Thorax Worksheet
... is the probable resting place for large aspirated objects. Specifically, the right lower lobar bronchus is the most vertical division of the right main stem bronchus, and small aspirated objects will likely rest here. What section of the lung is most likely to be involved in aspiration pneumonia (Me ...
... is the probable resting place for large aspirated objects. Specifically, the right lower lobar bronchus is the most vertical division of the right main stem bronchus, and small aspirated objects will likely rest here. What section of the lung is most likely to be involved in aspiration pneumonia (Me ...
Nerves injuries
... the Trapezium muscle in rotating the scapula above the 90 degrees in order to put the hand over the head . - the long thoracic nerve come from C5 , 6 , 7 and goes to serratus anterior - the long thoracic nerve can be injured by blows to or pressure on the posterior triangle of the neck or during the ...
... the Trapezium muscle in rotating the scapula above the 90 degrees in order to put the hand over the head . - the long thoracic nerve come from C5 , 6 , 7 and goes to serratus anterior - the long thoracic nerve can be injured by blows to or pressure on the posterior triangle of the neck or during the ...
Bob Caruthers, CST, PLD - Association of Surgical Technologists
... plexus, the levator veli palantini, musculus uvulae, pharyngopalatinus, and glossopalatinus, salpingopharyngeus and pharyngeal constrictors are innervated. The glottis, epiglottic and lingual rami, inferior pharyngeal constrictor and cricothyroid muscle are reached by fibers traveling in the superio ...
... plexus, the levator veli palantini, musculus uvulae, pharyngopalatinus, and glossopalatinus, salpingopharyngeus and pharyngeal constrictors are innervated. The glottis, epiglottic and lingual rami, inferior pharyngeal constrictor and cricothyroid muscle are reached by fibers traveling in the superio ...
Bone Practical Handout - Academic Resources at Missouri Western
... 3. Os Coxae (2)– hip bones: form the pelvic girdle a. three portions or regions (Note: these are separate bones in child) 1) ilium or iliac portion 2) ischium or ischial portion 3) pubis or pubic portion b. acetabulum (means "vinegar bowl") articulates with head of femur c. obturator foramen (obtura ...
... 3. Os Coxae (2)– hip bones: form the pelvic girdle a. three portions or regions (Note: these are separate bones in child) 1) ilium or iliac portion 2) ischium or ischial portion 3) pubis or pubic portion b. acetabulum (means "vinegar bowl") articulates with head of femur c. obturator foramen (obtura ...
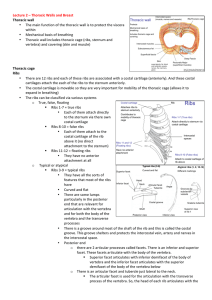
Thoracic Walls and Breast Thoracic wall • The main function of the
... and they descend posterior and lateral to the sternum all the way down the segments giving anterior intercostal arteries into the anterior aspect of the intercostal space. • Anterior and posterior intercostal nerves anastomose with each other somewhere on the anterior thoracic wall. This is im ...
... and they descend posterior and lateral to the sternum all the way down the segments giving anterior intercostal arteries into the anterior aspect of the intercostal space. • Anterior and posterior intercostal nerves anastomose with each other somewhere on the anterior thoracic wall. This is im ...
EMBRYOLOGY
... The major change that causes the intestine to assume their adult positions is a 2700 counterclockwise rotation of the caudal limb of the intestinal loop around the cephalic limb of the loop from its ventral aspect. The reference point for this rotation is the superior mesenteric artery. The main con ...
... The major change that causes the intestine to assume their adult positions is a 2700 counterclockwise rotation of the caudal limb of the intestinal loop around the cephalic limb of the loop from its ventral aspect. The reference point for this rotation is the superior mesenteric artery. The main con ...
Selected Synovial Joints
... • Inversion—turns sole medially • Eversion—turns sole laterally Special Movements ...
... • Inversion—turns sole medially • Eversion—turns sole laterally Special Movements ...
Human Anatomy — Biology 351
... 35. The long head of the biceps femoris is innervated by the common fibular nerve, while the short head is innervated by the tibial portion of the sciatic nerve. ...
... 35. The long head of the biceps femoris is innervated by the common fibular nerve, while the short head is innervated by the tibial portion of the sciatic nerve. ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 26 martini lecture Outline
... The first urge to urinate is when the urinary bladder fills to about 200 ml Greater than 200 ml will cause the internal urethral sphincter to open The external urethral sphincter will open (voluntarily) to expel the stored urine Between 500 ml and 800 ml, even the external urethral sphincter will op ...
... The first urge to urinate is when the urinary bladder fills to about 200 ml Greater than 200 ml will cause the internal urethral sphincter to open The external urethral sphincter will open (voluntarily) to expel the stored urine Between 500 ml and 800 ml, even the external urethral sphincter will op ...
Deep Muscles of the Leg and Foot
... Specific Injuries • Ankle Injuries: Sprains – Caused by sudden inversion or eversion ...
... Specific Injuries • Ankle Injuries: Sprains – Caused by sudden inversion or eversion ...
Anatomy of he Urinary System
... • The two layers extend medially to enclose the renal vessels and blend with vascular fascia • The two layers extend inferiorly to enclose the ureters as as Periuretric fascia • A layer of fat surrounding the ...
... • The two layers extend medially to enclose the renal vessels and blend with vascular fascia • The two layers extend inferiorly to enclose the ureters as as Periuretric fascia • A layer of fat surrounding the ...
