* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comprehensive Boards I
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
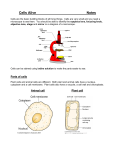
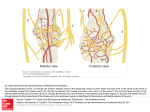
THE GREAT HOWARDO Comprehensive Boards I What comes out of L Atrium? Pulmonary Vein Platelets- Mast Cells Branch of external carotid- transverse cervical Sacrum AI right- SP left Tight ST on L- AI sacrum L Where do you take apex contact? Opposite side with lateral 1/3 thumb Logan says sacrum subluxates only AI Disc angle: 0-7 Sacral base angle: 26-55 As the strength of an acid increases, its pka decreases The primary structure of a protein is defined in terms of which type of intramolecular interaction? Covalent bonds The addition of an enzyme to a chemical RXN increases the rate This lipid is found as the major component of adipocytes: triacylglycerol The isoelectric point for an amino acid or protein is the name given to the ph at which the substance has net charge of zero The process polypeptide(straight chain)-> polypeptide(tertiary structure) is exothermic because H bonds are formed One of the processes carried out when hemoglobin functions as a buffer system is the neutralization of CO2 Invert sugar: mixture of different carbohydrates rather than a single sugar The Krebs Cycle converts the carbon atoms found in fatty acids, carbohydrates, and amino acids into CO2 Which hormone is classified as a polypeptide? Insulin Nitrogen normally enters the human organism in the form of amino acids and any excess is excreted as urea Which carpal bone articulates with the second metacarpal? Trapezoid In full extension of the knee what acts to lock the knee with weight bearing? Internal rotation of femur Which cells are responsible for removing calcium during bone remodeling? Osteoclasts Condyloid joint: tibiofemoral Pivot joint: proximal radial ulnar Ankylosing of the sternoclavicular joint would cause difficulty with abduction of shoulder Damage to the upper lateral popliteal fossa would result in damage to common peroneal nerve Dermatome to nipple: T4 The middle malleolus is formed by the tibia Only joint to articulate with the axial skeleton and upper limb: Sternoclavicular The red pulp is located in which organ? Spleen The anterior portion of the trigone is formed by the urethra Cerumen is found in external auditory meatus What is located between the isthmus and vagina? Cervix The superior portion of the uterus above the fallopian tubes is called the fundus The name of the ligament that goes from the ovary to the broad ligament: suspensory The remnant of the umbilical vein becomes the: teres ligament of the liver What ligament anchors the liver to the diaphragm? Coronary What forms the apex of the heart? Left ventricle Which ligament makes up the longitudinal arch of the foot? Spring ligament The ankle joint is made up of which bones? Tibia, fibula, talus What articulates with the anterior portion of the calcaneus? Cuboid The insertion of the psoas major is lesser trochanter Which muscle forms the anterior border of the axilla? Pectoralis major The greater omentum extends from the greater curvature of the stomach to the transverse colon What is the name of the pleura surrounding the lung? Visceral The anterior portion of the left kidney is in direct contact with the spleen What structure is located in the superior mediastinum? Arch of the aorta Which structure is retroperitoneal? Pancreas Which of the following organs has both endocrine and exocrine functions? Pancreas In which structure are the acini cells found? Pancreas The major calyces drain into which structure? Renal pelvis Which vein is most superficial on the posterior leg? Lesser saphenous Which of the following veins is most lateral above the elbow? Cephalic The external iliac artery supplies blood to lower limb Which nerve supplies the tensor fasciae latae? Superior gluteal Which of the following are the largest taste buds? Circumvillate At which level does the esophagus begin? Cricoid cartilage Which two bones go into the formation of the perpendicular plate? Vomer and ethmoid Taste to the epiglottis is via which cranial nerve? Vagus What does the corpus luteum produce? Progesterone Where does the medial collateral ligament attach? Medial humeral epicondyle Hair follicles are stimulated by pacinian corpuscles Damage to the posterior lateral knee would produce damage to which nerve? Common peroneal Spinothalamic and spinoreticular tracts are found in which part of the cord? Lateral fasciculus The T lymphocytes are derived from which organ? Thymus Which nerve runs through the cubital fossa? Median Which joint has an intra-articular disc? Radioulnar Which nerve innervates the sartorius? Femoral The radial nerve is a branch of which part of the brachial plexus? Posterior cord Which nerve supplies the hypothenar? Ulnar Which superficial muscle passes over the flexor retinaculum? Flexor carpi ulnaris Which artery supplies the deep palmar arch? Radial and ulnar Which artery supplies the blood to the majority of the hand? Ulnar What is the action of the gluteus minimus? Abduction and medial rotation of the thigh Which muscle is not part of the rotator cuff? Teres major If the femur moves anterior to the tibia it is due to damage to which of the following ligaments? Posterior cruciate The ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of which structures? Vas deferens and seminal vesicle What is the name of the veins located in the spermatic cord? Pampiniform plexus What type of cells line the vaginal canal? Non-keratinized stratified squamous The oblique fissure in the left lung divides the lung into superior and inferior lobes What divides the lateral aspect of the neck into the anterior and posterior