Shoulder pathologies and Physiotherapy
... Pt stdg, flexion 90°, adduction 15° with elbow extended Full MR so thumb pointing down Resist flexion Pt laterally rotates arm so thumb pointing up Resist flexion Positive test = Pain or painful clicking elicited with thumb down and decreased or eliminated with thumb up ...
... Pt stdg, flexion 90°, adduction 15° with elbow extended Full MR so thumb pointing down Resist flexion Pt laterally rotates arm so thumb pointing up Resist flexion Positive test = Pain or painful clicking elicited with thumb down and decreased or eliminated with thumb up ...
Chapter 8
... female pelvis adapted to form larger true pelvis for passage of infant at birth PELVIC LIMB -30 bones; thigh, leg, ankle and foot Femur – femoral region; longest, heaviest, strongest bone Parts of Femur: head – articulates with acetabulum of pelvis fovea capitis neck greater & lesser trochanters bod ...
... female pelvis adapted to form larger true pelvis for passage of infant at birth PELVIC LIMB -30 bones; thigh, leg, ankle and foot Femur – femoral region; longest, heaviest, strongest bone Parts of Femur: head – articulates with acetabulum of pelvis fovea capitis neck greater & lesser trochanters bod ...
Document
... Purpose of Directional Terms, Anatomic Planes, Abdominopelvic Regions, and Quadrants ...
... Purpose of Directional Terms, Anatomic Planes, Abdominopelvic Regions, and Quadrants ...
brachial plexus
... The boundaries of the infraclavicular fossa are the pectoralis minor and major muscles anteriorly, ribs medially, clavicle and the coracoid process superiorly, and humerus laterally. At this location, the brachial plexus is composed of cords. The sheath surrounding the plexus is delicate. It contain ...
... The boundaries of the infraclavicular fossa are the pectoralis minor and major muscles anteriorly, ribs medially, clavicle and the coracoid process superiorly, and humerus laterally. At this location, the brachial plexus is composed of cords. The sheath surrounding the plexus is delicate. It contain ...
File
... The inguinal canal is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. In the males, it allows structures of the spermatic cord to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen. In females, it allows the round ligament of the uterus to pass from the uterus to the labium majus ...
... The inguinal canal is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. In the males, it allows structures of the spermatic cord to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen. In females, it allows the round ligament of the uterus to pass from the uterus to the labium majus ...
the knee
... Standing, knee in about 30 degrees of flexion ◦ Two anchors about mid-thigh ◦ Two anchors about mid-calf ◦ Create a fan (elastic tape) Places one strip down center of joint Places one strip from anterior leg, crossing joint Places one strip from posterior leg, crossing joint All pulling dist ...
... Standing, knee in about 30 degrees of flexion ◦ Two anchors about mid-thigh ◦ Two anchors about mid-calf ◦ Create a fan (elastic tape) Places one strip down center of joint Places one strip from anterior leg, crossing joint Places one strip from posterior leg, crossing joint All pulling dist ...
Greater omentum
... Since the Aorta is retroperitoneal, if we have a ruptured aorta the bleeding will be outside the peritoneal cavity in the back, so the patient will have pain in his back. ...
... Since the Aorta is retroperitoneal, if we have a ruptured aorta the bleeding will be outside the peritoneal cavity in the back, so the patient will have pain in his back. ...
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
... Supplies all the hamstring muscles (mainly via tibial division but short head of biceps via common peroneal division) Tibial and common peroneal nerves usually separate in inferior part of thigh Tibial nerve (L4, L5, S1, S2, S3) runs behind the knee in the popliteal fossa Gives branches to the knee ...
... Supplies all the hamstring muscles (mainly via tibial division but short head of biceps via common peroneal division) Tibial and common peroneal nerves usually separate in inferior part of thigh Tibial nerve (L4, L5, S1, S2, S3) runs behind the knee in the popliteal fossa Gives branches to the knee ...
The Muscular System
... Thin Filaments Primarily, a thin filament consists of two intertwining strands of the protein actin. Two other proteins, called tropomyosin and troponin, are also present, as we will discuss later in this section. Sliding Filaments We will also see that when muscles are innervated, impulses travel d ...
... Thin Filaments Primarily, a thin filament consists of two intertwining strands of the protein actin. Two other proteins, called tropomyosin and troponin, are also present, as we will discuss later in this section. Sliding Filaments We will also see that when muscles are innervated, impulses travel d ...
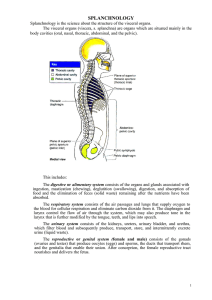
2. Splanchnology
... The periodontium consists of the supporting soft and hard dental tissues between and including portions of the tooth and the alveolar bone. The periodontium serves to support the tooth in its relationship to the alveolar bone. Thus, the periodontium includes the cementum, alveolar bone, the periodon ...
... The periodontium consists of the supporting soft and hard dental tissues between and including portions of the tooth and the alveolar bone. The periodontium serves to support the tooth in its relationship to the alveolar bone. Thus, the periodontium includes the cementum, alveolar bone, the periodon ...
ANS I
... resides in the brain or spinal column. • synapses with a second neuron (ganglionic neuron with postganglionic axon) in an autonomic ganglion outside the CNS • postganglionic axon extends to the effector organ (cell body of postganglionic neuron is in the ganglion) • pre-ganglionic neurons are lightl ...
... resides in the brain or spinal column. • synapses with a second neuron (ganglionic neuron with postganglionic axon) in an autonomic ganglion outside the CNS • postganglionic axon extends to the effector organ (cell body of postganglionic neuron is in the ganglion) • pre-ganglionic neurons are lightl ...
