olecranon bursitis
... Classic hinge joint Medial and lateral epicondyles are externally palpable bony landmarks Olecranon bursa independent of elbow joint space; inflammation called olecranon bursitis Trauma to nerve results in unpleasant sensations in the fingers and part of the hand supplied by the nerve; sever ...
... Classic hinge joint Medial and lateral epicondyles are externally palpable bony landmarks Olecranon bursa independent of elbow joint space; inflammation called olecranon bursitis Trauma to nerve results in unpleasant sensations in the fingers and part of the hand supplied by the nerve; sever ...
Lateral Shift of the Pelvis
... femoral head around a coronal axis through the head and neck of the femur. • The head spins posteriorly in flexion and anteriorly in extension. ...
... femoral head around a coronal axis through the head and neck of the femur. • The head spins posteriorly in flexion and anteriorly in extension. ...
The Lumbosacral Plexus HO
... vertebrae. In addition, the muscle is attached to the medial ends of Transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae. The muscle passes downwards along the pelvic brim, and then beneath the inguinal ligament into the thigh, where its tendon is attached to the lesser trochanter of the femur. The Lumbar ...
... vertebrae. In addition, the muscle is attached to the medial ends of Transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae. The muscle passes downwards along the pelvic brim, and then beneath the inguinal ligament into the thigh, where its tendon is attached to the lesser trochanter of the femur. The Lumbar ...
30-Urinary system
... The lower pole of the right kidney can be palpated in the right lumbar region at the end of deep inspiration in a person with poorly developed abdominal muscles. The normal left kidney which is higher than the right is not palpable. Surface Anatomy: On the anterior abdominal wall the hilum of each ...
... The lower pole of the right kidney can be palpated in the right lumbar region at the end of deep inspiration in a person with poorly developed abdominal muscles. The normal left kidney which is higher than the right is not palpable. Surface Anatomy: On the anterior abdominal wall the hilum of each ...
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY John Christiansen, PT, OCS, ATC
... a. Coracoclavicular- connects coracoid process and lateral clavicle b. Coracoacromial- connects coracoid process and acromion to form coracoacromial arch-key player in impingement c. Transverse humeral- unites lesser and greater tuberosities, holds long head of biceps d. Superior Glenohumeral- runs ...
... a. Coracoclavicular- connects coracoid process and lateral clavicle b. Coracoacromial- connects coracoid process and acromion to form coracoacromial arch-key player in impingement c. Transverse humeral- unites lesser and greater tuberosities, holds long head of biceps d. Superior Glenohumeral- runs ...
facial bones
... are separated by the infaorbital fissure (infraorbital & zygomatic nerves, infraorbital artery and inferior opthalmic vein) -continues on as the infraorbital sulcus -becomes the infraorbital canal -terminates on the facial surface as the infraorbital foramen (infraorbital nerve) ...
... are separated by the infaorbital fissure (infraorbital & zygomatic nerves, infraorbital artery and inferior opthalmic vein) -continues on as the infraorbital sulcus -becomes the infraorbital canal -terminates on the facial surface as the infraorbital foramen (infraorbital nerve) ...
ANNELID LAB Phylum Annelida Class Oligochaeta 1. Lumbricus
... segments and formed on the plan of a tubular jacket of muscle surrounding a fluid-filled coelom. Although lacking a rigid internal skeleton. annelids can use the hydrostatic pressure of coelomic fruit, acted upon by the muscular body wall, as a "fluid skeleton," aiding in extension and flexing of th ...
... segments and formed on the plan of a tubular jacket of muscle surrounding a fluid-filled coelom. Although lacking a rigid internal skeleton. annelids can use the hydrostatic pressure of coelomic fruit, acted upon by the muscular body wall, as a "fluid skeleton," aiding in extension and flexing of th ...
Muscles of the Knee
... Prepatellar bursa: located between the patella and the skin; allows free movement of the skin over the patella Suprapatellar bursa: located between the inferior aspect of the femur surface and the quadriceps muscle; allows free movement of the quadriceps tendon over the femur. Deep infrapatellar bur ...
... Prepatellar bursa: located between the patella and the skin; allows free movement of the skin over the patella Suprapatellar bursa: located between the inferior aspect of the femur surface and the quadriceps muscle; allows free movement of the quadriceps tendon over the femur. Deep infrapatellar bur ...
