Chapter 7
... the wrist. • The five metacarpal bones articulate with the distal carpal bones and make up the palm of the hand. • The fourteen phalanges of the hand make up the finger bones. ...
... the wrist. • The five metacarpal bones articulate with the distal carpal bones and make up the palm of the hand. • The fourteen phalanges of the hand make up the finger bones. ...
Heart
... List the 3 layers of the heart wall from superficial to deep. What type of tissue makes up each layer? Describe the structure of cardiac muscle tissue, including the characteristics of the individual cardiac muscle cells. What is an intercalated disc? Gap junction? Describe their importance in relat ...
... List the 3 layers of the heart wall from superficial to deep. What type of tissue makes up each layer? Describe the structure of cardiac muscle tissue, including the characteristics of the individual cardiac muscle cells. What is an intercalated disc? Gap junction? Describe their importance in relat ...
Type of Body Symmetry
... around a central axis and radiate from the central core like the spokes of a wheel exhibit radial symmetry. (Think of an orange.) 3. Organisms whose body parts are arranged along a longitudinal axis where right and left half are mirror images of each other exhibit bilaterial symmetry. (Think of a bu ...
... around a central axis and radiate from the central core like the spokes of a wheel exhibit radial symmetry. (Think of an orange.) 3. Organisms whose body parts are arranged along a longitudinal axis where right and left half are mirror images of each other exhibit bilaterial symmetry. (Think of a bu ...
Skull - Dr. Steve W. Altstiel
... bones to slide during birth – allow for growth of the brain. c. Sinuses – air-filled cavities – function to lighten bones – open into the nasal cavity. d. Foramina – “canals” – holes in the skull to allow passage of nerves, vessels, and spinal cord. e. Bones – 8 – (actually six named) ...
... bones to slide during birth – allow for growth of the brain. c. Sinuses – air-filled cavities – function to lighten bones – open into the nasal cavity. d. Foramina – “canals” – holes in the skull to allow passage of nerves, vessels, and spinal cord. e. Bones – 8 – (actually six named) ...
Bones, cartilage, joints, dislocations and fractures
... e.g. the coronal and sagittal sutures of the skull bones Fontanelles: wide sutures of the neonatal skull, separated by fibrous membrane, divided into anterior, posterior and lateral; permit the sliding of bones over each (=moulding) other during birth, and therefore facilitating the passage of the n ...
... e.g. the coronal and sagittal sutures of the skull bones Fontanelles: wide sutures of the neonatal skull, separated by fibrous membrane, divided into anterior, posterior and lateral; permit the sliding of bones over each (=moulding) other during birth, and therefore facilitating the passage of the n ...
Marine Flatworms of the World! - Introduction
... Animalia are unsegmented flat worms with a head and a tail end. They are considered the most primitive bilaterally symmetrical animals. Bilateral symmetry means that their body exists in mirror images about a long anterior-posterior axis with definite upper and lower surfaces and anterior and poster ...
... Animalia are unsegmented flat worms with a head and a tail end. They are considered the most primitive bilaterally symmetrical animals. Bilateral symmetry means that their body exists in mirror images about a long anterior-posterior axis with definite upper and lower surfaces and anterior and poster ...
Test #2
... Section 2: “Think Section” Carefully read the scenario below. Within it are several anatomical statements. In the space below you are to (a) one-by-one list the anatomical statements, (b) state whether or not the statements are true or false, and (c) if any of the statements are false state why they ...
... Section 2: “Think Section” Carefully read the scenario below. Within it are several anatomical statements. In the space below you are to (a) one-by-one list the anatomical statements, (b) state whether or not the statements are true or false, and (c) if any of the statements are false state why they ...
Quantitative Study of Muscle Spindles in
... Humans studies have shown that the “spindle density is highest in hand, foot and neck muscles, lowest in shoulder and thigh muscles and medium in the more distal muscles of the arm and leg.” “In general, high spindle densities have been associated with small muscles subserving fine motor tasks, as i ...
... Humans studies have shown that the “spindle density is highest in hand, foot and neck muscles, lowest in shoulder and thigh muscles and medium in the more distal muscles of the arm and leg.” “In general, high spindle densities have been associated with small muscles subserving fine motor tasks, as i ...
Body Systems Review Name: Period: _____ Date: ______ Which
... 14. Can you predict an outcome of what would happen to another body system if the muscular system failed? Provide one example of what would happen to that body system and explain why. ...
... 14. Can you predict an outcome of what would happen to another body system if the muscular system failed? Provide one example of what would happen to that body system and explain why. ...
appendicular skeleton
... Male and Female Pelvis • Female iliac bones are more flared. “Hips are wide” • female pubic arch angle is greater. • The sacral curvature is shorter and flatter. ...
... Male and Female Pelvis • Female iliac bones are more flared. “Hips are wide” • female pubic arch angle is greater. • The sacral curvature is shorter and flatter. ...
Four headed triceps brachii muscle
... Variations of the triceps brachii muscle are infrequent. We report a case of four headed triceps brachii muscle which originated from the posteromedial aspect of humerus just below the surgical neck. The fibers of this extra head blended with the muscle fibers of long head of triceps. The embryologi ...
... Variations of the triceps brachii muscle are infrequent. We report a case of four headed triceps brachii muscle which originated from the posteromedial aspect of humerus just below the surgical neck. The fibers of this extra head blended with the muscle fibers of long head of triceps. The embryologi ...
PowerPoint
... Tendons are structures that connect bone to muscle and Can have various shapes Typical is cord-like tendon of biceps Sheeths are common--”aponeuroses” e.g. acromiotrapezius origin from thoracic vertebral spines ...
