Body Systems - Enders Science Page
... Use the terms in the vocabulary box to fill in the blanks. Use each term only once. You will not need to use every term. 1. The ______________________________________ system controls breathing. 2. The ______________________________________ system has bones that support the body and work with muscles ...
... Use the terms in the vocabulary box to fill in the blanks. Use each term only once. You will not need to use every term. 1. The ______________________________________ system controls breathing. 2. The ______________________________________ system has bones that support the body and work with muscles ...
Incomplete outline Mollusks and Annelids
... Mollusks have a true ____________, (first group to have). The gut and other internal organs are suspended from the body wall and cushioned by the __________ within. Symmetry: _______________ True coelom - diagram Mollusks body plan 3 part body plan: 1. visceral mass – center section with ___________ ...
... Mollusks have a true ____________, (first group to have). The gut and other internal organs are suspended from the body wall and cushioned by the __________ within. Symmetry: _______________ True coelom - diagram Mollusks body plan 3 part body plan: 1. visceral mass – center section with ___________ ...
Functional Anatomy
... Definition: The bone surfaces are small and flat, or slightly concave and one bones slides over the other. ...
... Definition: The bone surfaces are small and flat, or slightly concave and one bones slides over the other. ...
Muscles of the Pelvic Floor (Pelvic Diaphragm)
... • The fibers which form a sling for the rectum are named the Puborectalis or Sphincter recti. • They arise from the lower part of the pubic symphysis, and from the superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm. • They meet with the corresponding fibers of the opposite side around the lower part of the ...
... • The fibers which form a sling for the rectum are named the Puborectalis or Sphincter recti. • They arise from the lower part of the pubic symphysis, and from the superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm. • They meet with the corresponding fibers of the opposite side around the lower part of the ...
Human Anatomy - Sport Books Publisher
... – E.g., The colon is the distal portion and stomach is the proximal portion of the digestive tract Sport Books Publisher ...
... – E.g., The colon is the distal portion and stomach is the proximal portion of the digestive tract Sport Books Publisher ...
Human Anatomy - Sport Books Publisher
... – E.g., The colon is the distal portion and stomach is the proximal portion of the digestive tract Sport Books Publisher ...
... – E.g., The colon is the distal portion and stomach is the proximal portion of the digestive tract Sport Books Publisher ...
Joint Movements - Cloudfront.net
... The distal portion moves in a circle Distal = the point on the limb that is furthest from the proximal ...
... The distal portion moves in a circle Distal = the point on the limb that is furthest from the proximal ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 39
... Briefly describe the basic mouthparts of an insect and how they are modified in specialist feeders such as a housefly and a female mosquito. (pp. 975–976) Mouthparts may taste food, hold it or prepare it for ingestion. In insects that bite and chew, these mouthparts consist of a pair of mandibles, a ...
... Briefly describe the basic mouthparts of an insect and how they are modified in specialist feeders such as a housefly and a female mosquito. (pp. 975–976) Mouthparts may taste food, hold it or prepare it for ingestion. In insects that bite and chew, these mouthparts consist of a pair of mandibles, a ...
Human Anatomy - Fisiokinesiterapia
... fused vertebrae that form both the sacrum and the coccyx The vertebral column has several functions: providing vertical support for the body supporting the weight of the head helping to maintain upright body position helping to transfer axial skeletal weight to the appendicular skeleton of ...
... fused vertebrae that form both the sacrum and the coccyx The vertebral column has several functions: providing vertical support for the body supporting the weight of the head helping to maintain upright body position helping to transfer axial skeletal weight to the appendicular skeleton of ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... fused vertebrae that form both the sacrum and the coccyx The vertebral column has several functions: providing vertical support for the body supporting the weight of the head helping to maintain upright body position helping to transfer axial skeletal weight to the appendicular skeleton of ...
... fused vertebrae that form both the sacrum and the coccyx The vertebral column has several functions: providing vertical support for the body supporting the weight of the head helping to maintain upright body position helping to transfer axial skeletal weight to the appendicular skeleton of ...