Tibialis anterior (7
... Tibialis anterior is the primary dorsi flexor of the ankle and an adequate knowledge of its normal anatomy and variations in attachments and course is required for clinicians. Ebraheim et al. (2003) found the muscle to be a relatively easy flap to use for covering anterior tibial open wounds. It is ...
... Tibialis anterior is the primary dorsi flexor of the ankle and an adequate knowledge of its normal anatomy and variations in attachments and course is required for clinicians. Ebraheim et al. (2003) found the muscle to be a relatively easy flap to use for covering anterior tibial open wounds. It is ...
Chemistry Problem Solving Drill
... The two major divisions of the skeletal system are the appendicular skeleton and the axial skeleton. The axial skeleton includes the bones of the skull, inner ear bones, vertebral column and the bones of the thorax. The major functions of the axial skeleton include: (1) protecting the organs in the ...
... The two major divisions of the skeletal system are the appendicular skeleton and the axial skeleton. The axial skeleton includes the bones of the skull, inner ear bones, vertebral column and the bones of the thorax. The major functions of the axial skeleton include: (1) protecting the organs in the ...
C. Nerve Plexuses - El Camino College
... 5) Musculocutaneous – from the lateral cord, descends along the anterior arm to just below the elbow; innervates elbow flexors and lateral forearm skin 3. Lumbar plexus - formed by T12-L4; innervates lower abdomen, anterior & medial lower extremity. Major nerves include: a. Femoral – courses near th ...
... 5) Musculocutaneous – from the lateral cord, descends along the anterior arm to just below the elbow; innervates elbow flexors and lateral forearm skin 3. Lumbar plexus - formed by T12-L4; innervates lower abdomen, anterior & medial lower extremity. Major nerves include: a. Femoral – courses near th ...
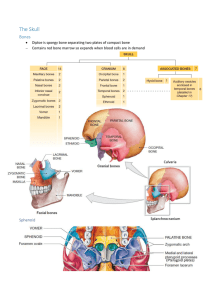
The Skull
... Temporomandibular joint Condylar head of ramus of mandible with glenoid fossa of temporal bone Cartilaginous disk between allows condyle to slide anteriorly and posteriorly on glenoid fossa Glenoid fossa Condylar head ...
... Temporomandibular joint Condylar head of ramus of mandible with glenoid fossa of temporal bone Cartilaginous disk between allows condyle to slide anteriorly and posteriorly on glenoid fossa Glenoid fossa Condylar head ...
Variation in Pattern of Rectus Sheath and Rectus Abdominis muscle
... In modern anatomy muscles are studied as a separate branch ‘Myology’. The name muscle was given on the basis of the shape i.e. ‘Mouse-like’. Acharya Sushruta said that 500 Peśi in the human male body and 520 in the female body. Out of 500 nearly 400 are present in the Śākha, 66 in the Koshtha and 34 ...
... In modern anatomy muscles are studied as a separate branch ‘Myology’. The name muscle was given on the basis of the shape i.e. ‘Mouse-like’. Acharya Sushruta said that 500 Peśi in the human male body and 520 in the female body. Out of 500 nearly 400 are present in the Śākha, 66 in the Koshtha and 34 ...
ON UNUSUAL THEROPODS FROM THE UPPER CRETACEOUS
... the length of the humerus. On its dorsolateral surface, along the entire length of the thickening, are noted the beginnings of m. deltoideus, which performed the function of pronation and supination of the shoulder. On the distal end of the deltopectoral crest remained a small swelling from the m. ...
... the length of the humerus. On its dorsolateral surface, along the entire length of the thickening, are noted the beginnings of m. deltoideus, which performed the function of pronation and supination of the shoulder. On the distal end of the deltopectoral crest remained a small swelling from the m. ...
Ministry of the Health of Ukraine
... 3. Superior (upper, cranial) and inferior (lower, caudal) 103. The horizontal plane divides the body into the following parts: 1. Superior (upper, cranial) and inferior (lower, caudal) 2. Anterior (front) and posterior (back) 3. Right (dexter) and left (sinister) ...
... 3. Superior (upper, cranial) and inferior (lower, caudal) 103. The horizontal plane divides the body into the following parts: 1. Superior (upper, cranial) and inferior (lower, caudal) 2. Anterior (front) and posterior (back) 3. Right (dexter) and left (sinister) ...