triangles? Sternocleidomastoid Which ligament restricts hip extension? Iliofemoral What is the location of the angle of Louis? Second rib The pectoralis minor muscle inserts into the corocoid of the scapula The temporalis muscle inserts into the coronoid What is the nerve supply to the diaphragm? C3, C4, C5 In which bone is the lateral malleolus? Fibula The proximal portion of the fibula articulates with the tibia Which bone is derived from intramembranous bone? Occiput The pharyngeal muscle just proximal to the esophagus is the inferior constrictor Appendages epiloicae and tenia coli are features of which structure? Colon Blood is supplied to the primary bronchi directly from where? Aorta Which of the following nerves is posterior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus? Ulnar Which muscle is supplied by the medial plantar nerve? Flexor hallicus brevis The gluteus medius is responsible for which hip action? Abduction Individual muscle fibers are invested in endomysium The tissue of the mitral and bicuspid valves are made up of endocardium Which structure drains into the left subclavian vein? Thoracic duct Which structure is on the distal portion of the ulna? Styloid process The Islet of Langerhans cells that secrete glucagons are what cells? Alpha The ulnar collateral ligament attaches the ulna to the medial epicondyle of the humerus The longus coli attaches to the anterior arch of C1 Which nerve would be damaged if there was a blow to the medial aspect of the popliteal fossa? Tibial The ligament that holds the hyoid bone in place is attached to the styloid process Which muscle originates on the zygomatic arch? Masseter The pharynx is innervated by which nerve? Glossopharyngeal Epinephrine and norepinephrine are released from which structure? Adrenal medulla The peroneus longus muscle is responsible for which action? Eversion and dorsiflexion Which nerve is responsible for the sense of taste? Chorda tympani The AV node is located in the right atrium Which of the following superficial veins drains the posterior aspect of the leg? Lesser saphenous The plane that divides the body into ventral and dorsal halves is called the coronal plane The fossa superior and anterior to the capitulum is the coronoid fossa Where is the most common location for a pulmonary infarct? Periphery of lung The posterior lobe of the prostate is the most common site for cancer A person experiences a hypersensitivity reaction after being exposed to an agent. He had no sensitivity to it when previously exposed. This is a typical example of a type I reaction Infectious mononucleosis causes lymphocytes to increase in the bloodstream Thromboembolism of which vessel can cause a transmural infarct to the small intestines? Superior mesenteric artery Axon regeneration grows at a rate of 1mm/day Congenital protrusion of the brain through the foramen magnum is called Arnold Chiari Genetic disorder caused by excess hexoaminidase A deficiency which also causes motor and mental disorientation and cherry red spots in the macula is called Tay Sachs Which of the following findings on the pap smear is characteristic of carcinoma in situ? Dysplasia What is the first process to be observed following a fracture? Generation of a hematoma What is characterized by chronic inflammation and fibrosis of the alveolar wall? Hamman rich syndrome A gumma is associated with what disease? Syphillis Which organism is associated most commonly with Toxic Shock Syndrome? Staphylococcus Which vitamin is necessary for collagen formation? Vitamin C Metaplasia most commonly occurs in which tissues? Bronchial epithelium Epitheliod tissues are derived from macrophages Local deposition of calcium in necrotic tissues is termed dystrophic calcification The local deposition of lipofuscin occurs in brown atrophy The Ghon lesion is associated with which agent? Acid fast The most common form of food poisoning is staphylococcus This condition leads to acute arthritis with urate crystal deposition? Gout An inverted T wave is an indication of myocardial infarction Pulmonary hypertension directly results in right-sided heart failure The liver and lung are the two most common organs involved in metastasis Which condition is worse at night and is relieved by aspirin? Osteoid osteoma The most common malignant tumor of the testes is called seminoma The change in cells to disorganization which can be returned to normal is called dysplasia What accommodates the cell change in the lung but it can lead to a more resistant cell type? Metaplasia A 25 year-old patient presents with soft tender red spots on the vulva and frothy foul smelling discharge. Which organism is suspected? Trichimonas A 59 year-old woman was walking in the woods and now presents with a bulls-eye rash behind the knee called erythema chronicum migrans. The most likely diagnosis is Lyme’s Disease Projectile vomiting in a newborn male is suggestive of which condition? Pyloric stenosis Which type of pneumonia is associated with AIDS? Pneumocystis carinii Where is the most common location for an aneurysm? Abdominal aorta A patient presents with uric acid deposition in the big toe. What disease is associated with this? Gout A lesion of substantia nigra in the basal ganglia is related to which disease? Parkinson’s Which organism has been linked to infectious mononucleosis? Epstein-Barr An extra X chromosome in a male leads to a condition called Kleinfelter Syndrome Kidney infection is not a part of the symptomotology of Reiter’s syndrome A 40 year-old male presents with weight loss, increased appetite, and tremors. Which of the following should be investigated? Hyperthyroidism A condition characterized by deposition of copper in the brain is called Wilson’s 20% of the male population who