The spinal nerves that constitute the lumbosacral plexus and their
... nerves was not the same owing to the different number of vertebrae in each species. The LSP formation was totally different from those reported for the rat22, agouti29 and porcupine4. A common nerve root was found in the LPS that gives rise to the nerves innervating the posterior limbs of the chinch ...
... nerves was not the same owing to the different number of vertebrae in each species. The LSP formation was totally different from those reported for the rat22, agouti29 and porcupine4. A common nerve root was found in the LPS that gives rise to the nerves innervating the posterior limbs of the chinch ...
File
... various regions of its wall and also due to its rotation around a longitudinal and anteroposterior axis. The stomach rotates 90° in clockwise direction around its longitudinal axis, thus its Lt. side becomes anterior and its Rt. Side becomes posterior. Simultaneously its nerves also change their pos ...
... various regions of its wall and also due to its rotation around a longitudinal and anteroposterior axis. The stomach rotates 90° in clockwise direction around its longitudinal axis, thus its Lt. side becomes anterior and its Rt. Side becomes posterior. Simultaneously its nerves also change their pos ...
Specific characteristics of innervation of gluteal muscles in the
... fetuses and 5 newborns in the area of its inferiorsuperior angle, is divided into superior and inferior stems, goes from the superior gluteal nerve to the exterior surface of the musculus gluteus minimus. Superior small trunk goes parallel to the superior margin of the musculus gluteus minimus herew ...
... fetuses and 5 newborns in the area of its inferiorsuperior angle, is divided into superior and inferior stems, goes from the superior gluteal nerve to the exterior surface of the musculus gluteus minimus. Superior small trunk goes parallel to the superior margin of the musculus gluteus minimus herew ...
A 42-year-old man visits his doctor after his cousin, who has not
... nerves has most likely been affected? A. Anterior interosseous nerve B. Median nerve C. Musculocutaneous nerve D. Radial nerve E. Ulnar nerve Explanation: The correct answer is B. This patient has acromegaly, which is characterized by overgrowth of the face, jaws, hands, and feet, enlargement of int ...
... nerves has most likely been affected? A. Anterior interosseous nerve B. Median nerve C. Musculocutaneous nerve D. Radial nerve E. Ulnar nerve Explanation: The correct answer is B. This patient has acromegaly, which is characterized by overgrowth of the face, jaws, hands, and feet, enlargement of int ...
– FINAL EXAM REVIEW LIVING ANATOMY Suprasternal notch
... o Patient prone. Place your partner’s hand in the small of his back to raise the medial border off the ribs. For more exposure, scoop and raise the shoulder with one hand. o Locate the spine of the scapula and glide your fingertips medially until they slide off the spine onto the medial border. o Fo ...
... o Patient prone. Place your partner’s hand in the small of his back to raise the medial border off the ribs. For more exposure, scoop and raise the shoulder with one hand. o Locate the spine of the scapula and glide your fingertips medially until they slide off the spine onto the medial border. o Fo ...
A. Paired bones of the braincase
... The ventral nasal concha is attached to the conchal crest on the medial wall of the maxilla. It is formed of primary and secondary bony scrolls. The space between the conchae and the nasal septum is the common meatus, whereas the space dorsal to the conchae is the middle meatus and the space ventral ...
... The ventral nasal concha is attached to the conchal crest on the medial wall of the maxilla. It is formed of primary and secondary bony scrolls. The space between the conchae and the nasal septum is the common meatus, whereas the space dorsal to the conchae is the middle meatus and the space ventral ...
Head_and_Neck_annotation
... Arterial supply to: deep neck, cervical spinal cord, spinal cord; medulla (dorsal motor nucleus of cranial nerve X, nucleus ambiguus, spinal accessory nucleus and hypoglossal nucleus) Anastomoses with the internal carotid artery in the cerebral arterial circle (of ...
... Arterial supply to: deep neck, cervical spinal cord, spinal cord; medulla (dorsal motor nucleus of cranial nerve X, nucleus ambiguus, spinal accessory nucleus and hypoglossal nucleus) Anastomoses with the internal carotid artery in the cerebral arterial circle (of ...
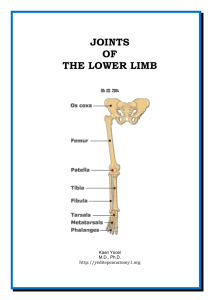
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Joints of the lower limb
... The joint capsule is strengthened by anterior and posterior ligaments of the fibular head, which pass superomedially from the fibular head to the lateral tibial condyle. 7. Movements of the knee joint Slight movement of the joint occurs during dorsiflexion of the foot as a result of wedging of the t ...
