifies blood -Heart- pumps blood throughout the body -Lungs- Takes in Oxygen and distributes to blood ...
Unit 10: Classification
... soft bodies divided into 4 parts: 1) ______________ contains digestive and excretory organs, and the heart 2) ____________ fleshy layer covering __________________ secretes ______________ 3) ____________ usually located on the _____________ side may be modified in different mollusks for ...
... soft bodies divided into 4 parts: 1) ______________ contains digestive and excretory organs, and the heart 2) ____________ fleshy layer covering __________________ secretes ______________ 3) ____________ usually located on the _____________ side may be modified in different mollusks for ...
Mollusks - SattlerScience
... symmetry and usually one or two shells with organs in a fluid-filled cavity. ...
... symmetry and usually one or two shells with organs in a fluid-filled cavity. ...
2016 - كلية طب الاسنان
... The subcutaneous tissue is a layer of fat and connective tissue that houses larger blood vessels and nerves. This layer is important in the regulation of the temperature of the skin itself and the body. The size of this layer varies throughout the body and from person to person. ...
... The subcutaneous tissue is a layer of fat and connective tissue that houses larger blood vessels and nerves. This layer is important in the regulation of the temperature of the skin itself and the body. The size of this layer varies throughout the body and from person to person. ...
Levels of Organization Notes
... 39 All of the following are types of tissue except: A muscle B epithelial ...
... 39 All of the following are types of tissue except: A muscle B epithelial ...
Vertebrates
... bodies, and had no well-developed vertebral column. Lampreys are parasites. Chondrichthyes means cartilage fish. Cartilaginous fishes have spiracles, internal fertilization, and gill slits. Eggs of sharks are fertilized internally. Eggs of many species of sharks hatch inside the mother’s body, where ...
... bodies, and had no well-developed vertebral column. Lampreys are parasites. Chondrichthyes means cartilage fish. Cartilaginous fishes have spiracles, internal fertilization, and gill slits. Eggs of sharks are fertilized internally. Eggs of many species of sharks hatch inside the mother’s body, where ...
Phylum Chordate
... Skeleton mostly made of cartilage Have scales made of dentin Excellent sense of smell ...
... Skeleton mostly made of cartilage Have scales made of dentin Excellent sense of smell ...
Chordates and Fishes
... Scales limit chemical exchanges through the skin; exchanges occur through the membranes of the gills: the external respiratory organs Lateral line system: consists of a row of sensory structures that run the length of the body and connected by nerves to the brain; detects vibrations ...
... Scales limit chemical exchanges through the skin; exchanges occur through the membranes of the gills: the external respiratory organs Lateral line system: consists of a row of sensory structures that run the length of the body and connected by nerves to the brain; detects vibrations ...
Virtual dissection website: http://www.froguts.com/flash_content
... color, if you have a particularly fat frog, these fat bodies may need to be removed to see the other structures. Usually they are located just on the inside of the abdominal wall. Peritoneum A spider web like membrane that covers many of the organs, you may have to carefully pick it off to get a cle ...
... color, if you have a particularly fat frog, these fat bodies may need to be removed to see the other structures. Usually they are located just on the inside of the abdominal wall. Peritoneum A spider web like membrane that covers many of the organs, you may have to carefully pick it off to get a cle ...
Bio212LabPract2StudyGuideWi2012_000
... functions and locations. Use Google when needed. Class Mammalia: Anatomy of a pig know the following structures trachea right and left atrium, ventricles = heart lungs diaphragm liver stomach pancreas small & large intestine kidneys urinary bladder umbilical cord ...
... functions and locations. Use Google when needed. Class Mammalia: Anatomy of a pig know the following structures trachea right and left atrium, ventricles = heart lungs diaphragm liver stomach pancreas small & large intestine kidneys urinary bladder umbilical cord ...
Definitions - Harris Training Institute, Inc.
... Sensory Organs - receive impulses from environment and relay impulses to brain including skin, tongue, nose, eyes, and ears Spinal Cord – located within the spine, connected to the brain and conducts messages between the brain and the body by pathways Cardiovascular System Anemia – low red blood cel ...
... Sensory Organs - receive impulses from environment and relay impulses to brain including skin, tongue, nose, eyes, and ears Spinal Cord – located within the spine, connected to the brain and conducts messages between the brain and the body by pathways Cardiovascular System Anemia – low red blood cel ...
PracticeExam_Phys - Napa Valley College
... – Echinoderms: seastars, urchins, etc – Chordates: notochord, tail past anus, dorsal nerve chord, pharyngeal slits • Vertebrates- increasingly adapted for land – Amphibians: poorly developed lung, can breath through skin – Reptiles: First amniotes (produce egg with hard shell), protective scales, fe ...