gets mumps will get orchitis demyelinization of the spinal cord is a major problem in which disease? Multiple sclerosis subarachnoid hemorrhage occurs most commonly in which vessel? Anterior cerebral artery Which type of necrosis is found in a myocardial infarction? Coagulation Which type of leukemia is most commonly seen in children? Acute lymphoblastic What is most likely to lead to fatty liver degeneration? Alcoholism Proliferative cells forming new cells from original cell types is called hyperplasia This type of cell is predominantly produced by an inflammatory response to salmonella infection? Neutrophil What is most likely to occur secondary to interluminal obstruction by fecoliths? Acute appendicitis What is the most common cause of pulmonary embolism? Deep vein thrombus Alkaline phosphatase, calcium, and phosphatase are characteristically within normal limits in osteopenia What does not make up a ninhydride? Sulfuric acid What is synthesized from the pentose phosphate shunt? NADPH and ribose What is the best source of pectin? Fruits and vegetables The first step of gluconeogenesis by the process of carboxylation would convert pyruvate into oxaloacetate What is the byproduct of the breakdown of muscle? Creatinine Which vitamin is necessary for the conversion of alphaketoglutarate to succinate? Niacin What carries the amino acids in protein synthesis? Trna The complement of 5’AGTC3’ is 3’TCAG5’ NADH is a cofactor for what? Dehydrogenase A proteolytic enzyme is most likely to catalyze proteins by which method? Hydrolysis What is the substrate for citrate synthetase? Oxaloacetate Alphaketoglutarate is an intermediate in which pathway? Tricarboxylic acid Which of the following steps in the glycolytic pathway is oxidative reductive? Glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate to glyceraldehydes 1,3 diphosphate The first chemical reaction in the catabolism of amino acids is deamination In the aerobic catabolism of carbohydrates and lipids what is the common product? Acetyl CoA A patient with galactosemia should not consume what? Milk Sucrose does not contain what? Free anomeric carbon with OH group What is the intermediate in the maltose acetate shuttle? Oxaloacetate During fatty acid synthesis acetyl CoA is transported from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm as citrate Ketone body synthesis takes place in which tissue? Liver Which type of bond is found in RNA? Phosphodiester Which amino acid is a precursor to nicotinic acid? Tryptophan Which amino acid is not found in DNA? Uracil Which amino acid is essential and aromatic? Tryptophan In starvation the carbon atom in hepatogluconeogenesis comes from muscle protein Disuse of which organ will directly impair the synthesis of urea? Liver Which of the following profoundly affects utilization of carbohydrates? Insulin Coenzyme A is associated with which vitamin? Pentothenic acid Which are pyrimidines? Thymine and uracil The stop and start codon must be nonparallel and noncomparable Glucagon and what other hormone have a similar effect upon the liver? Epinephrine Chondroitin sulfate is a type of proteoglycan which is commonly found in connective tissue Hydrolysis of amylopectin results in which end product? Maltose This carbohydrate is a soluble dietary fiber. Pectinose What is a Krebs cycle intermediate present in the lowest concentration? Oxaloacetate Alpha amylase is found in which body secretion? Pancreas A genetic lack of fructose 1,6 diphosphatase results in an inability to synthesize glucose from pyruvate In a free system what may stimulate an endergonic reaction? Increase temperature in reaction During aerobic glycolysis 1 molecule of glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvate The process of synthesizing glucose from amino acids is known as gluconeogenesis Pyruvate is converted to what prior to entering the TCA cycle? Acetyl CoA What is an intermediate in the synthesis of glucose from pyruvate? Glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate What is found in collagen? Proline The biosynthesis of FAD requires riboflavin This trace mineral is a component of the glucose tolerance factor? Chromium Components of the electron transport system are located in what region of a cell? Inner mitochondria What is a component of the electron transport chain? Ubiquinone What is the active form of folic acid? Tetrahydrofolate Which mineral is a component of cytochrome B? Iron The body converts beta keratine to retinol by which of the following mechanisms? Oxidative lysis What bioactivates thymine in pyrixodine? Phosphorylation The final stage in the formation of 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol occurs primarily in the kidney In the production of purine nucleotides the formal group is provided by B9 What is synthesized by intestinal flora, becomes deficient due to antibiotic therapy, and is the enzyme for carboxylation? Biotin NADPH contains which vitamin? Niacin Which vitamin is required for the hydroxylation of amino acids to proline? Ascorbate The function of the nonsense codon is that it stops ribosome action in a line for protein release Which form of iron is most readily absorbed in the intestinal tract? Ferrous Which enzyme contains selenium? Flutathione pyroxidase Phytate and oxalate inhibit the absorption of dietary calcium What is the primary end product of purine catabolism? Urate Liver, dried fruit, and molasses all contain iron During the production of purine nucleotides the formal group is provided by tetrahydrofolate What promotes protein synthesis in humans? Methionine The complement base pairs of DNA double helix are held together by what bond? Hydrogen The DNA of an organism which contains 3% cytosine contains 40% thymine What is mRNA