Thorax - 山东大学医学院人体解剖学教研室
... Ascending along the right side of vertebral column Joins superior vena cava by aching above right lung root at level of T4 to T5 Receives right posterior intercostals and subcostal veins plus some of bronchial, esophageal and pericardial veins, and hemiazygos vein ...
... Ascending along the right side of vertebral column Joins superior vena cava by aching above right lung root at level of T4 to T5 Receives right posterior intercostals and subcostal veins plus some of bronchial, esophageal and pericardial veins, and hemiazygos vein ...
13-ear Final2015-09-07 03:334.4 MB
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
Xray Review Chapter
... A patient is placed in a supine position with the mentomeatal line and the median sagittal plane adjusted perpendicular to the film. The central ray should be directed _____ in order to demonstrate the orbits projected superior to the petrous pyramids. a. b. c. d. ...
... A patient is placed in a supine position with the mentomeatal line and the median sagittal plane adjusted perpendicular to the film. The central ray should be directed _____ in order to demonstrate the orbits projected superior to the petrous pyramids. a. b. c. d. ...
phylum Porifera
... Sponges are among the simplest of animals in terms of organization of the body. While they do possess differentiated cells, they do not possess true tissues, or organs, or organ systems. In many ways, the body of a sponge is not that different from a colonial group of cells. The general body structu ...
... Sponges are among the simplest of animals in terms of organization of the body. While they do possess differentiated cells, they do not possess true tissues, or organs, or organ systems. In many ways, the body of a sponge is not that different from a colonial group of cells. The general body structu ...
pdf View
... separated in the proximal aspect from the muscle bellies of the VI and VL. In the remaining 4/26 cases, no clear proximal separation was possible. All three muscles—the VL, the TVI, and the VI— presented a common, hardly-divisible origin between the intertrochanteric line and greater trochanter (Com ...
... separated in the proximal aspect from the muscle bellies of the VI and VL. In the remaining 4/26 cases, no clear proximal separation was possible. All three muscles—the VL, the TVI, and the VI— presented a common, hardly-divisible origin between the intertrochanteric line and greater trochanter (Com ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... plevic inlet,and is limited below by the plevic diaphragm. The cavity is curved in such a way that is is first directed downwards and backwards, and then downwards and forwards. It has unequal walls, measuring only about 5 cm anteriorly and 15 cm posteriorly.The cavity is more larger in female than ...
... plevic inlet,and is limited below by the plevic diaphragm. The cavity is curved in such a way that is is first directed downwards and backwards, and then downwards and forwards. It has unequal walls, measuring only about 5 cm anteriorly and 15 cm posteriorly.The cavity is more larger in female than ...
ThoracoAbdominbal Nerves Subcostal Nerve
... 3. Then lateral to the intenal iliac vessels and ureter 4. Lies against the obturator internus muscle 5. Accompanies the obturator artery and vein to the oobturator foramen and 6. passes with them through the obturator canal into the thigh 7. in the canal divides into anterior and posterior branches ...
... 3. Then lateral to the intenal iliac vessels and ureter 4. Lies against the obturator internus muscle 5. Accompanies the obturator artery and vein to the oobturator foramen and 6. passes with them through the obturator canal into the thigh 7. in the canal divides into anterior and posterior branches ...
NEUROANATOMY NOTES 07/21/99 Profesor: Dr. Martinez
... seen running above the insular cortex, immediately below the inferior longitudinal fasiculus. So these are only...which of the following are association tracts in the brain? superior, inferior longitudinal, cingulate, arcuate, and uncinate fasciculi. The cingulate fasciculus is part of the papes cir ...
... seen running above the insular cortex, immediately below the inferior longitudinal fasiculus. So these are only...which of the following are association tracts in the brain? superior, inferior longitudinal, cingulate, arcuate, and uncinate fasciculi. The cingulate fasciculus is part of the papes cir ...
Biol 241 Spring 13 Syllabus
... Anatomy and Physiology is a course that requires a strong commitment in order to succeed. It is not an easy course: the subject-matter is difficult and learning the terminology can be like learning a foreign language. To successfully complete this course you must commit to attend all lectures and la ...
... Anatomy and Physiology is a course that requires a strong commitment in order to succeed. It is not an easy course: the subject-matter is difficult and learning the terminology can be like learning a foreign language. To successfully complete this course you must commit to attend all lectures and la ...
TOES
... 1. Metatarsophalangeal joint flexor muscles of the four toes (Lumbricals Muscles): - Patient Starting Position: Back lying, affected leg extended. - Therapist Position and Grasps: Standing beside the table at the level of the patient feet. The proximal hand grasps the patient’s forefoot to stabilize ...
... 1. Metatarsophalangeal joint flexor muscles of the four toes (Lumbricals Muscles): - Patient Starting Position: Back lying, affected leg extended. - Therapist Position and Grasps: Standing beside the table at the level of the patient feet. The proximal hand grasps the patient’s forefoot to stabilize ...
Palpable Bony Landmarks
... 5. Palpate your mandible. As you move your fingers towards your ear you can feel them rise up over the posterior ascending ramus. (Ramus means “branch”). To feel you temporomandibular joint in action, place a finger directly in front of the external auditory meatus and open and close you mouth sever ...
... 5. Palpate your mandible. As you move your fingers towards your ear you can feel them rise up over the posterior ascending ramus. (Ramus means “branch”). To feel you temporomandibular joint in action, place a finger directly in front of the external auditory meatus and open and close you mouth sever ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.