Bones and bone markings list
... Calcaneus - Tarsal bone that forms the heel and is inferior to the talus Talus - articulates with the tibia and fibula to form ankle joint; lies between tibia and calcaneus Articulations Diarthroses (synovial) Structure of a movable joint - Joint cavity - Articular (hyline) cartilage; covers articul ...
... Calcaneus - Tarsal bone that forms the heel and is inferior to the talus Talus - articulates with the tibia and fibula to form ankle joint; lies between tibia and calcaneus Articulations Diarthroses (synovial) Structure of a movable joint - Joint cavity - Articular (hyline) cartilage; covers articul ...
THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
... but they fuse to form one bone. The ilium is the superior bone, contains the iliac crest, anterior and posterior superior and inferior iliac spine, greater sciatic notch and iliac fossa. The auricular surface articulates with the sacrum to form the sacroiliac joint. The ischium is the middle bone. P ...
... but they fuse to form one bone. The ilium is the superior bone, contains the iliac crest, anterior and posterior superior and inferior iliac spine, greater sciatic notch and iliac fossa. The auricular surface articulates with the sacrum to form the sacroiliac joint. The ischium is the middle bone. P ...
March presentation
... Epidermis (epi = outer dermis = skin – this is the outer layer of skin. (The layer you can see right now) Dermis – located below the epidermis Hypodermis (hypo = below dermis = skin The inner most layer that contains fat ...
... Epidermis (epi = outer dermis = skin – this is the outer layer of skin. (The layer you can see right now) Dermis – located below the epidermis Hypodermis (hypo = below dermis = skin The inner most layer that contains fat ...
Chapter 10 Powerpoint
... • Blows to the coccyx can result from landing on the buttocks. • Fractures of the coccyx result in severe pain, point tenderness, swelling, and bruising. Refer athlete to physician for evaluation. ...
... • Blows to the coccyx can result from landing on the buttocks. • Fractures of the coccyx result in severe pain, point tenderness, swelling, and bruising. Refer athlete to physician for evaluation. ...
Body regions
... has 2 cavities inside: 1. Cranial Cavity: formed by the skull, contains the brain. 2. Spinal or Vertebral Cavity: formed by the spine and contains the spinal cord. Ventral Cavity ( 2 parts) separated by the diaphragm) 1. Thoracic: heart and lungs found here 2. Abdominal Cavity: liver, stomach, intes ...
... has 2 cavities inside: 1. Cranial Cavity: formed by the skull, contains the brain. 2. Spinal or Vertebral Cavity: formed by the spine and contains the spinal cord. Ventral Cavity ( 2 parts) separated by the diaphragm) 1. Thoracic: heart and lungs found here 2. Abdominal Cavity: liver, stomach, intes ...
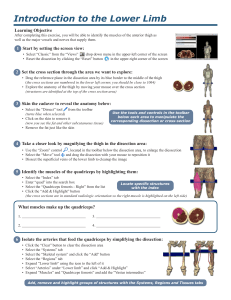
Introduction to the Lower Limb
... Select the “Skeletal system” and click the “Add” button Select the “Regions” tab Expand “Lower limb” using the icon to the left of it Select “Arteries” under “Lower limb” and click “Add & Highlight” Expand “Muscles” and “Quadriceps femoris” and add the “Vastus intermedius” Add, remove and highlight ...
... Select the “Skeletal system” and click the “Add” button Select the “Regions” tab Expand “Lower limb” using the icon to the left of it Select “Arteries” under “Lower limb” and click “Add & Highlight” Expand “Muscles” and “Quadriceps femoris” and add the “Vastus intermedius” Add, remove and highlight ...
Weather Forecasting Web Quest
... your name, the date, and answer the following: Give an example of how specific parts of the respiratory system work together with the circulatory system to deliver oxygen to the cells of the body (list the specific parts of each system). ...