guided protein synthesis? Translation Transcription requires DNA template to produce RNA What occurs in DNA but not in RNA? Uracil Which hormone promotes glycogen synthesis in the liver and muscle? Insulin Under resting conditions what stimulates the synthesis of hepatic glycogenic enzymes? Insulin Epinephrine affects adipose tissue by promoting release of fatty acids The process of fat metabolism in adipose tissue is initiated by high levels of epinephrine Epinephrine is synthesized and secreted principally by the adrenal medulla Biosynthesis of testosterone utilizes cholesterol Which hormone increases lipogenesis? Insulin What makes up the color of the eye? Melanin What has a transfer methyl group? Methionine The peripheral vasculature under the least control of the sympathetic nervous system are the capillaries Which substance has the greatest permeability across a lipid bilayer of the cell membrane? Water In the sarcomere structure of skeletal muscle, the H-band contains myosin fibrils During the middle of diastole aortic pressure is falling Which cell is not regarded as a tissue macrophage? Plasma cell A mismatched blood transfusion will result in blood hemoglobin binding to free hemoglobin In exercise, gut blood flow decreases The kinesthetic sensations are detected mainly by what kind of receptor? Joint receptor The distance by which two touch stimuli must be separated to be perceived as two distinct stimuli is greatest on the center of the back If the myenteric plexus is damaged or nonfunctional, the following processes will be compromised: gastrotic, gastric motility, and peristaltic movements will be diminished or completely stopped Pain that is felt at a sight other than the site of damage is termed referred pain Two-point discrimination is possible because lateral inhibition enhances the contrast and the tactile pattern reaching the cortex The high-energy phosphate compound that is stored in skeletal muscle is called phosphocreatine As one increases the temperature of a protein the protein begins to denature Carbohydrate digestion converts any carbohydrate into an array of simple sugars before absorption into the blood plasma A lower motor neuron lesion is characterized by skeletal atrophy and flaccidity What is present in normal concentrations in the putamen and caudate nucleus and has shown to be at reduced concentrations in Parkinson’s disease? Dopamine Damage to the posterior tracts of the spinal cord will typically result in defects such as ataxia and Romberg’s sign Damage to the anterior horn of the spinal cord will typically result in defects such as flaccid paralysis Damage to the cortical spinal tracts of the spinal cord will typically result in defects such as ataxia The spinal subarachnoid space normally lies between the pia and arachnoid mater Each nerve fiber is individually wrapped in a thin connective tissue called endoneurium Assuming a person had received enough exposure to x-ray to the whole body to destroy cells as they attempt to divide, which one of the functions would best survive? Cardiac contractions Hydroxyappetite crystals form at different angles in each concentric circle of the osteon and contribute to existant shearing forces in compact bone of the femur Which is most numerous in a normal blood smear? Neutrophils Tendons are composed of dense, regularly arranged connective tissue Hydration of the cartilage matrix is dependant upon proteoglycan aggregates The cells which are typically seen in parasitic infections are eosinophils The pathological condition in which one type of adult tissue is replaced by another type of tissue is termed metaplasia Which tumor has been clearly associated with production of carcinoembryonic antigen? Carcinoma of the colon Tumors of which organ would most likely metastisize to bone? Breast The most serious complication of lower extremity thrombophlebitis is pulmonary infarction AIDS is usually characterized by loss of T helper cells Radiodensities in the ephyseal lines were attributed to chronic poisoning with lead Elevation of serum bilirubin and alkaline phosphate levels is most characteristic of extrahepatic biliary obstruction Varicose veins in the lower esophagus are complications of cirrhosis Clinical manifestations of Lime disease have been directly linked to interleukin production A deadly cardiovascular lesion is typically seen in the advanced stages of syphilis Walter-Reed staging is used to classify HIV Pearly cataracts in a newborn is due to rubella virus Cervix carcinoma is linked to human papilloma and herpes virus A patient showing persistent cough, night sweat, spitting of blood, and weight loss is most likely to be suffering from tuberculosis What has been referred to as one of the most controversial antibiotics? Chloramphenicol What is most likely to cause death in individuals between 6 months and 2 years? Meningitis from hemophilus influenza The CNS is derived from ectoderm Somites are derived from mesoderm and give rise to dermatomes, myotomes, and sclerotomes The notochord becomes incorporated into the vertebrae The adrenal medulla is derived from the neural crest cells Which embryonic development occurs first? The neural groove Which muscle is a lateral rotator of the arm? Infraspinatus Hilton’s Law tends to be followed by peripheral nerves and nerve plexuses Lumbrical muscles of the hand have among the smallest motor units in the body. Which of them are innervated by the ulnar nerve? Third and fourth What is an example of a fibrous type of joint? Interosseous membrane The external anal sphincter is innervated by inferior rectal nerves The rhomboid muscles insert on the vertebral border of the scapula What is found in the posterior mediastinum? Azygous vein For a person to stay