MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY Muscles of the
... Obturator externus: flat, triangular muscle, which covers outer surface of the anterior wall of pelvis; rotates the femur outward; extends the femur, supports knee in the extended position ...
... Obturator externus: flat, triangular muscle, which covers outer surface of the anterior wall of pelvis; rotates the femur outward; extends the femur, supports knee in the extended position ...
Health Related Fitness Study Guide
... 4. Flexibility: The ability to use your joints fully through a wide range of motion. You are flexible when your muscles are long enough and your joints are free enough to allow movement. People with good flexibility have fewer sore or injured muscles. 5. % Body Fat: The percentage of weight that is ...
... 4. Flexibility: The ability to use your joints fully through a wide range of motion. You are flexible when your muscles are long enough and your joints are free enough to allow movement. People with good flexibility have fewer sore or injured muscles. 5. % Body Fat: The percentage of weight that is ...
March 11, 2016 Please Do Now
... What type of muscles can you control? A type of muscle you can control is called a ______________ muscle. ...
... What type of muscles can you control? A type of muscle you can control is called a ______________ muscle. ...
Knee Unit Worksheets
... 12-18. ( Illustration taken from http://www.exrx.net/Lists/Directory.html on April 25, 2008 ExRx.net Exercise & Muscle Directory) and to the illustrations at the bottom left & right for questions 19 and 20 respectively. ...
... 12-18. ( Illustration taken from http://www.exrx.net/Lists/Directory.html on April 25, 2008 ExRx.net Exercise & Muscle Directory) and to the illustrations at the bottom left & right for questions 19 and 20 respectively. ...
Evaluation-The Foot and Toes
... • Those that originate and insert in the foot are called intrinsic foot muscles. These directly influence the foot and toes. • Those that originate in the lower leg are called extrinsic foot muscles. These influence motion at the ankle and knee as well as the foot and toes. • If the muscle name begi ...
... • Those that originate and insert in the foot are called intrinsic foot muscles. These directly influence the foot and toes. • Those that originate in the lower leg are called extrinsic foot muscles. These influence motion at the ankle and knee as well as the foot and toes. • If the muscle name begi ...
File - Ms. Zhong`s Classes
... • Trochlea (Trok’le-ah) and capitulum (kah’pit’ulum): both articulate with bones of the forearm • Coronoid and olecranon (o-lek’rah-non) fossa: these two depressions allow the corresponding processes of the ulna to move freely when the elbow is bent and extended ...
... • Trochlea (Trok’le-ah) and capitulum (kah’pit’ulum): both articulate with bones of the forearm • Coronoid and olecranon (o-lek’rah-non) fossa: these two depressions allow the corresponding processes of the ulna to move freely when the elbow is bent and extended ...
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY
... Explain why directional terms are relative and must be used in reference to body structures or a body in anatomical position. Explain how anatomical terms are derived ...
... Explain why directional terms are relative and must be used in reference to body structures or a body in anatomical position. Explain how anatomical terms are derived ...
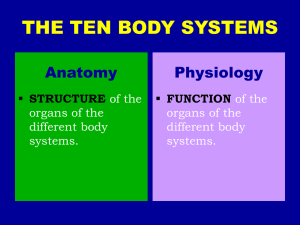
Ten Body Systems
... and responds to sensations to maintain homeostasis Monitors and controls body activities ...
... and responds to sensations to maintain homeostasis Monitors and controls body activities ...
MP1250 Head Neck Shoulder with angiosomes
... sternocleidomastoid muscles largely removed, to expose the pathway of the common carotid arteries, internal and external carotid arteries, and the vagus nerves. On the right side, the great auricular nerve ascends towards the face, while the hypoglossal nerve can be seen adjacent to the exposed styl ...
... sternocleidomastoid muscles largely removed, to expose the pathway of the common carotid arteries, internal and external carotid arteries, and the vagus nerves. On the right side, the great auricular nerve ascends towards the face, while the hypoglossal nerve can be seen adjacent to the exposed styl ...
File anatomy & physiology ch. 1
... midline, away from the midline, and between a more medial and lateral structure ...
... midline, away from the midline, and between a more medial and lateral structure ...
Kinesiology of Exercise Glossary
... PRONATED GRIP. A grip with the palms of the hands facing down or in. PRONATION. Rotating the forearm so that the hand is turned palm down. PRONE. Lying face downward. PROXIMAL RADIO-ULNAR JOINT. A radio-ulnar joint at the elbow that is a pivot joint between the head of the radius and the radial notc ...
... PRONATED GRIP. A grip with the palms of the hands facing down or in. PRONATION. Rotating the forearm so that the hand is turned palm down. PRONE. Lying face downward. PROXIMAL RADIO-ULNAR JOINT. A radio-ulnar joint at the elbow that is a pivot joint between the head of the radius and the radial notc ...