Lecture 11- ear final
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
Case report Analysis of bony bridge over bicipital groove
... attachment through histological studies. This revealed the absence of elastin fibres, which are more commonly seen in ligamentous structures and are typically absent from tendinous structures. These studies reveal that the bridging seen over bicipital groove cover the muscle fibres rather than ligam ...
... attachment through histological studies. This revealed the absence of elastin fibres, which are more commonly seen in ligamentous structures and are typically absent from tendinous structures. These studies reveal that the bridging seen over bicipital groove cover the muscle fibres rather than ligam ...
Thigh and Gluteal Regions
... The adductor canal is an intermuscular space linking the apex of the femoral triangle to the popliteal fossa. It is a space beneath sartorius and between the borders of the vastus medialis, adductor longus and adductor magnus and the contents include femoral artery, femoral vein, and branches of the ...
... The adductor canal is an intermuscular space linking the apex of the femoral triangle to the popliteal fossa. It is a space beneath sartorius and between the borders of the vastus medialis, adductor longus and adductor magnus and the contents include femoral artery, femoral vein, and branches of the ...
Popliteus Anatomy
... Popliteus Superior attachment (origin): Lateral condyle of the femur, the lateral meniscus, fibular head Inferior attachment (insertion): Posterior aspect of the proximal tibia above the soleal line ...
... Popliteus Superior attachment (origin): Lateral condyle of the femur, the lateral meniscus, fibular head Inferior attachment (insertion): Posterior aspect of the proximal tibia above the soleal line ...
Nerve Injury
... - muscles supplied and its function: Moreover, there is a loss of function in the small muscles of the hand and you will find thenar muscle, hypothenar muscles and interossi muscles having an atrophy as they are supplied by ulnar and median nerve, this leads to paralysis in the muscles and this stat ...
... - muscles supplied and its function: Moreover, there is a loss of function in the small muscles of the hand and you will find thenar muscle, hypothenar muscles and interossi muscles having an atrophy as they are supplied by ulnar and median nerve, this leads to paralysis in the muscles and this stat ...
The Elbow - Cat`s TCM Notes
... Important Anatomical Facts Median nerve and brachial artery lie medial to the biceps tendon and superficial to brachialis muscle The radial nerve and its branch posterior interosseus nerve lie lateral to the biceps tendon Ulnar nerve at the elbow lies behind (posterior) to the medial epicondyle ...
... Important Anatomical Facts Median nerve and brachial artery lie medial to the biceps tendon and superficial to brachialis muscle The radial nerve and its branch posterior interosseus nerve lie lateral to the biceps tendon Ulnar nerve at the elbow lies behind (posterior) to the medial epicondyle ...
Chapter 3
... • Gliding movements occur when relatively flat bone surfaces move back and forth and from side to side with respect to one another (Figure 9.4). • In gliding joints there is no significant alteration of the angle between the bones. • Gliding movements occur at plantar joints. ...
... • Gliding movements occur when relatively flat bone surfaces move back and forth and from side to side with respect to one another (Figure 9.4). • In gliding joints there is no significant alteration of the angle between the bones. • Gliding movements occur at plantar joints. ...
Unit 33: Anterior and Medial Thigh
... ischiopubic ramus and inserts with the sartorius below the medial condyle of the tibia. It adducts the thigh and helps in flexing the leg at the knee. The pectineus muscle takes origin from the upper surface of the superior ramus of the pubic bone. It inserts on the pectineal line of the femur below ...
... ischiopubic ramus and inserts with the sartorius below the medial condyle of the tibia. It adducts the thigh and helps in flexing the leg at the knee. The pectineus muscle takes origin from the upper surface of the superior ramus of the pubic bone. It inserts on the pectineal line of the femur below ...
Thoracic Body- heart shaped and in mid
... Thoracic Body- heart shaped and in mid. Thoracic region. Two costal demi-facets (one above and one near the root of pedicle) are covered with cartilage. Pedicles- directed back and slightly up; Deeper than in any other region of the vertebral column. Lamina- Overlap subjacent vertebrae (tile’s on ro ...
... Thoracic Body- heart shaped and in mid. Thoracic region. Two costal demi-facets (one above and one near the root of pedicle) are covered with cartilage. Pedicles- directed back and slightly up; Deeper than in any other region of the vertebral column. Lamina- Overlap subjacent vertebrae (tile’s on ro ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.