healthy it is expected a cholesterol level of 200 mg per 100ml of blood or lower is maintained People in the United States consume about 800 mg of cholesterol per day Immunity through placental transfer of immunoglobulins to the new-born is natural passive immunity A blood alcohol concentration of 0.10 percent is considered as the legal limit of drinking and driving Calcified lesions in lungs are typically seen in pneumonia Widal test is used for the diagnosis of typhoid Rheumatic fever is a post streptococcal condition Streptococcus pyogenes is a common pharyngitis causing organism The immunoglobulin most likely to be found in secretions is IgA Blood stores in the spleen can reach the general circulation by way of the splenic vein, portal vein, liver, and inferior vena cava The lateral wall of the nasal cavity include the ethmoid bulla and semilunar hiatus The air sinuses observed in dried skulls are present in frontal, ethmoid, maxillary, and sphenoid bones The nasopharynx is superior to the uvula and soft palate The right and left hepatic ducts unite to form the common hepatic duct The internal thoracic artery passes through an opening at the sternal origin of the diaphragm and becomes the superior epigastric artery The nerve which may be exposed emerging from the anterior surface of the psoas major muscle is the genitofemoral nerve The sigmoid colon gains its parasympathetic nerve supply from the pelvic splanchnic nerves Lies in the epidural space of vertical columns: venous plexus CNI passes through the ethmoid White rami communicantes include preganglionic symptoms Obstruction of the Foramen of Monroe will raise pressure in the lateral ventricle Scalene tubercle is located at the first rib Oral cavity and the esophagus are lined with non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium Which tract is utilized for voluntary motor control? Lateral corticospinal What is the middle layer of the meninges? Arachnoid Transverse sinus crosses which 2 cranial bones? Temporal and occipital Serratus posterior is innervated by what? Costal nerves Fusion of which part of the vertebrae forms the spinous processes? Lamina What level does the posterior longitudinal ligament descend? S-1 Type C fibers are responsible for what? Nociception Adult spinal cord is derived from what embryonic spinal cord structure? Central canal of neural tube What portion of the lumbar vertebrae are the mamillary processes? Superior articular facet Vertebral artery does not pass through C7 Superior articular facets of S1 face dorsomedial Which vertebrae has smallest transverse process? C1 Which ligament prevents lateral flexion of the spine? Intertransverse Which part of the rib attaches to the transverse process? Tubercle Motor innervation to anterior belly of digastric muscle is via what? Mylohyoid- division of V3 What is the innervation of the rhomboid muscle? Dorsal scapular Fascia of the inguinal ligament attaches from ASIS to pubic tubercle Goes to ventral anterior and ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus: cerebellum and globus pallidus Eversion of foot is accomplished by innervation from superficial peroneal Spinal levels innervate the thumb: C6 Spinal level of umbilicus: T10 Nerves of olfaction synapse on mitral nuclei Lesion in optic chiasm will cause bitemporal hemiatopsia Sella turcica is located in sphenoid bone Chorda tympani supplies taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue Posterior inferior cerebellar artery is a branch of the vertebral artery Greater spanchnic nerve is derived from T5-T9 Middle and lateral geniculate bodies are located in metathalamus Superior articular facets of T6 are directed posterolaterally Taste sensation of posterior 1/3 tongue: bitter S2 to S4 nerves are considered to be preganglionic parasympathetic CN III innervates levator palpebrae supinous Posterior inferior serratus is innervated by lower 4 intercostal nerves IVD is composed of fibrocartilage Median sacral crest is formed by remnants of spinous process Stapes is derived from second brachial arch (hyoid arch) Endolymph (cochlea) flows through temporal bone Transitional vertebrae which goes from the lordosis of cervical spine to kyphosis of thoracic spine: C7 Central canal of spinal cord is confluent with fourth vertebrae Nucleus of origin is located in pons and extends its tract to C2: cervical trigeminal Damage to pons affects trigeminal nerve Striae of cochlea produce endolymph What are the three portions of the cochlea? Scala vestibuli, scala tympani, scala media Sensory innervation to paranasal sinuses is derived from CN V Corpus striatum projects fibers to the thalamus and then the projection terminates at the angulus Superior gluteal nerve supplies gluteus medius and gluteus minimus Inferior margins of the IVF of the typical thoracic vertebrae are formed by pedicles Uncinate processes of C3-C7 are located on vertebral bodies Responsible for neck flexion: splenius cervicis Innervates buccinator muscle: facial nerve Nonencapsulated receptor: free nerve ending Mylohyoid is innervated by CNV Internal capsule separates the lenticulate nucleus from the caudate nucleus Articular process between 2 thoracic vertebrae are classified as plantar joints What innervates the platysma muscle? Facial nerve Guides flexion and extension in cervical spine: uncinate process Forms anterolateral wall of pelvis: obturator internus Vomer articulates with the ethmoid This vertebrae has dual demifacets and dual costal facets: T1 Which cervical level does middle trunk of brachial plexus arise? C7 Mandibular nerve exits through ovale Limits rotation of atlas and axis? Cruciate Lumbar plexus forms in the body of psoas major structure Formed by occipital myotomes: lingual muscles Pyramid is part