Vertebras and Pelvic Girdle
... http://content.answers.com/main/content/wp/ en/thumb/6/62/200px-Gray100.png ...
... http://content.answers.com/main/content/wp/ en/thumb/6/62/200px-Gray100.png ...
Full Text - Journal of IMAB
... The phrenic nerve is known to be a major branch of the cervical plexus. The fourth cervical spinal nerve takes part in its formation and in some cases it receives fibers from the third and fifth cervical spinal nerves. It is the major motor nerve of the cervical plexus and contains motor, viscerose ...
... The phrenic nerve is known to be a major branch of the cervical plexus. The fourth cervical spinal nerve takes part in its formation and in some cases it receives fibers from the third and fifth cervical spinal nerves. It is the major motor nerve of the cervical plexus and contains motor, viscerose ...
Chapter 7
... 1. The nasal septum, formed by the vomer, septal cartilage, and perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, divides the nasal cavity into right and left compartments. 2. The orbits are deep sockets (each having a roof, lateral wall, floor, and medial wall), formed by several bones, that house the eyeba ...
... 1. The nasal septum, formed by the vomer, septal cartilage, and perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, divides the nasal cavity into right and left compartments. 2. The orbits are deep sockets (each having a roof, lateral wall, floor, and medial wall), formed by several bones, that house the eyeba ...
Chapter 120: Trachea - Physiology
... of the surrounding smooth muscles brings about longitudinal folds, which allow a faster transportation of secretions as compared with that of the anterior and lateral walls, which can be observed easily during tracheoscopy. Neural Regulation Although the innervation of the trachea and bronchia has b ...
... of the surrounding smooth muscles brings about longitudinal folds, which allow a faster transportation of secretions as compared with that of the anterior and lateral walls, which can be observed easily during tracheoscopy. Neural Regulation Although the innervation of the trachea and bronchia has b ...
essential skills. FIBULARIS MUSCLE AND
... THEFIBULARISLONGUS) Perform the same action as in the previous test, but with the foot in plantar flexion. This position stresses the fibularis longus more than the brevis. If the structure is injured, the client will feel pain at tbe lateral foot or ankle or in the lower leg (Image 4). PALPATION TE ...
... THEFIBULARISLONGUS) Perform the same action as in the previous test, but with the foot in plantar flexion. This position stresses the fibularis longus more than the brevis. If the structure is injured, the client will feel pain at tbe lateral foot or ankle or in the lower leg (Image 4). PALPATION TE ...
Lecture 6
... At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the “Mediastinum”. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of each division. Describe the relations between the important structures in each division. ...
... At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the “Mediastinum”. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of each division. Describe the relations between the important structures in each division. ...
Anatomy of Respiratory System
... Walls are lined by a mucosa and contain skeletal muscles that are primarily used for swallowing. Partitioned into three adjoining regions: nasopharynx oropharynx laryngopharynx ...
... Walls are lined by a mucosa and contain skeletal muscles that are primarily used for swallowing. Partitioned into three adjoining regions: nasopharynx oropharynx laryngopharynx ...
PowerPoint Sunusu - Yeditepe University Faculty of
... Depresses the shoulder, preventing its upward movement. Thoracodorsal nerve The arm is abducted 90° and then adducted against resistance provided by the examiner. If the muscle is normal, the anterior border of the muscle can be seen and easily palpated in the posterior axillary fold. ...
... Depresses the shoulder, preventing its upward movement. Thoracodorsal nerve The arm is abducted 90° and then adducted against resistance provided by the examiner. If the muscle is normal, the anterior border of the muscle can be seen and easily palpated in the posterior axillary fold. ...
Anatomy and Physiology of the Larynx
... The arterial supply to the larynx comes from the superior and inferior laryngeal arteries; the venous supply mirrors the arterial supply. The superior laryngeal artery is a branch of the superior thyroid artery, which arises directly from the external carotid. The superior laryngeal artery branches ...
... The arterial supply to the larynx comes from the superior and inferior laryngeal arteries; the venous supply mirrors the arterial supply. The superior laryngeal artery is a branch of the superior thyroid artery, which arises directly from the external carotid. The superior laryngeal artery branches ...
The skeletal system - Mrs. Pronger`s Science Class
... Long bones – longer than wide, shaft with head on both ends, mostly compact bone, all limb bones except wrist and ankles ...
... Long bones – longer than wide, shaft with head on both ends, mostly compact bone, all limb bones except wrist and ankles ...
Lecture 21
... harmful stimuli that cause pain Cranial nerves cranial nerves attach to the brain and pass through foramina in the skull innervate only head and neck structures (except for the vagus nerve, X) Spinal nerves 31 pairs of nerves attach to the spinal cord innervate most of the body inferior to the head ...
... harmful stimuli that cause pain Cranial nerves cranial nerves attach to the brain and pass through foramina in the skull innervate only head and neck structures (except for the vagus nerve, X) Spinal nerves 31 pairs of nerves attach to the spinal cord innervate most of the body inferior to the head ...
Baker`s Cyst
... The lump looks most obvious when the child is standing with their knee straight (Figure 1). The area at the back of the knee is called the ‘popliteal space’, so a Baker’s cyst is also called a ‘popliteal cyst’. Baker’s cysts occur more commonly in boys between 4–8 years old. They present as a painle ...
... The lump looks most obvious when the child is standing with their knee straight (Figure 1). The area at the back of the knee is called the ‘popliteal space’, so a Baker’s cyst is also called a ‘popliteal cyst’. Baker’s cysts occur more commonly in boys between 4–8 years old. They present as a painle ...