... The joint capsule is strengthened by anterior and posterior ligaments of the fibular head, which pass superomedially from the fibular head to the lateral tibial condyle. 7. Movements of the knee joint Slight movement of the joint occurs during dorsiflexion of the foot as a result of wedging of the t ...
Applied Endoscopic Anatomical Evaluation of the Lacrimal Sac
... cheek (3). Balloon dilatation, external DCR and, more recently, endoscopic DCR, with or without silicone tubes, are performed to correct these obstructions (4–6). An anatomical evaluation is necessary for close surgical approach through the nose. Knowledge of the anatomy of the lacrimal apparatus wi ...
... cheek (3). Balloon dilatation, external DCR and, more recently, endoscopic DCR, with or without silicone tubes, are performed to correct these obstructions (4–6). An anatomical evaluation is necessary for close surgical approach through the nose. Knowledge of the anatomy of the lacrimal apparatus wi ...
Median and anterior interosseous nerve entrapment syndromes
... sleeping. She would sleep with her elbow flexed and forearm pronated. To relieve her symptoms, she would stretch her right arm. The stretch, as demonstrated by the patient, consisted of abduction of the arm to 90 degrees, external rotation of the arm, complete supination of the forearm and extension ...
... sleeping. She would sleep with her elbow flexed and forearm pronated. To relieve her symptoms, she would stretch her right arm. The stretch, as demonstrated by the patient, consisted of abduction of the arm to 90 degrees, external rotation of the arm, complete supination of the forearm and extension ...
Anatomy and pathology of the aging spine1
... ossified vertebral rims of two adjacent vertebrae. In these places the collagenous fibers penetrate into the bony structure as Sharpey’s fibers. This special configuration of the fibers is particularly suitable for compensation of shear forces. The fibers additionally take care of the forces transmi ...
... ossified vertebral rims of two adjacent vertebrae. In these places the collagenous fibers penetrate into the bony structure as Sharpey’s fibers. This special configuration of the fibers is particularly suitable for compensation of shear forces. The fibers additionally take care of the forces transmi ...
25-autonomic supply of head & neck
... • Beginning: At the base of the skull, as the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion • Termination: It passes in front of the neck of first rib, and becomes continuous with the thoracic part of sympathetic trunk • Course and relations: 1. It descends, behind the carotid sheath (separating it from co ...
... • Beginning: At the base of the skull, as the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion • Termination: It passes in front of the neck of first rib, and becomes continuous with the thoracic part of sympathetic trunk • Course and relations: 1. It descends, behind the carotid sheath (separating it from co ...
The "Unseen" Posterior Intermeniscal Ligament of the Knee
... similar findings in the posterior horns of the menisci although a bucket handle tear had been ruled out ( Fig. 8 on page 8 ). ...
... similar findings in the posterior horns of the menisci although a bucket handle tear had been ruled out ( Fig. 8 on page 8 ). ...
Perineum - gmch.gov.in
... • Placed between two ischiopubic rami • In male contains urethra enclosed by root of penis, scrotum • In females contains urethral and vaginal orifice & female external genitalia • Three membranes • Two spaces ...
... • Placed between two ischiopubic rami • In male contains urethra enclosed by root of penis, scrotum • In females contains urethral and vaginal orifice & female external genitalia • Three membranes • Two spaces ...
Mammals. By WK Gregory..................................... 515
... The palheontological collections of the world contain great numbers of fossil skeletons which have been described minutely and accurately, but seldom with any detailed reference to the muscles that once moved them. In general, comparative osteology and palheontology are treated in one set of works a ...
... The palheontological collections of the world contain great numbers of fossil skeletons which have been described minutely and accurately, but seldom with any detailed reference to the muscles that once moved them. In general, comparative osteology and palheontology are treated in one set of works a ...
Skull
... (1). Point of intersection of frontal, parietal, sphenoid, & temporal (2). Clinically important because a branch of the middle meningeal a. runs in an internal calvarial groove that crosses pterion; fractures at pterion may tear the artery & result in extradural hematoma F. Internal surface of skull ...
... (1). Point of intersection of frontal, parietal, sphenoid, & temporal (2). Clinically important because a branch of the middle meningeal a. runs in an internal calvarial groove that crosses pterion; fractures at pterion may tear the artery & result in extradural hematoma F. Internal surface of skull ...
I The head
... 3. In the successive transverse sections of brain,tell the morphous chandes of cerebral falx from superior to inferior. 4. In the sections along Raid baseline from superior to inferior,tell the morphous chandes and significance of tentorium of cerebellum. 5. Describe the variation of position betwee ...