of medulla Cerebellum arises from rhombencephalon General somatosensory information from the nose is provided by trigeminal nerve Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by ependymal cells Responsible for sensation to the nape of the neck: third occipital Hypothalamus is located in the diencephalon This drains the aqueous humor in the eye: canal of schlemm End of spinal cord is known as conus medullaris Otolithic membrane is found in the macula of inner ear Anterior portion of the parahippocampal gyrus is called the uncus This ligament attaches the head of a rib to the vertebral body: radiate The celiac ganglion does not contain parasympathetic nerve supply Rotator muscles extend the spinal column and rotate it in the contralateral direction Fibers of the lateral spinothalamic tract decussate in the anterior white commissure What are the three layers of the cerebellum? Molecular-outer (stellate and basket cells), purkinje-middle (purkinje cells), granular-inner (granular and golgi cells, cerebellar glomeruli) The second cervical spinal nerve exits between which two vertebrae? C1 & C2 Which ligament attaches to the tips of the spinous processes from C7 to the sacrum? Supraspinous Tic douloureux is associated with which cranial nerve? V The inguinal ligament lies inferior to the external oblique muscle In a typical cervical vertebrae which structure is between the spinous and transverse processes? Lamina What type of joint is a costovertebral joint? Synovial The joint that contains hyaline cartilage is what type of joint? Synchondrosis What is the most common displacement of the nucleus pulposus? Posterolateral The middle meningeal artery passes through what foramen? Foramen spinosum The scalenus posterior does not attach to the first rib The inion is a landmark of the occipital bone The anterior clinoid fossa is located on the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone Which rib contacts a thoracic vertebrae and has a full articular facet? 10 The intermediate sacral crest is formed by the fusion of the articular processes The accessory process of a lumbar vertebrae arises from the junction of the transverse process and the pedicle The posterior portion of the IVF is formed by the articular process The borders of the vertebral canal include the flaval and the posterior longitudinal ligaments Which ligament maintains a normal spatial relationship between the odontoid process and the atlas? Cruciate Uncinate processes are located on the cervical vertebral bodies Pectoralis major attaches to the scapula The deepest layer in the abdominal wall is the transverse abdominus During rotation the articular facets in the lumbar spine are most restricted in rotation The zygopophyseal joints are classified as diarthrodial joints The median atlantoaxial joint is classified as a pivot joint The articulations of the sphenoid bone and other bones in the cranium are classified as fibrous joints The posterior longitudinal ligament attaches to the vertebral bodies The apical ligament attaches the dens to the anterior portion of the foramen magnum Calcification of the posterior atlantooccipital ligaments forms the posterior ponticle Which ligament attaches to the lamina of adjacent vertebrae? Flaval The articular facets in the lumbar spine are angled 90 degrees to the transverse plane Which temperomandibular joint ligament attaches to the lingual of the mandible? Sphenomandibular The sacrotuberous ligament is continuous with the dorsal sacral iliac ligament The iliolumbar ligament is continuous with the anterior sacral iliac ligament The carotid tubercle is located on the C6 transverse process The internal carotid artery is located in the cavernous sinus The anterior fasciculus of the spinal cord is primarily supplied by branches of the anterior spinal artery The dorsal root ganglion is derived from the neural crest The pons and cerebellum are derived from the metencephalon The medulla oblongata is derived from the myencephalon The interventricular foramen of Monroe connects which of the following ventricles? Lateral and third Cerebral spinal fluid is produced by choroid plexus The choroid plexus is composed of ependymal cells What type of synapse is the most important type in the CNS? Axodendritic Fibers from the neurons of 7 lamina comprise the majority of spinothalamic tracts Maintaining consciousness and awareness is a function of the reticular formation What do the spinothalamic tracts all have in common? All are located in the same area of the brain Facets in the thoracic spine are directed coronally Which two bones are separated by the coronal suture? Frontal and parietal Downward gaze of the eye indicates weakness of which muscles? Superior rectus and inferior oblique The brachial plexus exits between which muscles? Scalenus anterior and medius The suboccipital nerve lies in the arcuate foramen The saphenous nerve supplies the anteromedial portion of the leg The hypoglossal nerve has its origin on the medulla oblongata The masseter muscle has its origin on the zygomatic arch Parkinson’s disease is caused by a lesion in the substantia nigra The olfactory nerve goes through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone Nerves that emit from the conus medullaris are called cauda equina The center for voluntary control of eye movement is located in the frontal lobe of the brain The hyoid bone is attached by a ligament to the styloid portion of the temporal bone The pyramidal cells of Betz are located in the precentral gyrus Primary afferents are located in the dorsal nerve root Single largest killer in US: strep pneumoniae Chlamydia is considered an energy parasite Botulism causes bulbar paralysis, nystagmus, and general flaccidity The #1 cause of morbidity