Unusual Topography of Posterior Antebrachial
... compartment of hand. In a study of first extensor compartment in 159 hands of 80 cadavers, accessory tendons of EPB and APL were recorded, however, abnormal morphological fusion of extensor muscles was not reported (Shiraishi & Matsumure 2005). Our case presents rare occurence of abnormal morphology ...
... compartment of hand. In a study of first extensor compartment in 159 hands of 80 cadavers, accessory tendons of EPB and APL were recorded, however, abnormal morphological fusion of extensor muscles was not reported (Shiraishi & Matsumure 2005). Our case presents rare occurence of abnormal morphology ...
Learning objectives Liver Liver HEPATIC LOBES Left lobe,
... Portal vein, hepatic artery and hepatic plexus of nerves enter in liver through this fissure. While the right and left hepatic ducts and few lymphatics leave it (known as hilum of liver) Vein, artery, duct (VAD): Behind to forward relations of structures in porta hepatis. ...
... Portal vein, hepatic artery and hepatic plexus of nerves enter in liver through this fissure. While the right and left hepatic ducts and few lymphatics leave it (known as hilum of liver) Vein, artery, duct (VAD): Behind to forward relations of structures in porta hepatis. ...
Human Body
... 6d. Identify the dependent and controlled variables in an investigation. 6e. Identify a single independent variable in a scientific investigation and explain how this variable can be used to collect information to answer a question about the results of the experiment. 6f. Select appropriate tools (e ...
... 6d. Identify the dependent and controlled variables in an investigation. 6e. Identify a single independent variable in a scientific investigation and explain how this variable can be used to collect information to answer a question about the results of the experiment. 6f. Select appropriate tools (e ...
Continuous joints
... Medial and lateral rotation Pronation ans supination Inversion and eversion ...
... Medial and lateral rotation Pronation ans supination Inversion and eversion ...
Segments of liver
... Portal vein, hepatic artery and hepatic plexus of nerves enter in liver through this fissure. While the right and left hepatic ducts and few lymphatics leave it (known as hilum of liver) Vein, artery, duct (VAD): Behind to forward relations of structures in porta hepatis. ...
... Portal vein, hepatic artery and hepatic plexus of nerves enter in liver through this fissure. While the right and left hepatic ducts and few lymphatics leave it (known as hilum of liver) Vein, artery, duct (VAD): Behind to forward relations of structures in porta hepatis. ...
Arthrology 关节学
... Combination of flexion, extension, adduction and abduction Occurs at ball and socket, saddle and condyloid joints ...
... Combination of flexion, extension, adduction and abduction Occurs at ball and socket, saddle and condyloid joints ...
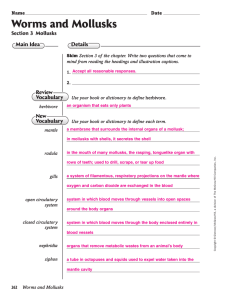
25.3 Mollusks
... a system of filamentous, respiratory projections on the mantle where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the blood ...
... a system of filamentous, respiratory projections on the mantle where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the blood ...
EYE2
... moving the eye in almost any direction. Six extrinsic eye muscles move each eye: the superior rectus, inferior rectus, lateral rectus, medial rectus, superior oblique, and inferior oblique. They are supplied by cranial nerves III, IV, or VI. In general, the motor units in these muscles are small. So ...
... moving the eye in almost any direction. Six extrinsic eye muscles move each eye: the superior rectus, inferior rectus, lateral rectus, medial rectus, superior oblique, and inferior oblique. They are supplied by cranial nerves III, IV, or VI. In general, the motor units in these muscles are small. So ...
Median nerve and brachial artery entrapment in the tendinous arch
... Coracobrachialis is a weak muscle of the anterior compartment of the arm. The muscle takes origin from the tip of the coracoid process in common with the short head of the biceps brachii. It is inserted to the middle 5 cm of the medial border of the humerus. The muscle is pierced by musculocutaneous ...
... Coracobrachialis is a weak muscle of the anterior compartment of the arm. The muscle takes origin from the tip of the coracoid process in common with the short head of the biceps brachii. It is inserted to the middle 5 cm of the medial border of the humerus. The muscle is pierced by musculocutaneous ...
chirurgia 3 dad_c 4`2006 a.qxd
... convergence of the exterior right iliac vein and the resulting venous trunk by junction of left common iliac vein with the right internal iliac vein (Fig. 2). ...
... convergence of the exterior right iliac vein and the resulting venous trunk by junction of left common iliac vein with the right internal iliac vein (Fig. 2). ...
The morphogenesis of human sphincter urethrae muscle
... urogenital diaphragm up to the vesicourethraltransition in both sexes.At first it is representedby condensation of myoblasts only (up to 30 mm crown-rump length); later on myotubes and muscularfibres are seen. 2. The phaseof sexualdimorphic development(until birth). This phase is related to the deve ...
... urogenital diaphragm up to the vesicourethraltransition in both sexes.At first it is representedby condensation of myoblasts only (up to 30 mm crown-rump length); later on myotubes and muscularfibres are seen. 2. The phaseof sexualdimorphic development(until birth). This phase is related to the deve ...
Feely`s Abridged Osteopathic Dictionary
... -IIlium, somatic dysfunction of:anterior (forward) innominate (iliac) rotation: a somatic dysfunction in which the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) is anterior and inferior to the contralateral landmark; the ilium moves more freely in an anterior inferior direction, and is restricted in posterio ...
... -IIlium, somatic dysfunction of:anterior (forward) innominate (iliac) rotation: a somatic dysfunction in which the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) is anterior and inferior to the contralateral landmark; the ilium moves more freely in an anterior inferior direction, and is restricted in posterio ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.