... 3. In the successive transverse sections of brain,tell the morphous chandes of cerebral falx from superior to inferior. 4. In the sections along Raid baseline from superior to inferior,tell the morphous chandes and significance of tentorium of cerebellum. 5. Describe the variation of position betwee ...
PTHY 6401 Kinesiology I Lab
... palpated on each side of the notch. Movement at the joint can be palpated during elevation/depression or protraction/retraction of the scapulae and clavicles. The clavicles are notably curved with the anterior surface convex medially and concave laterally (the opposite is true of the posterior surfa ...
... palpated on each side of the notch. Movement at the joint can be palpated during elevation/depression or protraction/retraction of the scapulae and clavicles. The clavicles are notably curved with the anterior surface convex medially and concave laterally (the opposite is true of the posterior surfa ...
03 Wysocki.p65
... 3 parts: petrous, tympanic and squamous. The squamous part is relatively small. However the petrous and the tympanic parts are quite considerable in size. Measurements of the selected parameters characterising the temporal bone are presented in Table 1. The greatest air space of the guinea pig tempo ...
... 3 parts: petrous, tympanic and squamous. The squamous part is relatively small. However the petrous and the tympanic parts are quite considerable in size. Measurements of the selected parameters characterising the temporal bone are presented in Table 1. The greatest air space of the guinea pig tempo ...
HERNIA
... abdominal and pelvic wall. In such case all visceral organs covered by parietal peritoneum and skin are not damaged. Internal hernia is such disease, visceral organs hit the peritoneum pouch. It formed in the place of natural peritoneum fold or recess and generally kept in the abdominal cavity. ...
... abdominal and pelvic wall. In such case all visceral organs covered by parietal peritoneum and skin are not damaged. Internal hernia is such disease, visceral organs hit the peritoneum pouch. It formed in the place of natural peritoneum fold or recess and generally kept in the abdominal cavity. ...
The evolution of the skull and the cephalic muscles
... The reasons for this conclusion will be found in the text, but, apart from the circumstantial evidence specifically applicable to each case, there is collateral evidence of a quite general kind in support. The wide variation observable in the muscles of the vertebrates justifies the belief that "mus ...
... The reasons for this conclusion will be found in the text, but, apart from the circumstantial evidence specifically applicable to each case, there is collateral evidence of a quite general kind in support. The wide variation observable in the muscles of the vertebrates justifies the belief that "mus ...
Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin
... towards the midline of the body, or towards the midline of a limb. Dropping the arms to the sides, or bringing the knees together, are examples of adduction. In the case of the fingers or toes, adduction is closing the digits together. ...
... towards the midline of the body, or towards the midline of a limb. Dropping the arms to the sides, or bringing the knees together, are examples of adduction. In the case of the fingers or toes, adduction is closing the digits together. ...
Cranial Fossa
... internal carotid artery, to the orbit. *The superior orbital fissure which is a Slit-like opening between the lesser and the greater wings of the sphenoid, transmits the lacrimal, frontal, trochlear, oculomotor, nasociliary, and abducent nerves, together with the superior ophthalmic vein. The spheno ...
... internal carotid artery, to the orbit. *The superior orbital fissure which is a Slit-like opening between the lesser and the greater wings of the sphenoid, transmits the lacrimal, frontal, trochlear, oculomotor, nasociliary, and abducent nerves, together with the superior ophthalmic vein. The spheno ...
Anatomy of Orbit
... predominance of lacrimal bone, while a more posteriorly placed suture line indicates a predominance of maxillary bone in the anastomotic relationship. The lacrimal bone at the level of lacrimal fossa is pretty thin (106 micrometer). This bone can be easily penetrated during dacryocystorhinostomy sur ...
... predominance of lacrimal bone, while a more posteriorly placed suture line indicates a predominance of maxillary bone in the anastomotic relationship. The lacrimal bone at the level of lacrimal fossa is pretty thin (106 micrometer). This bone can be easily penetrated during dacryocystorhinostomy sur ...
Practice Exam for Anatomy Exam 3 Two types of movements occur
... 64. An avid golfer comes to your clinic with pain over his medial epicondyle. You diagnose him with medial epicondylitis or “golfer’s elbow.” He has a valgus stress overuse injury of the _________ group a. Flexor-supinator b. Flexor-pronator c. Extensor-supinator d. Extensor-pronator 65. A patient h ...
... 64. An avid golfer comes to your clinic with pain over his medial epicondyle. You diagnose him with medial epicondylitis or “golfer’s elbow.” He has a valgus stress overuse injury of the _________ group a. Flexor-supinator b. Flexor-pronator c. Extensor-supinator d. Extensor-pronator 65. A patient h ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.