Evolutionary Evidence - Northwest ISD Moodle
... • I can analyze vestigial structures between species and determine the likelihood of common ancestry. • I can analyze homologous structures between species and determine the likelihood of common ancestry. • I can analyze analogous structures between species and determine the likelihood of common anc ...
... • I can analyze vestigial structures between species and determine the likelihood of common ancestry. • I can analyze homologous structures between species and determine the likelihood of common ancestry. • I can analyze analogous structures between species and determine the likelihood of common anc ...
THE STRUCTURE OF THE BODY Cells Tissue Organs Systems The
... There are ten systems in the Human Body. 1. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Bones, joints. Provides a rigid framework which supports the body. 2. THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Muscles, tendons. Moves limbs and drives blood around the body. 3. THE SKIN SYSTEM Skin, nails, hair. Provides a barrier that protects the body an ...
... There are ten systems in the Human Body. 1. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Bones, joints. Provides a rigid framework which supports the body. 2. THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Muscles, tendons. Moves limbs and drives blood around the body. 3. THE SKIN SYSTEM Skin, nails, hair. Provides a barrier that protects the body an ...
Human Body Vocabulary
... hollow spaces in the bones of the head, helps regulate temperature of air breathed in ...
... hollow spaces in the bones of the head, helps regulate temperature of air breathed in ...
a downloadable version of this article as it was printed
... and lungs. They pass the blood back and forth between them. The lungs give oxygen to the blood and gives that life-giving blood back to the heart to circulate. The lungs also help us to Trust and to let go. Breath is life. Breath is awareness. Breath involves Trust, because when we breathe out, we t ...
... and lungs. They pass the blood back and forth between them. The lungs give oxygen to the blood and gives that life-giving blood back to the heart to circulate. The lungs also help us to Trust and to let go. Breath is life. Breath is awareness. Breath involves Trust, because when we breathe out, we t ...
Chapter 8: The Appendicular Skeleton
... process of the ulna during flexion (joint angle decreases) of the forearm ...
... process of the ulna during flexion (joint angle decreases) of the forearm ...
AXIAL SKELETON
... Inferior nasal conchae: Scroll-like bones that project horizontally and medially from the lateral walls of the nasal cavity. Covered w/mucuous membrane to warm, moisten/clean inhaled air AXIAL Skeleton: Page 2 of 4 ...
... Inferior nasal conchae: Scroll-like bones that project horizontally and medially from the lateral walls of the nasal cavity. Covered w/mucuous membrane to warm, moisten/clean inhaled air AXIAL Skeleton: Page 2 of 4 ...
Human body
... 1. The ____________ system supports and protects, regulates body temperature, makes chemicals and hormones, and acts as a sense organ. 2. The _____________ system supports and protects, makes movement easier (with joints), stores minerals, and makes blood cells. 3. The __________ system brings about ...
... 1. The ____________ system supports and protects, regulates body temperature, makes chemicals and hormones, and acts as a sense organ. 2. The _____________ system supports and protects, makes movement easier (with joints), stores minerals, and makes blood cells. 3. The __________ system brings about ...
Rat Dissection-Circulation
... 1. Open the thoracic cavity by extending your original cut up the midline from the abdomen to the thorax up to the base of the neck. Make a second cut along the base of the neck. Pull the skin out to the sides and pin if necessary. 2. Cut through the rib cage just lateral to the sternum. Keep the cu ...
... 1. Open the thoracic cavity by extending your original cut up the midline from the abdomen to the thorax up to the base of the neck. Make a second cut along the base of the neck. Pull the skin out to the sides and pin if necessary. 2. Cut through the rib cage just lateral to the sternum. Keep the cu ...
Lecture 3 - Fredonia.edu
... Respiratory System • Respiration: exchange of gas between an organism & its environment. • Inspiration: Inhalation; drawing air into the lungs • Expiration: The expulsion of air from the lungs • Alveoli: Minute air sacs within the lung tissue ...
... Respiratory System • Respiration: exchange of gas between an organism & its environment. • Inspiration: Inhalation; drawing air into the lungs • Expiration: The expulsion of air from the lungs • Alveoli: Minute air sacs within the lung tissue ...
Anatomy and Physiology Part I
... An arm-like branch off the body of a bone. A cavity within a cranial bone. A relatively long, thin projection or bump. Articulation between cranial bones. ...
... An arm-like branch off the body of a bone. A cavity within a cranial bone. A relatively long, thin projection or bump. Articulation between cranial bones. ...
Body Organization: regions, sections, planes, and cavities
... The person is upright, with arms down and palms to the front. ...
... The person is upright, with arms down and palms to the front. ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.