is influenza HIV is #8 killer Infant mortality is 10 out of 1000 Yesinia pestis is not associated with HIV Mycosis is histoplasmosis Water-borne dysentery is shigella Diarrhea and weight loss for 2 weeks should be tested for HIV Plasma cells come from where? Megakaryocytes Arnold-Chiari Syndrome: congenital; part of brainstem and cerebellum extends down thru foramen magnum; is not associated with cerebrospinal fluid drainage into skin If a baby, who is 3 weeks old, starts throwing up, what is the diagnosis? Pyloric stenosis Proteinuria and RBC casts in urine is glomerulonephritis Alcoholic cirrhosis is Laennac’s What causes lung abscesses? Bronchiectasis Infectious endocarditis is due to bacteria Monocyte is agranular Acute infection: bradykinin What causes duodenal ulcers? Increased acid production Patient with fever, nightsweats, and loss of weight indicates secondary tuberculosis Still-born baby? Anacephally Only muscles of body innervated by dorsal primary rami are those muscles of the deep back What does the first dorsal interosseous muscle do? Abducts the second digit The third lumbricle is innervated by what? Ulnar nerve The rhomboid minor inserts on the vertebral border of the scapula The vertebral artery is a branch of the first part of the subclavian artery The opthalamic artery is not a branch of the maxillary artery Levator ani muscle is in the pelvic diaphragm The phrenic nerve comes from C3, C4, C5 Inferior thoracic artery goes into superior epigastric artery Weight bearing capabilities of hyaline cartilage matrix are due to: solvation water bound to the negative charges of glycosaminoglycans Where is nerve tissue derived? Neural crest cells of inner ear (external meatus) Where is part of the ear derived? Surface ectode Tired patient with low hematocrit and low folate indicates pernicious anemia What is tinnitis? Ringing in ear (coclear nerve) Resting potential of cell is dependant on cell membrane permeability to potassium What is a sign of a lower motor neuron lesion? Skeletal atrophy Patient presents with unsteadiness; decreased position sense, vibration sense, and stereognosis; wabbling with eyes closed. What is the diagnosis? Dorsal columns, bilateral PA: used to determine TLD & TSA SA: ½ of measurement added to vertebral measurement TSA: determined by ½ of PA LD: may be functional or structural TLD: determined by 1/3 of PA ROM of lumbar spine in flexion is 60 degrees ROM of lumbar spine in extension is 20 degrees Total range of flexion of spinal column is 110 degrees Lateral flexion of the lumbar spine ROM is 25 degrees Axial rotation of the lumbar spine is 10-15 degrees Female pelvis: can be described as pelvic brim is larger and more wide-mouthed Iliolumbar ligaments: attached laterally to the lateral aspects of the PSIS Sacroiliac ligament: consists of an anterior and intermediate plane Sacrospinous ligaments: goes from ischial spine to lateral border of sacrum and coccyx Sacrotuberous ligament: crosses obliquely on the posterior aspect of the sacrospinous ligament Short axial ligament: consists of a superior and inferior band TRUE: the chiropractic subluxation syndrome can be divided into the biomechanical cause and the paraphysiological effects Lumbar curvature is concave posteriorly The nucleus pulposus consists of 88% water The nucleus pulposus allows the following movements: flexion, rotation, extension During axial compression forces the nucleus bears what % of the force? 95% Due to water imbibition by the nucleus one is shorter at night than in the morning The disc/body ratio of the lumbar spine is 1/3 Schmorls node: abnormal ossification leading to epiphysitis (depressions) Dynamic curvature: pronounced curvature Delmas index: used to determine the significance of curvatures Static curvature: attenuated curvature Scheaerumann’s disease: roughening of the epiphyseal end plates TRUE: there are no blood vessels penetrating the nucleus, however, there is a vast amount of innervation When is the A-P spine balanced? Anterior tubercle of atlas over sacral base Most common lower cervical subluxation is rotation Retrolisthesis is also known as direct foraminal compression Decussation of pyramids takes place in medulla oblongata Carotid sinus is innervated by cranial nerves IX and X Plasma cells come from megakaryocytes Proteinuria and RBC casts? Glomerulonephritis Alcoholic cirrhosis? Laennad’s What causes lung abscesses? Bronchiectasis Infectious endocarditis is due to bacteria Gluconeogenesis starts with what? Lactate Primary structure of protein is what? Covalent bonds Upper Motor Neuron Lesion: spastic paralysis, increased DTR, muscle atrophy, clonus, positive extensor (Babinski) reflex Lower Motor Neuron Lesion: flaccid paralysis, hyporeflexia, muscle atrophy, hypotonus Valgus: lateral deviation of distal end of joint Varus: medial deviation of distal end of joint Cycle: the sequence of motions occurring between 2 consecutive contacts of the same leg Stance: support of body weight, advancement of the body over the supporting leg; weight bearing Swing: leg advancement; weight unloading Wexler scale of DTR: 0 absent with reinforced maneuver; 1 hypoactive with reinforcement; 2 normal (sluggish or brisk); 3 hyperactive (moving thru ROM); 4 hyperactive with transient clonus; 5 hyperactive with sustained clonus Muscle grading: 0 no ROM; no palpable contraction; no joint motion; 1 no ROM; traceable palpable contractions; 2 ROM present without gravity; 3 fair; ROM vs. gravity only; 4 good; ROM with slight resistance; 5 normal Vestigial arch: 5th Week of gestulation: second Adrenal medulla derivation: ectoderm Smooth muscle of the jejunum derivation: endoderm Graafian follicles: ovum Dorsal primary rami: innervates muscles and skin of back Ankle joint