Structures
... pharynx, larynx, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small and large intestines, Function: Breaks down foods into simple molecules that can be used by the body for respiration and building cells ...
... pharynx, larynx, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small and large intestines, Function: Breaks down foods into simple molecules that can be used by the body for respiration and building cells ...
Chapter 2
... articulate- To fit into each other fracture- A break in the bone skeletal (voluntary) muscle- Muscle that is under direct voluntary control of the brain smooth muscle- The muscles found in the walls of the internal organs and blood vessels, generally not under voluntary control involuntary muscle- S ...
... articulate- To fit into each other fracture- A break in the bone skeletal (voluntary) muscle- Muscle that is under direct voluntary control of the brain smooth muscle- The muscles found in the walls of the internal organs and blood vessels, generally not under voluntary control involuntary muscle- S ...
Anatomical Terminology
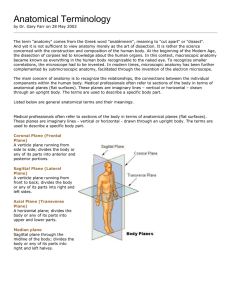
... And yet it is not sufficient to view anatomy merely as the art of dissection. It is rather the science concerned with the construction and composition of the human body. At the beginning of the Modern Age, the dissection of corpses led to knowledge about the human organs. In this context, macroscopi ...
... And yet it is not sufficient to view anatomy merely as the art of dissection. It is rather the science concerned with the construction and composition of the human body. At the beginning of the Modern Age, the dissection of corpses led to knowledge about the human organs. In this context, macroscopi ...
Parade of Kingdoms musical chairs
... in an early _____________ embryo, the resulting organism will be missing body parts and will not survive. PROTOSTOME ...
... in an early _____________ embryo, the resulting organism will be missing body parts and will not survive. PROTOSTOME ...
Galen - The British Empire
... – Pigs, dogs and Barbary Apes • Made some serious mistakes in describing Human Anatomy – Eg Only two chambers in Heart ...
... – Pigs, dogs and Barbary Apes • Made some serious mistakes in describing Human Anatomy – Eg Only two chambers in Heart ...
Revision Sheet Quarter 1 2014-2015 Department:
... 6.Which term describes the type of digestion that results from chewing and crushing food into smaller pieces? A. absorption B. peristalsis C.chemical digestion D.mechanical digestion 7. In the female reproductive system, which structure is most important in protecting and nourishing the embryo duri ...
... 6.Which term describes the type of digestion that results from chewing and crushing food into smaller pieces? A. absorption B. peristalsis C.chemical digestion D.mechanical digestion 7. In the female reproductive system, which structure is most important in protecting and nourishing the embryo duri ...
Bio chapter 30 ppt
... An organ system is a group of organs that perform closely related functions. An example of an organ system is the brain and spinal cord, these two are organs of nervous system. The organ systems interact to maintain homeostasis in the body as a whole. ...
... An organ system is a group of organs that perform closely related functions. An example of an organ system is the brain and spinal cord, these two are organs of nervous system. The organ systems interact to maintain homeostasis in the body as a whole. ...
Introduction to Physiology The Human Body
... function (epithelia, connective, muscle and nervous). 3- Organ: An organ is a structure consisting of a group of tissues that perform a specialized function (skin, heart, brain, etc…). 4- System: A system is a group of organs that act together to perform a specialized function. a. cardiovascular sys ...
... function (epithelia, connective, muscle and nervous). 3- Organ: An organ is a structure consisting of a group of tissues that perform a specialized function (skin, heart, brain, etc…). 4- System: A system is a group of organs that act together to perform a specialized function. a. cardiovascular sys ...
Phylum Platyhelminthes
... One planarian can learn to pass through a maze by eating another one that already knows the way!!!!! ...
... One planarian can learn to pass through a maze by eating another one that already knows the way!!!!! ...
Science - Respiratory System
... Capillary: a tiny blood vessel Corpuscle: an unattached body cell Diaphragm: a thin sheet of muscle just below the lungs (breathing always starts with the diaphragm) Larynx: also called the voice box, a part of the body that holds the vocal cords. Template © 2012, Core Knowledge Foundation. All righ ...
... Capillary: a tiny blood vessel Corpuscle: an unattached body cell Diaphragm: a thin sheet of muscle just below the lungs (breathing always starts with the diaphragm) Larynx: also called the voice box, a part of the body that holds the vocal cords. Template © 2012, Core Knowledge Foundation. All righ ...
Connor P Body Exhibit Interactive Activity
... Tissues for getting carbon dioxide out are cardiac, lung, epithelial, and blood. Organs for getting nutrients are stomach, bloodstream, mouth, small intestine, large intestine, and heart. Organs for getting in oxygen are heart and lungs. The organs to getting rid of liquid waste are kidney, heart, a ...