... – Echinoderms: seastars, urchins, etc – Chordates: notochord, tail past anus, dorsal nerve chord, pharyngeal slits • Vertebrates- increasingly adapted for land – Amphibians: poorly developed lung, can breath through skin – Reptiles: First amniotes (produce egg with hard shell), protective scales, fe ...
Introduction to Kingdom Animalia
... • The Bilateria are triploblastic; in addition to the ectoderm and endoderm they produce a third germ layer, the mesoderm • Mesoderm - germ layer between the ectoderm and the endoderm; gives rise to muscles and to most other organs ...
... • The Bilateria are triploblastic; in addition to the ectoderm and endoderm they produce a third germ layer, the mesoderm • Mesoderm - germ layer between the ectoderm and the endoderm; gives rise to muscles and to most other organs ...
The Respiratory System
... large network of capillaries. It is through these capillaries that gas exchange takes place. Capillaries are also connected to the circulatory system. This is a good thing because the body needs the blood in it to transport the oxygen and carbon dioxide around the body. The inspiration and exhalatio ...
... large network of capillaries. It is through these capillaries that gas exchange takes place. Capillaries are also connected to the circulatory system. This is a good thing because the body needs the blood in it to transport the oxygen and carbon dioxide around the body. The inspiration and exhalatio ...
Introduction to Animal Evolution What is an animal?
... Describe at least two functions of amoebocytes. How would you describe the feeding strategy? • No gastrulation occurs during development; no true tissues If sponges have no muscle or nerve tissues, how do they accomplish movement of water into the spongocoel? ...
... Describe at least two functions of amoebocytes. How would you describe the feeding strategy? • No gastrulation occurs during development; no true tissues If sponges have no muscle or nerve tissues, how do they accomplish movement of water into the spongocoel? ...
Body Systems - Science
... soft tissue called red marrow. • Major quantities of calcium and phosphorous compounds are stored in the skeleton for later use. Calcium and phosphorus make bones hard ...
... soft tissue called red marrow. • Major quantities of calcium and phosphorous compounds are stored in the skeleton for later use. Calcium and phosphorus make bones hard ...
Zoology - Edublogs
... on land, all animals respire, which means they take in oxygen and give off carbon dioxide. – Some can rely on diffusion of these substances through their skin – Most have evolved complex tissues and organ systems for respiration ...
... on land, all animals respire, which means they take in oxygen and give off carbon dioxide. – Some can rely on diffusion of these substances through their skin – Most have evolved complex tissues and organ systems for respiration ...
Wild Structure
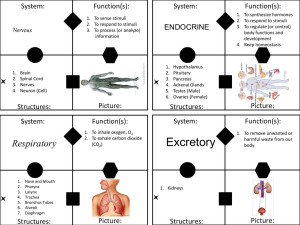
... 1. To synthesize hormones 2. To respond to stimuli 3. To regulate (or control) body functions and development 4. Keep homeostasis ...
... 1. To synthesize hormones 2. To respond to stimuli 3. To regulate (or control) body functions and development 4. Keep homeostasis ...
Study questions - test 2 Excretory systems ch.42 Digestion ch.43
... 7) various types of circulatory systems, and the types of organisms that they are found in... 8) what are the differences between open and closed circulatory systems? 9) tetrapods -- differences in circulatory systems... 10) what is double circulation? • what problem does this solve? • how is this r ...
... 7) various types of circulatory systems, and the types of organisms that they are found in... 8) what are the differences between open and closed circulatory systems? 9) tetrapods -- differences in circulatory systems... 10) what is double circulation? • what problem does this solve? • how is this r ...
Life Science TEST REVIEW: NEXT WED IS SECOND SECTION OF periodic assessment Warm-up:
... skeleton (40% of an adult body weight and work in pairs). These muscles are the ones you see and exercise. (voluntary) Smooth Muscle: makes up the walls of your internal organs (involuntary). Cardiac muscle is muscle found only in the heart. This muscle tissue is called myocardium (involuntary) ...
... skeleton (40% of an adult body weight and work in pairs). These muscles are the ones you see and exercise. (voluntary) Smooth Muscle: makes up the walls of your internal organs (involuntary). Cardiac muscle is muscle found only in the heart. This muscle tissue is called myocardium (involuntary) ...
ARTHROPODS - Bishop Shanahan High School
... INSECTS TO SPREAD OUT 3 BODY REGIONS: head; thorax; abdomen 3 PAIRS OF LEGS ON THORAX: walking; jumping; hold food 1 ANTENNAE 1 PAIR OF COMPOUND EYES: many lenses ...
... INSECTS TO SPREAD OUT 3 BODY REGIONS: head; thorax; abdomen 3 PAIRS OF LEGS ON THORAX: walking; jumping; hold food 1 ANTENNAE 1 PAIR OF COMPOUND EYES: many lenses ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.