... Tendons are structures that connect bone to muscle and Can have various shapes Typical is cord-like tendon of biceps Sheeths are common--”aponeuroses” e.g. acromiotrapezius origin from thoracic vertebral spines ...
The+Appendicular+Skeleton
... The female inlet is larger and more circular The female pelvis as a whole is shallower, and the bones are lighter and thinner The female ilia flare more laterally The female sacrum is shorter and less curved The female ischial spines are shorter and farther apart; thus the outlet is larger ...
... The female inlet is larger and more circular The female pelvis as a whole is shallower, and the bones are lighter and thinner The female ilia flare more laterally The female sacrum is shorter and less curved The female ischial spines are shorter and farther apart; thus the outlet is larger ...
OMM in the ED - The American College of Osteopathic Emergency
... L4: Pain over the low back, hip, posterolateral thigh, and anterior leg. Numbness of the anteromedial thigh and knee. Weakness and atrophy of the quadriceps. Knee jerk reflex diminished. L5: Pain over the sacroiliac joint, hip, lateral thigh, and leg. Numbness of the lateral leg and web of the great ...
... L4: Pain over the low back, hip, posterolateral thigh, and anterior leg. Numbness of the anteromedial thigh and knee. Weakness and atrophy of the quadriceps. Knee jerk reflex diminished. L5: Pain over the sacroiliac joint, hip, lateral thigh, and leg. Numbness of the lateral leg and web of the great ...
Bones of the Pelvic Girdle
... bone. The ischial tuberosity is a roughened area that receives body weight when you are sitting. The ischial spine, superior to the tuberosity, is another important anatomical landmark, particularly in the pregnant woman, because it narrows the outlet of the pelvis through which the baby must pass d ...
... bone. The ischial tuberosity is a roughened area that receives body weight when you are sitting. The ischial spine, superior to the tuberosity, is another important anatomical landmark, particularly in the pregnant woman, because it narrows the outlet of the pelvis through which the baby must pass d ...
Ch28
... 3. Two basic body forms: polyp and medusa. 4. Exoskeleton or endoskeleton of chitinous, calcareous, or protein components in some. 5. Body with two layers, epidermis and gastrodermis; with mesoglea (diploblastic); mesoglea with cells and connective tissue in some (triploblastic). 6. Gastrovascular c ...
... 3. Two basic body forms: polyp and medusa. 4. Exoskeleton or endoskeleton of chitinous, calcareous, or protein components in some. 5. Body with two layers, epidermis and gastrodermis; with mesoglea (diploblastic); mesoglea with cells and connective tissue in some (triploblastic). 6. Gastrovascular c ...
Uyanga Ganbold-Battulga Mr. Miller Period 4 25 November 2010
... It is reponsible for transporting oxygen, which acounts for color of blood. Red blood cells are elastic and are able to squeeze through tiny vessels (capillaries). When worn out, they are destroyed in the liver.White bloods cells are colorless. They are bigger than red blood cells, but fewer in num ...
... It is reponsible for transporting oxygen, which acounts for color of blood. Red blood cells are elastic and are able to squeeze through tiny vessels (capillaries). When worn out, they are destroyed in the liver.White bloods cells are colorless. They are bigger than red blood cells, but fewer in num ...
Original description (NemasLan)
... two ventrally submedian teeth ; -conoid, acute, slightly arcuate nearly axial, and reaching in among the lips when these latter are closed. These onchia are about one-fourth an long as the head is wide. The dorsal one extends ventrad beyond the axis of the head and between the two subventral ones, s ...
... two ventrally submedian teeth ; -conoid, acute, slightly arcuate nearly axial, and reaching in among the lips when these latter are closed. These onchia are about one-fourth an long as the head is wide. The dorsal one extends ventrad beyond the axis of the head and between the two subventral ones, s ...
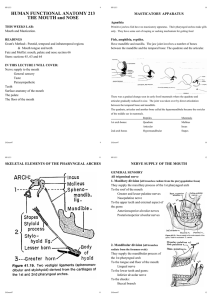
HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY 213 THE MOUTH and NOSE
... The soft palate contains glandular, aponeurotic and muscular tissue. ...
... The soft palate contains glandular, aponeurotic and muscular tissue. ...
ch_8_9outline
... Direction of rotation from anatomical position Relative to longitudinal axis of body Left or right rotation Medial rotation (inward rotation) • Rotates toward axis • Lateral rotation (outward rotation) • Rotates away from axis • Pronation • Rotates forearm, radius over ulna • Supination • Forearm in ...
... Direction of rotation from anatomical position Relative to longitudinal axis of body Left or right rotation Medial rotation (inward rotation) • Rotates toward axis • Lateral rotation (outward rotation) • Rotates away from axis • Pronation • Rotates forearm, radius over ulna • Supination • Forearm in ...
From Molecules to Organisms Classwork 4th Grade PSI Science
... 42. The lower part of the brain (brain stem) routes information to the correct region of the brain. 43. Actions are sent out from the brain. 44. Reflexes are automatic and do not require any thought, while actions require ...
... 42. The lower part of the brain (brain stem) routes information to the correct region of the brain. 43. Actions are sent out from the brain. 44. Reflexes are automatic and do not require any thought, while actions require ...
Notes on the Thorax
... • The lung receive air by the trachea • The trachea ends in the upper part of the thorax by branching into two main bronchi • The right main bronchus branches into 3 labor bronchi (one for each of the 3 lobes) • The left main bronchus branches into 2 labor ...
... • The lung receive air by the trachea • The trachea ends in the upper part of the thorax by branching into two main bronchi • The right main bronchus branches into 3 labor bronchi (one for each of the 3 lobes) • The left main bronchus branches into 2 labor ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.