* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY John Christiansen, PT, OCS, ATC
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
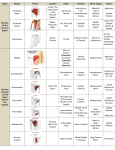
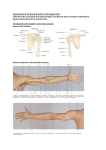
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY John Christiansen, PT, OCS, ATC Advanced Rehabilitation Clinics 1. Clavicle: articulates with sternoclavicular joint medially and acromioclavicular joint laterally muscle attachments: pectoralis major, deltoid, trapezius and subclavius 2. 1st Rib: articulates with T1 and manubrium muscle attachments: middle scalene and subclavius 3. Coracoid Process: coracoclavicular and coracoacromial ligaments muscle attachment: pectoralis minor 4. Acromion Process: articulates with clavicle muscle attachments: deltoid 5. Greater Tuberosity: muscle attachments: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, pect major (lateral lip of intertubercular groove) 6. Lesser Tuberosity: ligamentus attachments: superior glenohumeral, middle glenohumeral, transverse humeral muscle attachment: subscapularis 7. Ligaments: a. Coracoclavicular- connects coracoid process and lateral clavicle b. Coracoacromial- connects coracoid process and acromion to form coracoacromial arch-key player in impingement c. Transverse humeral- unites lesser and greater tuberosities, holds long head of biceps d. Superior Glenohumeral- runs from glenoid to superior lesser tuberosity, contributes to posterior and inferior stabilization and resists inferior translation of humerus in unloaded, abducted shoulder e. Middle Glenohumeral- runs from glenoid to medial lesser tuberosity, limits ER in lower abducted ranges and provides anterior stability in 45° abduction f. Inferior Glenohumeral- composed of 3 parts- anterior and posterior bands and an axillary pouch, tightens as abduction in increased, at 90° abduction primary restraint to anterior and posterior dislocation, axillary pouch acts a hammock resisting inferior translation 8. Muscles: a. Subscapularis- O: medial 2/3 costal surface of scapula I: lesser tuberosity I: subscapular nerves (C5,6,7) A: shoulder adduction, interior rotation b. Supraspinatus-O: supraspinous fossa I: upper facet of greater tuberosity I: suprascapular nerve (C4,5,6) A: initiates abduction c. Infraspinatus- O: infraspinous fossa I: middle facet of greater tuberosity I: suprascapular nerve (C4,5,6) A: external rotation of humerus d. Teres Minor- O: upper 2/3 lateral border of scapula I: inferior facet of greater tuberosity I: axillary nerve (C4,5,6) A: adduction and external rotation of humerus e. Teres Major- O: inferior angle and lateral border of scapula I: medial lip of intertubercular groove I: lower subscapular nerve (C6,7) A: extend shoulder, adduct and medially rotate humerus f. SubclaviusO: junction of 1st rib ad costal cartilage I: inferior surface of middle 1/3 of clavicle I: nerve to subclavius (C5,6) A: stabilizes clavicle with shoulder motions g. Pect. Minor- O: ribs 3,4,5 I: coracoid process I: medial pectoral nerve (C6,7,8) A: scapular protraction and downward rotation h. Pect Major- O: clavicle, manubrium, sternum and 1-6 costal cartilage I: lateral lip of intertubercular groove I: medial and lateral pectoral nerves ( C5,6,7,8, T1) A: adduction and interior rotation of humerus i: Serratus Anterior-O: ribs 1-8 I: medial aspect of costal surface of scapula I: long thoracic nerve (C5,6,7) A: protract and upwardly rotate scapula j. Levator Scapulae- O: T.P. pf C1-4 I: medial superior ankle of scapula I: dorsal scapular nerve (C4,5) A: retract and elevate scapula k. Rhomboids- l. Trapezius- m. Deltoid- O: S.P. of C7, T1-5 I: medial border of scapula I: dorsal scapular nerve (C4,5) A: retract and elevate scapula O: nuchal line, ligamentum nuchae, S.P. of C7-T12 I: lateral 1/3 clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula I: spinal root of accessory nerve (CNXI) A: upper- elevates scapula middle- retract scapula lower- depress scapula O: lateral 1/3 clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula I: deltoid tuberosity I: axillary nerve (C5,6) A: anterior- flex and internally rotate humerus middle- abduct humerus posterior- extend and externally rotate humerus