innervation: tibial nerve Posterior mediastinum: azygous vein Rectus abdominus arterial supply: inferior and superior epigastric arteries Radial nerve innervation: abductor pollicis longus, triceps, forearm extensors, brachioradialis Innervation of external anal sphincter: perineal nerve; inferior rectal nerve Posterior triangle floor components: first rib, serratus anterior, splenius capitis, levator scapulae, posterior/middle scalenes RBC production: spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow Diastolic aortic wave: third heart sound Pulmonary dysfunction with heroine addicts: pulmonary edema Production of most ATP when metabolized: 18 Intermediate in all carbohydrate metabolism: pyruvate Lipid present on cytoplasm: sphingomyelin Neutral fat: triglyceride Trematodes are round worms? False Trematodes are members of platyhelminthes What type of antibodies are found most frequently in human milk to offer protection against microbial diseases? IgA A parasitic organism that may be responsible for blocking the lumen of the intestinal tract is ascaris What is the single largest cause of death in individuals between 15 and 25 years old? Accidents Name a kind of disinfecting agent that is responsible for the lysis of cell walls and cell membranes? Detergent A public health officer in each state is appointed by who? Governor in each state Which agency of the US public health services is assigned to participate in international health efforts? CDC Who guards the safety of medical devices? FDA 6th leading cause of death in the US today? Influenza and pneumonia what agency operates national institute of occupational safety and health (NIOSH)? CDC OSHA falls under the department of what? Labor Nasopharyngeal cancer and adhesive caused dermatitis is seen in carpenters Pin worm infections are caused by enterobus vermicularis An agent that is known to block the lymphatic system is what? Wuchereria Flukes of flat worms are what? Trematodes About how many people die every year as a result of accidents that take place at homes? 140,000 to 150,000 How many people suffer disabling injuries as a result of accidents? 500,000 Morbidity, as a term, talks about what? Illnesses of all types The host range for paragonimus wetermani is what? Humans, cats In the adult P. westermani the larva are also called what? Miracidium Name the stages the sporocytes go through in P. wetermani. Redia I, redia II, then cercaria Paragonimus are hermaphrodites? True If the cercaria are picked up by snails or crabs they will become what? Metacercaria In schistosomas the female is larger than the male? True Schistosomas are hermaphrodites? False What trematode is known for the most complex lifecycle? P. westermani Which trematode is the most common and a major killer in the world? Schistoma Schistosomas are found where in the body? Blood vessels Schistosomas have a metacercaria larvae stage? False What is left behind once schistosomas have left the skin? Tail Where are larva in schistosomas released at? Feces What trematode is known for bilharziasis/schistosomiasis? S haematobium S. haematobium host range is what? Humans, monkeys S. haemotobium is both dioceous and monoceous? True Which trematode is known for swimmer’s itch? S. mansoni S. mansoni is transmitted how? Bird feces In paragonimus how are they released from their host? Coughed out What drug is used to treat both paragonimus and schistosomas? Praziquantal Bakers: asthma Dry cleaners: liver disease, dermatitis Dye workers: bladder cancer, dermatitis Foundry workers: silicosis Glass workers: cataracts Insulators: asbestosis, lung cancer, mesothlioma Jack hammer: Raynaud’s phenomenon Miners: pneumoconiosis, lung cancer What is the biggest of the trematodes? Fasciolopsis buski Opisthorchis: Chinese liver fluke Heterophyes heterophyes: smallest worm Fasciolopsis buski: biggest worm Fasciola hepatica: sheep liver fluke Pneumoconiosis: foreign substance in lungs, fibrous growth Byssiniosis: cotton fiber, textile mills, cotton mills Silicosis: marble statutes, sandblasters, construction Siderosis: iron oxide rust Mining industry: black lung disease Talcum powder: calcium Are all pneumoconiosis cancer causing? False What year did congress create OSHA? 1970 After company has how many employees is it require to be inspected by OSHA? 12 The EPA is part of OSHA? False NIOSH is part of what? CDC NIOSH does what? Research agency, ergonomics, to make work place safe NIOSH is located where? Philadelphia Stress is not usually responsible for accidents in the work place. False As physicians we are required to report injuries from occupational hazards. True Occupational hazards are reported to the justice department. False, labor dept The fourth leading cause of death in the US is what? Accidents What percent of accidents are catastrophies? 2% How many deaths have to occur from a single accident to be considered a catastrophe? 5 What % of people killed in accidents are innocent bystanders? 70% What % of all deaths involve people influenced by alcohol? 50% 90% of all accidents are preventable 1% of all accidents are non-preventable 9% of all accidents are natural disasters Every how many seconds does an accident occur? 3 seconds What age group has the highest % of deaths due to accidents? 15 to 25 years Every how many minutes is someone killed due to an accident? 4 to 5 minutes .01 to .05: Normal .05 to .09: impaired and talkative .10: legally drunk .2 to .3: in a stupor .3 to .45: in a coma .45 or higher: dead from respiratory failure Which agency works internationally? CDC What % of the health care budget is spent by the CDC? 20% Which agency is responsible for imported produce or added materials is safe and does not contain toxic materials or banned materials? USDA