... Tissues for getting carbon dioxide out are cardiac, lung, epithelial, and blood. Organs for getting nutrients are stomach, bloodstream, mouth, small intestine, large intestine, and heart. Organs for getting in oxygen are heart and lungs. The organs to getting rid of liquid waste are kidney, heart, a ...
Document
... • Water Vascular System - network of fluid-filled canals that function in locomotion, feeding, and gas exchange. • Branches of the WVS become extended when filled with fluid (tube feet) • Ampulla - round muscular sac at the base of the foot, stores fluid and operates tube foot • Well developed coelo ...
... • Water Vascular System - network of fluid-filled canals that function in locomotion, feeding, and gas exchange. • Branches of the WVS become extended when filled with fluid (tube feet) • Ampulla - round muscular sac at the base of the foot, stores fluid and operates tube foot • Well developed coelo ...
Introduction to animals
... 1. Simple skeletons (sponges) 2. Fluid-filled body cavity (roundworms) ...
... 1. Simple skeletons (sponges) 2. Fluid-filled body cavity (roundworms) ...
DEFENSE - muscular and skeletal systems 14-15
... Skeletal Body System Interactions: • Circulatory System: bones help produce new blood cells in addition to storing minerals transported by the circulatory system. • Muscular System: bones and muscles work in opposing pairs to perform body movement. Muscles and bones support, protect, and maintain p ...
... Skeletal Body System Interactions: • Circulatory System: bones help produce new blood cells in addition to storing minerals transported by the circulatory system. • Muscular System: bones and muscles work in opposing pairs to perform body movement. Muscles and bones support, protect, and maintain p ...
Insight - Human Body Systems
... support the transport of materials. Students know how blood circulates through the heart chambers, lungs, and body and how carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen (O2) are exchanged in the lungs and tissues. Students know how blood circulates through the heart chambers, lungs, and body and how carbon dioxid ...
... support the transport of materials. Students know how blood circulates through the heart chambers, lungs, and body and how carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen (O2) are exchanged in the lungs and tissues. Students know how blood circulates through the heart chambers, lungs, and body and how carbon dioxid ...
Topic 10 BIOL1030NR
... IV. Subkingdom Parazoa – Phylum Porifera - the sponges A. actually appears to be a grade ...
... IV. Subkingdom Parazoa – Phylum Porifera - the sponges A. actually appears to be a grade ...
Topic 10 BIOL1030NR
... Subkingdom Parazoa – Phylum Porifera - the sponges A. actually appears to be a grade ...
... Subkingdom Parazoa – Phylum Porifera - the sponges A. actually appears to be a grade ...
Chapter 3
... o The headquarters of the human nervous system. o Divided into the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. Spinal cord o Soft column of nerve tissue continuous with the lower part of the brain. o Enclosed in the bony vertebral column. o It is vulnerable to injury. o Damage to the spinal cord is almo ...
... o The headquarters of the human nervous system. o Divided into the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. Spinal cord o Soft column of nerve tissue continuous with the lower part of the brain. o Enclosed in the bony vertebral column. o It is vulnerable to injury. o Damage to the spinal cord is almo ...
File - Northwoods 5th Grade
... senses, thinking, imagining… 72.Dendrites – part of a neuron that brings information to the cell body 73.Nerves – bundle of fibers that send messages from the brain to other parts of the body 74. Neurons – specialized, impulse-conducting cells (made of cell body, axon, and dendrites). 75.Peripheral ...
... senses, thinking, imagining… 72.Dendrites – part of a neuron that brings information to the cell body 73.Nerves – bundle of fibers that send messages from the brain to other parts of the body 74. Neurons – specialized, impulse-conducting cells (made of cell body, axon, and dendrites). 75.Peripheral ...
Summary
... perform the same essential tasks: feeding and digestion, respiration, circulation, excretion, response, movement and support, and reproduction. Feeding The simplest animals—sponges—break down food inside their cells. Mollusks, annelids, arthropods, and echinoderms use extracellular digestion. Food i ...
... perform the same essential tasks: feeding and digestion, respiration, circulation, excretion, response, movement and support, and reproduction. Feeding The simplest animals—sponges—break down food inside their cells. Mollusks, annelids, arthropods, and echinoderms use extracellular digestion. Food i ...
Simple Animals
... Coral is actually a colony of polyps, most of which are the size of a single hydra – they just make a case around them for their home. ...
... Coral is actually a colony of polyps, most of which are the size of a single hydra – they just make a case around them for their home. ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.