... your name, the date, and answer the following: Give an example of how specific parts of the respiratory system work together with the circulatory system to deliver oxygen to the cells of the body (list the specific parts of each system). ...
Standard procedure for shoulder reconstruction The patient is
... Steindler Procedure Steindler procedure was the first choice for reconstruction of elbow flexion as long as the power strength of the forearm muscles was strong enough to transfer. Steindler procedure was done in the first stage as a part of two stage operation in two cases. The incision begins post ...
... Steindler Procedure Steindler procedure was the first choice for reconstruction of elbow flexion as long as the power strength of the forearm muscles was strong enough to transfer. Steindler procedure was done in the first stage as a part of two stage operation in two cases. The incision begins post ...
Course of the Median Nerve
... This document was created by Alex Yartsev ([email protected]); if I have used your data or images and forgot to reference you, please email me. ...
... This document was created by Alex Yartsev ([email protected]); if I have used your data or images and forgot to reference you, please email me. ...
Zoology - Central Lyon CSD
... 1. Enable the body to move 2. Support body organs 3. Protect body organs 4. Some muscles to know… a. Rectus Abdominus – stomach muscles b. Latissimus Dorsi – rotates arms c. Pectoralis – adducts arms d. Triceps femoris – 3 headed leg muscle e. Gastrocnemius – calf muscle ...
... 1. Enable the body to move 2. Support body organs 3. Protect body organs 4. Some muscles to know… a. Rectus Abdominus – stomach muscles b. Latissimus Dorsi – rotates arms c. Pectoralis – adducts arms d. Triceps femoris – 3 headed leg muscle e. Gastrocnemius – calf muscle ...
Ch 25 Introduction to Animals
... Differentiation of germ layers Formation of body cavities Patterns of embryological development, segmentation, cephalization, and limb formation. ...
... Differentiation of germ layers Formation of body cavities Patterns of embryological development, segmentation, cephalization, and limb formation. ...
25.2_Animal_Body_Plans_and_Evolution
... Differentiation of germ layers Formation of body cavities Patterns of embryological development, segmentation, cephalization, and limb formation. ...
... Differentiation of germ layers Formation of body cavities Patterns of embryological development, segmentation, cephalization, and limb formation. ...
The Circulatory System
... cranio-caudal gradient. Sagittal, frontal and horizontal sections of the body. Development of the human body from the fertilized egg-cell to the adult form which includes the next stages: prenatal ontogenesis (embryonic, fetal); organization of embryo body (ectoderm, entoderm, dorsal and ventral mes ...
... cranio-caudal gradient. Sagittal, frontal and horizontal sections of the body. Development of the human body from the fertilized egg-cell to the adult form which includes the next stages: prenatal ontogenesis (embryonic, fetal); organization of embryo body (ectoderm, entoderm, dorsal and ventral mes ...
Organ Systems
... left upper quadrant (LUQ) left lower quadrant (LLQ) cranial cavity -body cavity within the skull, containing the brain dorsal body cavity -located in the back of body, protects the nervous system separated into cranial cavity and spinal/vertebral cavity pleura -membrane that surrounds the lungs pleu ...
... left upper quadrant (LUQ) left lower quadrant (LLQ) cranial cavity -body cavity within the skull, containing the brain dorsal body cavity -located in the back of body, protects the nervous system separated into cranial cavity and spinal/vertebral cavity pleura -membrane that surrounds the lungs pleu ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM
... A. Autonomic nervous system helps to balance the tone of bronchial and arteriolar muscles of the lung 1. regulates involuntary vital functions 2. contain two divisions a. sympathetic nervous system b. parasympathetic nervous system B. Sympathetic nervous system 1. stimulation can cause epinephrine o ...
... A. Autonomic nervous system helps to balance the tone of bronchial and arteriolar muscles of the lung 1. regulates involuntary vital functions 2. contain two divisions a. sympathetic nervous system b. parasympathetic nervous system B. Sympathetic nervous system 1. stimulation can cause epinephrine o ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.