Comprehensive Boards I
... If the femur moves anterior to the tibia it is due to damage to which of the following ligaments? Posterior cruciate The ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of which structures? Vas deferens and seminal vesicle What is the name of the veins located in the spermatic cord? Pampiniform plexus What ...
... If the femur moves anterior to the tibia it is due to damage to which of the following ligaments? Posterior cruciate The ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of which structures? Vas deferens and seminal vesicle What is the name of the veins located in the spermatic cord? Pampiniform plexus What ...
Chapter 3: Cardiorespiratory Endurance
... 3. The oxidative (aerobic) energy system is used during activities that last longer than about two minutes. Oxygen is required for ATP generation, so this is considered an aerobic system. a. The aerobic system can supply energy for a long period of time by producing ATP in the mitochondria of a cell ...
... 3. The oxidative (aerobic) energy system is used during activities that last longer than about two minutes. Oxygen is required for ATP generation, so this is considered an aerobic system. a. The aerobic system can supply energy for a long period of time by producing ATP in the mitochondria of a cell ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Handbook
... Opening Ventral Body Cavities 1. Use scissors to longitudinally cut through abdominal muscles at the midline, anterior to the umbilical cord. 2. Cut laterally to the sternum, ending at lower lip. 3. Cut around each side of the umbilical cord, continuing to genital area. 4. Cut horizontally on each ...
... Opening Ventral Body Cavities 1. Use scissors to longitudinally cut through abdominal muscles at the midline, anterior to the umbilical cord. 2. Cut laterally to the sternum, ending at lower lip. 3. Cut around each side of the umbilical cord, continuing to genital area. 4. Cut horizontally on each ...
Answers to Even Questions
... Question 2: Oligodendroglia, in the central nervous, and Schwann cells, in the peripheral nervous system, are responsible for the formation of myelin sheaths around axons. Since axons may be very long, numerous oligodendroglia or Schwann cells are required to line up along the axon to perform the my ...
... Question 2: Oligodendroglia, in the central nervous, and Schwann cells, in the peripheral nervous system, are responsible for the formation of myelin sheaths around axons. Since axons may be very long, numerous oligodendroglia or Schwann cells are required to line up along the axon to perform the my ...
My Body
... cells. To stay alive, a person needs healthy, living cells. Without oxygen, these cells would die. And you can not live without oxygen- rich cells. Look at the paragraph below for more info. The circulatory system is extremely important to your body, escpecially your blood flow. The circulatory syst ...
... cells. To stay alive, a person needs healthy, living cells. Without oxygen, these cells would die. And you can not live without oxygen- rich cells. Look at the paragraph below for more info. The circulatory system is extremely important to your body, escpecially your blood flow. The circulatory syst ...
Work Related Somatic Dysfunction
... – Transverse process of atlas may feel posterior or closer to mastoid process on rotated side – Transverse process of atlas may feel anterior or closer to mandible on opposite side of rotation ...
... – Transverse process of atlas may feel posterior or closer to mastoid process on rotated side – Transverse process of atlas may feel anterior or closer to mandible on opposite side of rotation ...
Clinico-anatomical considerations of unilateral bipartite abductor
... ADM were placed in two planes - superficial and deep. The lateral belly was superficial and lateral in comparison to the medial belly which was deep and more medially displaced. Additionally, the morphology of the two bellies varied with the lateral belly being musculotendinous while the medial bell ...
... ADM were placed in two planes - superficial and deep. The lateral belly was superficial and lateral in comparison to the medial belly which was deep and more medially displaced. Additionally, the morphology of the two bellies varied with the lateral belly being musculotendinous while the medial bell ...
15-perineum
... a result of catching on the fold of the mucous membrane by the edges of the fecal mass. The elongated ulcer known as an anal fissure . It occurs mostly in the midline posteriorly or ,less anteriorly. The cause is due to sweep of the superficial part of the external sphincter in the lateral sides of ...
... a result of catching on the fold of the mucous membrane by the edges of the fecal mass. The elongated ulcer known as an anal fissure . It occurs mostly in the midline posteriorly or ,less anteriorly. The cause is due to sweep of the superficial part of the external sphincter in the lateral sides of ...
femur
... bone), which connects the skeleton of the lower limb to the vertebral column. • The hip bones articulate posteriorly with the sacrum and meet anteriorly at the ...
... bone), which connects the skeleton of the lower limb to the vertebral column. • The hip bones articulate posteriorly with the sacrum and meet anteriorly at the ...
Dr. D`s Gluteal Lecture
... Iliotibial tract (anterior surface of lateral condyle of tibia) ACTION Maintains knee extended (assists gluteus maximus) and abducts hip NERVE Superior gluteal nerve (L4, 5, S1) ...
... Iliotibial tract (anterior surface of lateral condyle of tibia) ACTION Maintains knee extended (assists gluteus maximus) and abducts hip NERVE Superior gluteal nerve (L4, 5, S1) ...
NEPHRON 1 The nephron – the functional unit of the kidney
... The kidney is an important excretory organ in the body as it is responsible for the evacuation of urine and retention and excretion of different electrolytes (Netter, 2014). In essence, the different physiological processes are helpful in the maintenance of homeostasis. The absence of kidney functio ...
... The kidney is an important excretory organ in the body as it is responsible for the evacuation of urine and retention and excretion of different electrolytes (Netter, 2014). In essence, the different physiological processes are helpful in the maintenance of homeostasis. The absence of kidney functio ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.